Cork insulation offers natural thermal and acoustic benefits, making it an eco-friendly choice with excellent breathability and moisture resistance, ideal for sustainable building projects in Cork. Foam insulation, on the other hand, provides superior R-values and faster installation, effectively sealing gaps to enhance energy efficiency in both residential and commercial properties. Selecting between cork and foam insulation depends on priorities such as environmental impact, budget, and specific performance needs in Cork's climate.
Table of Comparison
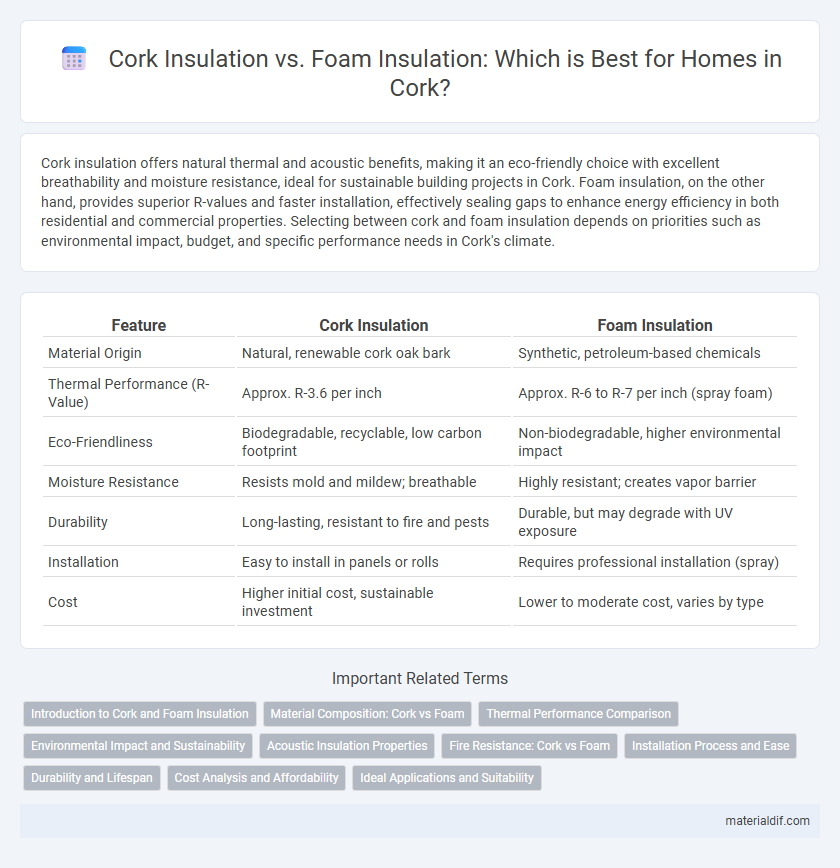
| Feature | Cork Insulation | Foam Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Natural, renewable cork oak bark | Synthetic, petroleum-based chemicals |
| Thermal Performance (R-Value) | Approx. R-3.6 per inch | Approx. R-6 to R-7 per inch (spray foam) |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, recyclable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher environmental impact |
| Moisture Resistance | Resists mold and mildew; breathable | Highly resistant; creates vapor barrier |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resistant to fire and pests | Durable, but may degrade with UV exposure |
| Installation | Easy to install in panels or rolls | Requires professional installation (spray) |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, sustainable investment | Lower to moderate cost, varies by type |
Introduction to Cork and Foam Insulation
Cork insulation, derived from the bark of the cork oak tree, offers natural thermal and acoustic properties, making it an eco-friendly choice with excellent breathability and moisture resistance. Foam insulation, typically made from polyurethane or polystyrene, provides superior R-values and air-sealing capabilities, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency for building envelopes. Evaluating the thermal conductivity, environmental impact, and installation process of both materials helps determine the most suitable insulation for specific construction needs.
Material Composition: Cork vs Foam
Cork insulation is composed of natural bark harvested from cork oak trees, offering a renewable and biodegradable material with excellent thermal and acoustic properties. Foam insulation, typically made from polyurethane or polystyrene, consists of synthetic polymers designed for high R-values and moisture resistance. The natural cellular structure of cork provides breathability and mold resistance, contrasting with the denser, less permeable foam insulation.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Cork insulation offers exceptional thermal performance with a low thermal conductivity of around 0.040 W/m*K, providing natural breathability and excellent moisture regulation. Foam insulation, such as polyurethane spray foam, typically has a lower thermal conductivity near 0.020 W/m*K, delivering superior immediate thermal resistance and airtightness. Cork's sustainability and natural resilience balance foam's higher R-value and airtight seal, affecting long-term energy efficiency in building applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cork insulation is a renewable resource harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, promoting biodiversity and carbon sequestration, whereas foam insulation often relies on petroleum-based chemicals with higher environmental footprints. Cork's natural biodegradability and recyclability contribute to its sustainability, while many foam insulations persist in landfills and may release harmful greenhouse gases during production and disposal. Choosing cork insulation supports eco-friendly building practices in Cork, aligning with local efforts to reduce carbon emissions and minimize environmental impact.
Acoustic Insulation Properties
Cork insulation offers superior acoustic dampening due to its natural cellular structure, effectively reducing sound transmission and echo within interior spaces. Foam insulation, while providing good thermal properties, often lacks the density and resilience needed for high-performance sound attenuation in comparison to cork. The choice of cork over foam insulation significantly enhances noise control in residential and commercial buildings, making it ideal for environments requiring quiet and comfort.
Fire Resistance: Cork vs Foam
Cork insulation offers superior fire resistance compared to foam insulation due to its natural fire-retardant properties, which slow flame spread and reduce toxic smoke emissions. Foam insulation, while effective for thermal performance, often contains combustible chemicals that can ignite more easily and produce harmful fumes when burned. In applications requiring enhanced fire safety, cork's ability to self-extinguish and maintain structural integrity under heat provides a significant advantage over foam materials.
Installation Process and Ease
Cork insulation features a straightforward installation process, often involving simple cutting and placing between studs or joists without the need for specialized equipment, making it suitable for DIY projects. Foam insulation typically requires professional application, including spraying or injecting, which demands expertise and safety precautions due to chemical handling and expansion control. The ease of cork installation contrasts with foam's complexity, offering more immediate placement but less mold resistance and air sealing capability than foam.
Durability and Lifespan
Cork insulation offers exceptional durability due to its natural resistance to mold, mildew, and insect damage, maintaining performance for over 40 years. Foam insulation, particularly closed-cell spray foam, provides a highly durable barrier that resists moisture and compression, typically lasting 20 to 30 years with proper installation. Cork's renewable and biodegradable nature combined with its long lifespan makes it a sustainable choice compared to synthetic foam materials.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Cork insulation generally offers a higher upfront cost compared to foam insulation but provides long-term savings through its durability and natural thermal properties, reducing energy bills over time. Foam insulation, particularly spray foam, is more affordable initially and offers excellent air sealing, which can lead to immediate energy savings. When considering affordability, foam insulation is often preferred for budget-conscious projects, while cork insulation is a cost-effective option for those prioritizing sustainability and longevity.
Ideal Applications and Suitability
Cork insulation excels in sustainable building projects and environments requiring natural, non-toxic materials due to its excellent thermal and acoustic properties. Foam insulation, such as spray foam or rigid panels, is ideal for high-performance thermal barriers in tight spaces, providing superior air sealing and moisture resistance. Cork suits eco-friendly homes and renovations, while foam insulation is preferable for modern constructions needing maximum energy efficiency and quick installation.
Cork insulation vs Foam insulation Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com