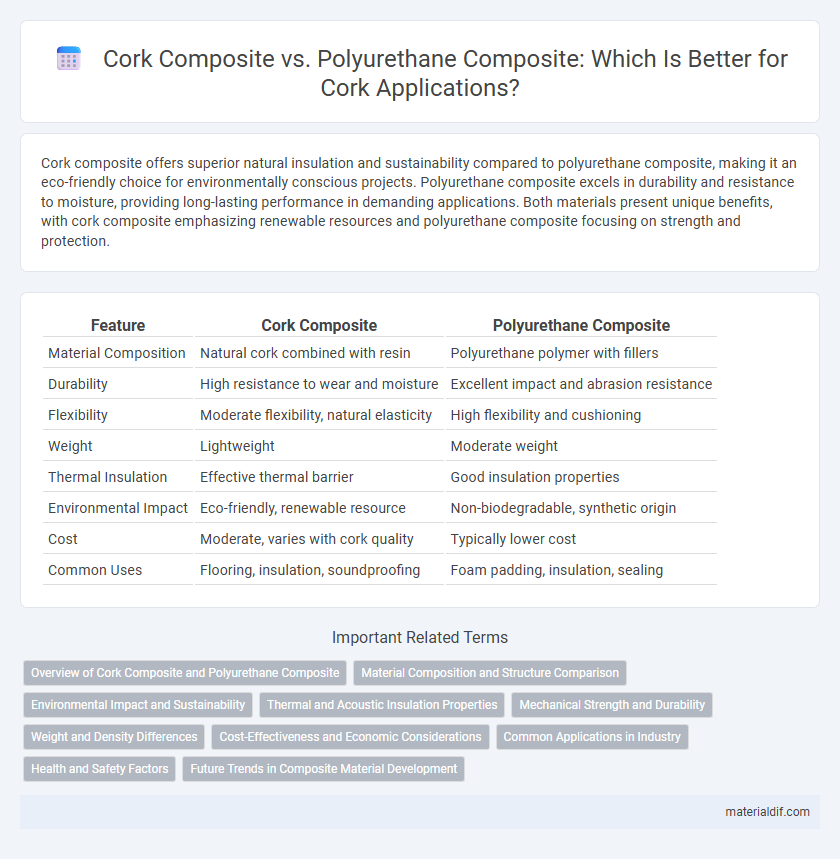
Cork composite offers superior natural insulation and sustainability compared to polyurethane composite, making it an eco-friendly choice for environmentally conscious projects. Polyurethane composite excels in durability and resistance to moisture, providing long-lasting performance in demanding applications. Both materials present unique benefits, with cork composite emphasizing renewable resources and polyurethane composite focusing on strength and protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cork Composite | Polyurethane Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural cork combined with resin | Polyurethane polymer with fillers |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and moisture | Excellent impact and abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, natural elasticity | High flexibility and cushioning |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight |
| Thermal Insulation | Effective thermal barrier | Good insulation properties |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, renewable resource | Non-biodegradable, synthetic origin |
| Cost | Moderate, varies with cork quality | Typically lower cost |
| Common Uses | Flooring, insulation, soundproofing | Foam padding, insulation, sealing |
Overview of Cork Composite and Polyurethane Composite
Cork composite is a sustainable, natural material made from granulated cork combined with binders, offering excellent insulation, moisture resistance, and soundproofing properties ideal for flooring and wall applications. Polyurethane composite consists of polyurethane resin mixed with various fillers, providing superior durability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength suited for automotive, construction, and industrial uses. Both composites serve distinct functions, with cork composites emphasizing eco-friendliness and thermal comfort, while polyurethane composites prioritize robustness and versatility.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Cork composites consist primarily of natural cork granules bound with resins, offering a lightweight, flexible structure ideal for insulation and soundproofing. Polyurethane composites combine rigid polyurethane foam with reinforcing fibers or fillers, resulting in a denser, more durable material commonly used for thermal insulation and structural applications. The key difference lies in cork's renewable, porous cellular structure versus polyurethane's synthetic, closed-cell foam matrix, affecting their performance, sustainability, and mechanical properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cork composite offers superior environmental benefits over polyurethane composite due to its renewable harvesting from cork oak trees, which promotes carbon sequestration and reduces ecological footprint. Polyurethane composites, derived from petroleum-based chemicals, contribute to higher greenhouse gas emissions and pose challenges in biodegradability and recycling processes. Sustainable applications in construction and design increasingly favor cork composites for their recyclability, biodegradability, and minimal toxic emissions during production and disposal.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Cork composites offer superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.04 W/mK, making them highly effective for maintaining indoor temperatures, while polyurethane composites typically have thermal conductivity around 0.02-0.03 W/mK, providing excellent heat resistance but less breathability. In terms of acoustic insulation, cork composites excel due to their natural cellular structure, offering high sound absorption coefficients and reducing noise transmission substantially, whereas polyurethane composites provide moderate acoustic dampening but may struggle with low-frequency noise. The choice between cork and polyurethane composites largely depends on prioritizing natural thermal regulation and soundproofing versus higher insulation R-values and structural flexibility.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Cork composites exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability due to their natural cellular structure, which provides excellent impact resistance and flexibility in cushioning applications. Polyurethane composites, while offering high tensile strength and abrasion resistance, tend to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV radiation and moisture. In environments requiring long-term resilience and mechanical integrity, cork composites outperform polyurethane composites by maintaining structural stability and resisting wear over time.
Weight and Density Differences
Cork composites are significantly lighter than polyurethane composites, with cork densities typically ranging from 120 to 200 kg/m3 compared to polyurethane composites that range between 300 to 600 kg/m3. The lower density of cork composites makes them ideal for applications requiring lightweight materials without compromising insulation properties. Polyurethane composites, though denser, offer higher strength and durability, suitable for structural uses where weight is less critical.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Cork composites offer a cost-effective solution in Cork-based construction and manufacturing due to their renewable sourcing and lower processing expenses compared to polyurethane composites. While polyurethane composites provide enhanced durability and chemical resistance, their higher material and production costs often make them less economically viable for large-scale applications in Cork. Evaluating lifecycle costs reveals cork composites' advantage in sustainability-driven projects, balancing upfront savings with long-term economic benefits.
Common Applications in Industry
Cork composites are widely used in automotive and aerospace industries for vibration damping and thermal insulation due to their lightweight and sustainable properties. Polyurethane composites find common applications in construction and furniture manufacturing, providing durable and flexible solutions for insulation and cushioning. Both materials serve as effective components in sealing, gasketing, and soundproofing across diverse industrial sectors.
Health and Safety Factors
Cork composites are naturally hypoallergenic, antimicrobial, and free from harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making them a safer choice for indoor air quality. Polyurethane composites may release isocyanates and other toxic emissions during production and over time, posing potential respiratory and skin irritation risks. Cork's breathable and non-toxic properties reduce the likelihood of mold growth, enhancing overall health and safety in living environments.
Future Trends in Composite Material Development
Cork composites offer renewable, biodegradable properties and superior thermal insulation, making them a sustainable choice for future material developments. Polyurethane composites excel in durability and flexibility, with ongoing advancements in bio-based polyols enhancing their environmental profile. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid composites that combine cork's eco-friendly attributes with polyurethane's mechanical strength to meet evolving industry demands.
Cork Composite vs Polyurethane Composite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com