Cork offers a natural, renewable alternative to EVA foam with superior breathability and eco-friendliness, making it ideal for sustainable footwear and accessories. Cork's unique cellular structure provides excellent cushioning and moisture-wicking properties without the environmental drawbacks of synthetic EVA foam. While EVA foam is lightweight and flexible, cork's durability and biodegradability present a more environmentally responsible choice for consumers seeking green materials.
Table of Comparison
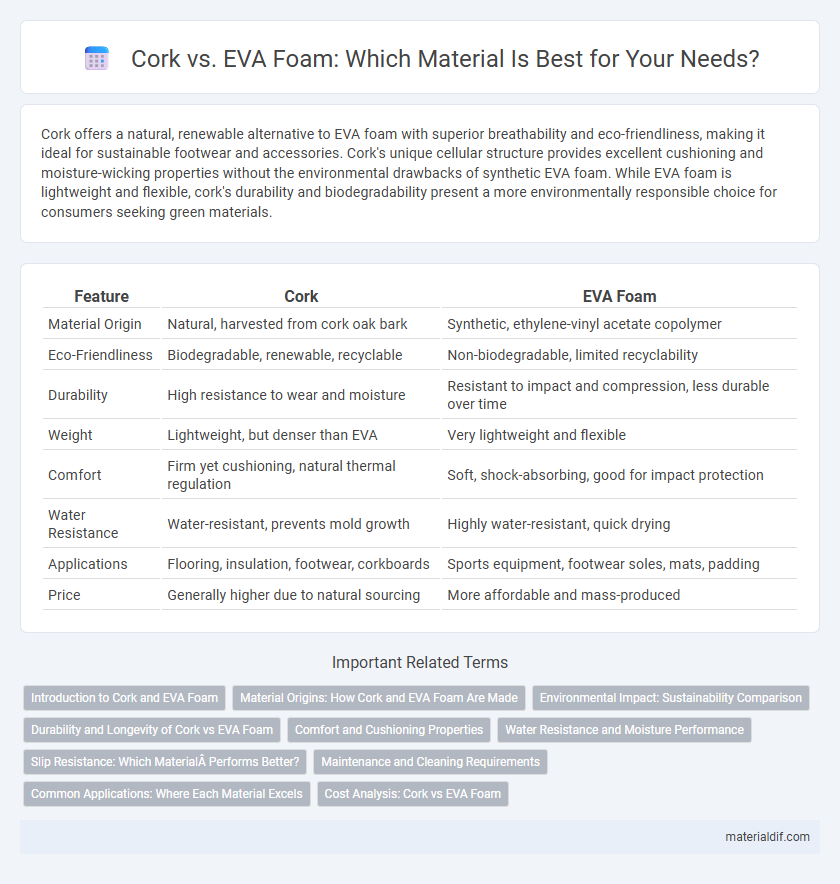
| Feature | Cork | EVA Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Natural, harvested from cork oak bark | Synthetic, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, renewable, recyclable | Non-biodegradable, limited recyclability |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and moisture | Resistant to impact and compression, less durable over time |
| Weight | Lightweight, but denser than EVA | Very lightweight and flexible |
| Comfort | Firm yet cushioning, natural thermal regulation | Soft, shock-absorbing, good for impact protection |
| Water Resistance | Water-resistant, prevents mold growth | Highly water-resistant, quick drying |
| Applications | Flooring, insulation, footwear, corkboards | Sports equipment, footwear soles, mats, padding |
| Price | Generally higher due to natural sourcing | More affordable and mass-produced |
Introduction to Cork and EVA Foam
Cork is a natural, sustainable material harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, prized for its durability, elasticity, and eco-friendly properties. EVA foam, or ethylene vinyl acetate foam, is a lightweight, flexible synthetic material known for its shock absorption and waterproof qualities. Both materials are widely used in industries such as footwear, packaging, and sports equipment, but cork offers a renewable resource advantage while EVA foam provides superior cushioning and resilience.
Material Origins: How Cork and EVA Foam Are Made
Cork is harvested from the bark of Quercus suber trees primarily found in Mediterranean regions, making it a natural and renewable material. EVA foam, or ethylene-vinyl acetate foam, is a synthetic polymer produced through the polymerization of ethylene and vinyl acetate, relying on petrochemical resources. Cork's sustainable extraction process contrasts with EVA foam's industrial production, highlighting differences in environmental impact and material origin.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Comparison
Cork is a highly sustainable material harvested from the bark of cork oak trees without harming the tree, allowing for natural regeneration and carbon sequestration. EVA foam, typically derived from petrochemicals, has a larger environmental footprint due to non-renewable resource extraction and limited biodegradability. Cork's natural biodegradability and renewability make it a preferable eco-friendly option compared to the synthetic, more pollutive nature of EVA foam.
Durability and Longevity of Cork vs EVA Foam
Cork offers superior durability and longevity compared to EVA foam, maintaining its natural resilience and structural integrity over time without significant deformation. Unlike EVA foam, which tends to compress and degrade with prolonged use, cork resists wear and tear due to its cellular structure and moisture resistance. This makes cork an ideal choice for applications requiring sustainable, long-lasting materials with consistent performance.
Comfort and Cushioning Properties
Cork provides natural cushioning with its cellular structure, offering firm yet responsive support that adapts to pressure points. EVA foam excels in shock absorption and lightweight comfort, delivering softer, more resilient cushioning ideal for prolonged use. While cork is eco-friendly and breathable, EVA foam's superior elasticity enhances overall comfort, especially in athletic and footwear applications.
Water Resistance and Moisture Performance
Cork naturally repels water due to its cellular structure filled with suberin, making it highly water-resistant and preventing moisture absorption. EVA foam, while lightweight and flexible, tends to absorb moisture over time, which can degrade its performance in wet conditions. For applications requiring superior moisture resistance, cork outperforms EVA foam by maintaining structural integrity and resisting mold and mildew growth.
Slip Resistance: Which Material Performs Better?
Cork offers superior slip resistance due to its natural texture and porosity, providing a stable grip even in wet conditions. EVA foam, while softer and more cushioned, tends to become slippery when wet, reducing its effectiveness in slippery environments. For applications requiring enhanced slip performance, cork is the more reliable material choice.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Cork flooring requires gentle cleaning with a damp mop and mild detergent to maintain its natural texture and prevent moisture damage, while EVA foam demands minimal maintenance due to its water-resistant and stain-proof properties. Cork's porous surface tends to absorb spills, necessitating prompt cleanup, whereas EVA foam's closed-cell structure allows for easy wiping and quick drying. Both materials benefit from regular dusting, but cork may need periodic sealing compared to the virtually maintenance-free EVA foam.
Common Applications: Where Each Material Excels
Cork excels in applications requiring natural insulation, sustainability, and sound absorption, making it ideal for flooring, wall panels, and coasters. EVA foam is preferred for cushioning and shock absorption in sports equipment, footwear soles, and protective gear due to its lightweight and flexible properties. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with cork favored for eco-friendly decor and EVA foam dominating in comfort and impact resistance products.
Cost Analysis: Cork vs EVA Foam
Cork typically costs between $5 and $10 per square foot, reflecting its natural, sustainable sourcing and durability, while EVA foam ranges from $2 to $6 per square foot, making it a more budget-friendly option for applications requiring lightweight cushioning. The longevity and eco-friendliness of cork often justify its higher upfront cost compared to EVA foam, which may degrade faster under heavy use or exposure to heat. Businesses and consumers must weigh initial expenses against long-term performance and environmental impact when choosing between cork and EVA foam.
Cork vs EVA Foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com