Flooring-grade cork offers a dense, durable surface ideal for high-traffic areas, providing both comfort and resilience underfoot. Insulation-grade cork excels in thermal and acoustic performance, making it perfect for energy efficiency and soundproofing in walls and ceilings. Each type of cork is engineered to maximize its specific benefits, enhancing either structural comfort or environmental control in building projects.
Table of Comparison
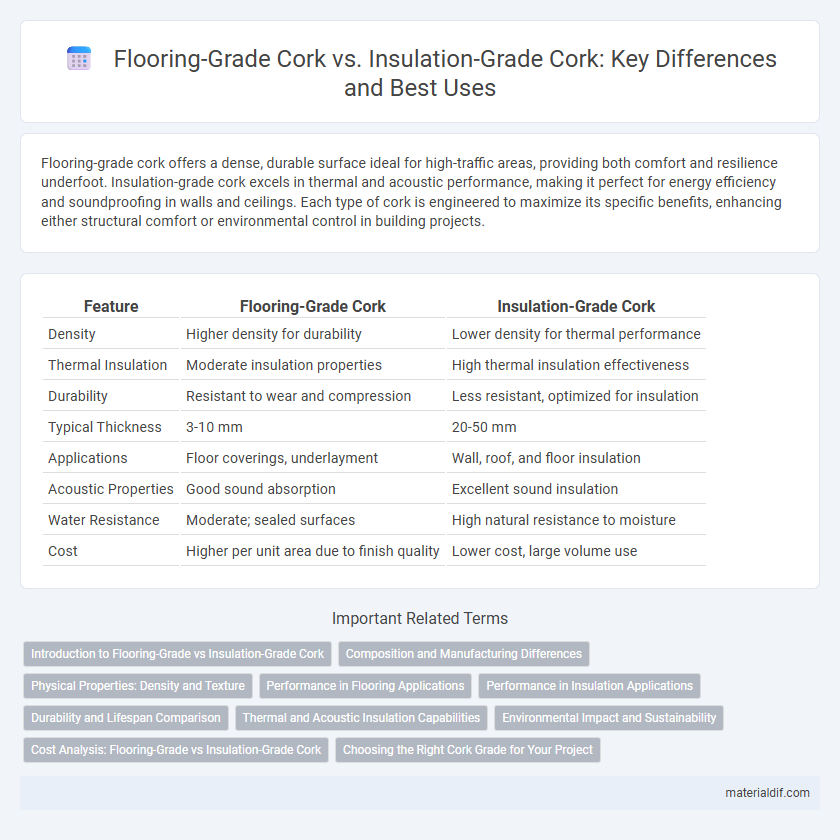
| Feature | Flooring-Grade Cork | Insulation-Grade Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Higher density for durability | Lower density for thermal performance |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation properties | High thermal insulation effectiveness |
| Durability | Resistant to wear and compression | Less resistant, optimized for insulation |
| Typical Thickness | 3-10 mm | 20-50 mm |
| Applications | Floor coverings, underlayment | Wall, roof, and floor insulation |
| Acoustic Properties | Good sound absorption | Excellent sound insulation |
| Water Resistance | Moderate; sealed surfaces | High natural resistance to moisture |
| Cost | Higher per unit area due to finish quality | Lower cost, large volume use |
Introduction to Flooring-Grade vs Insulation-Grade Cork
Flooring-grade cork offers high durability, natural resilience, and a smooth finish, making it ideal for residential and commercial flooring applications. Insulation-grade cork, on the other hand, is specifically designed for thermal and acoustic insulation, featuring a coarser texture and superior compressibility to reduce heat transfer and noise. Both types utilize the natural properties of cork bark but serve distinct functional purposes based on their density and treatment.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Flooring-grade cork is composed of tightly compressed cork granules, providing durability and resilience ideal for heavy foot traffic, while insulation-grade cork features a more expanded, less dense structure optimized for thermal and acoustic insulation. Manufacturing flooring cork involves pressing granules under high pressure and heat to create a solid, dense material, whereas insulation cork is produced by lightly compressing larger cork pieces to retain air pockets that enhance insulating properties. These compositional and manufacturing differences result in distinct performance characteristics tailored to flooring's wear resistance and insulation's energy-saving capabilities.
Physical Properties: Density and Texture
Flooring-grade cork typically features a higher density, around 180-220 kg/m3, providing enhanced durability and resistance to wear, while insulation-grade cork has a lower density, usually between 90-130 kg/m3, optimizing its thermal and acoustic insulating properties. The texture of flooring-grade cork is finer and more uniform, allowing for smoother finishes and better aesthetic appeal, whereas insulation-grade cork is coarser and more porous to trap air effectively for superior insulation. These physical distinctions make flooring-grade cork ideal for surfaces subjected to foot traffic and insulation-grade cork suitable for thermal and sound barrier applications in construction.
Performance in Flooring Applications
Flooring-grade cork offers superior durability and resilience, providing excellent impact absorption and comfort underfoot, which enhances its performance in high-traffic areas. In contrast, insulation-grade cork is primarily optimized for thermal and acoustic insulation, lacking the enhanced density and surface finish required for flooring applications. Performance in flooring depends on cork's density and finish, with flooring-grade cork designed to resist wear and moisture, ensuring long-lasting functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Performance in Insulation Applications
Insulation-grade cork offers superior thermal and acoustic properties compared to flooring-grade cork, making it ideal for energy efficiency and noise reduction in buildings. Its low thermal conductivity, approximately 0.04 W/m*K, enhances temperature regulation and minimizes heat loss. Flooring-grade cork, while durable and comfortable underfoot, typically lacks the density and porosity required for optimal insulation performance.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Flooring-grade cork is engineered for high durability, offering resistance to wear, impact, and moisture, which results in a lifespan of 15 to 30 years under regular residential use. Insulation-grade cork, while providing excellent thermal and acoustic properties, is less dense and more prone to compression and damage, typically lasting around 10 to 20 years depending on environmental conditions. The greater density and surface treatment of flooring-grade cork significantly enhance its longevity compared to insulation-grade cork, making it a preferred choice for areas subject to foot traffic.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Capabilities
Flooring-grade cork offers moderate thermal insulation, enhancing indoor comfort by maintaining consistent temperatures, while its density provides effective sound absorption to reduce noise levels. Insulation-grade cork excels in both thermal and acoustic performance due to its higher density and cellular structure, making it ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes and noise control. The superior thermal resistance of insulation-grade cork lowers heat transfer, contributing to energy savings, whereas its soundproofing properties minimize external noise intrusion.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Flooring-grade cork typically requires higher density and durability, often involving more intensive processing that can increase its environmental footprint compared to insulation-grade cork, which is generally less processed and uses lower density material. Insulation-grade cork offers superior thermal and acoustic properties with minimal environmental impact due to its lower energy consumption during production and high recyclability. Sustainable cork harvesting practices ensure both grades maintain cork oak forest health, supporting biodiversity and carbon sequestration crucial for climate change mitigation.
Cost Analysis: Flooring-Grade vs Insulation-Grade Cork
Flooring-grade cork typically costs more per square meter due to its higher durability, finish quality, and aesthetic appeal compared to insulation-grade cork, which is primarily valued for its thermal and acoustic properties. The production process for flooring-grade cork involves additional treatments such as sealing and surface texturing, increasing its price by approximately 20-30% over insulation-grade cork. Insulation-grade cork remains the cost-effective choice for large-area applications where thermal efficiency takes precedence over surface finish.
Choosing the Right Cork Grade for Your Project
Flooring-grade cork offers durability and a harder surface ideal for high-traffic areas, while insulation-grade cork excels in thermal and acoustic properties for energy efficiency. Selecting the appropriate cork grade depends on project requirements, prioritizing either strength and wear resistance or insulating performance. Understanding these distinctions ensures optimal functionality and longevity in residential or commercial applications.
flooring-grade cork vs insulation-grade cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com