Cork veneer offers a thin, flexible layer of natural cork ideal for decorative finishes and lightweight applications, while cork sheets are thicker and provide enhanced durability and insulation properties. Cork veneer is perfect for covering furniture surfaces or creating aesthetic designs, whereas cork sheets are better suited for flooring, bulletin boards, or soundproofing projects. Choosing between cork veneer and cork sheets depends on the specific requirements of the project, including thickness, durability, and application.
Table of Comparison
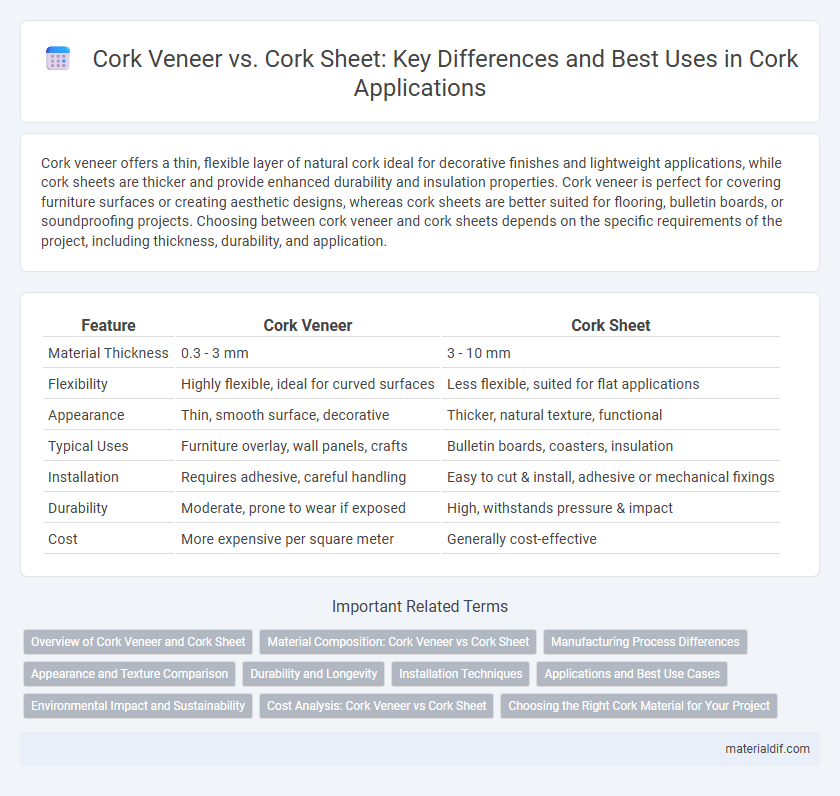
| Feature | Cork Veneer | Cork Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | 0.3 - 3 mm | 3 - 10 mm |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, ideal for curved surfaces | Less flexible, suited for flat applications |
| Appearance | Thin, smooth surface, decorative | Thicker, natural texture, functional |
| Typical Uses | Furniture overlay, wall panels, crafts | Bulletin boards, coasters, insulation |
| Installation | Requires adhesive, careful handling | Easy to cut & install, adhesive or mechanical fixings |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear if exposed | High, withstands pressure & impact |
| Cost | More expensive per square meter | Generally cost-effective |
Overview of Cork Veneer and Cork Sheet
Cork veneer is a thin layer of cork sliced from natural cork bark, primarily used as a decorative surface or laminate for furniture and wall paneling, offering flexibility and ease of application. Cork sheets are thicker, dense blocks of compressed cork granules, providing superior insulation, cushioning, and durability for flooring, gaskets, and bulletin boards. Both materials leverage cork's natural properties such as lightweight, water resistance, and thermal insulation but differ significantly in thickness, texture, and typical use cases.
Material Composition: Cork Veneer vs Cork Sheet
Cork veneer consists of thinly sliced layers of natural cork bonded to a backing material, offering flexibility and ease of application on curved surfaces. Cork sheets are thicker, solid blocks of compressed cork granules, providing greater durability and insulation properties. The material composition difference impacts their use, with veneer suited for decorative finishes and sheets ideal for soundproofing and thermal insulation.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Cork veneer is produced by slicing thin layers from a cork block, preserving the natural grain and texture, while cork sheets are manufactured by compressing granulated cork particles under heat and pressure to form uniform, dense panels. The slicing process of veneer requires precise cutting equipment to maintain thinness and flexibility, whereas sheet production relies on agglomeration techniques for durability and consistency. These manufacturing differences impact the material's applications, with veneer preferred for decorative surfaces and sheets favored for insulation and sealing purposes.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Cork veneer features a thinner, more refined surface with a consistent grain pattern, creating a smooth and elegant appearance ideal for decorative applications. Cork sheet tends to be thicker and more robust, exhibiting a natural, slightly uneven texture that emphasizes its organic origin and durability. Both materials showcase the unique warm tones and porous characteristics of cork, but veneer offers a sleeker aesthetic while sheets provide a tactile, rustic feel.
Durability and Longevity
Cork veneer offers a thin, flexible layer ideal for decorative applications, but its durability is limited compared to cork sheets, which are thicker and provide enhanced resistance to wear and tear. Cork sheets exhibit superior longevity due to their denser composition, making them suitable for flooring and insulation where long-term performance is critical. The resilience of cork sheets against moisture and mechanical damage significantly surpasses that of cork veneer, ensuring extended lifespan in demanding environments.
Installation Techniques
Cork veneer installation typically requires precise adhesive application and careful alignment on smooth surfaces to ensure a thin, flexible finish ideal for furniture and wall panels. In contrast, cork sheet installation involves cutting to size and can be glued directly onto floors or walls, offering a thicker, more durable layer with soundproofing and insulation properties. Both methods demand moisture barriers on damp surfaces to prevent warping and enhance longevity.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Cork veneer offers a thin, flexible surface ideal for decorative applications such as furniture inlays, wall coverings, and cabinetry, providing a natural aesthetic with easy installation. Cork sheets, being thicker and more durable, are best suited for soundproofing, insulation, and flooring where cushioning and resilience are essential. Selecting between cork veneer and cork sheets depends on the specific architectural or design requirements, balancing appearance with functional performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cork veneer offers a sustainable alternative by utilizing thin layers of cork harvested without damaging the tree, preserving the cork oak forests that capture significant amounts of CO2 annually. Cork sheets, while thicker and often harvested less frequently, also support environmental conservation by promoting natural regeneration and maintaining biodiversity in Mediterranean ecosystems. Both materials are biodegradable, renewable, and contribute to reducing carbon footprints in construction and design projects.
Cost Analysis: Cork Veneer vs Cork Sheet
Cork veneer typically costs more than cork sheets due to its thinner, high-quality finish ideal for decorative applications, whereas cork sheets offer a more affordable, thicker option suited for insulation or underlayment. The price difference stems from production techniques, with veneer requiring precise slicing and higher-grade cork material, leading to increased labor and processing costs. Selecting between cork veneer and cork sheet depends on budget constraints and intended use, where veneers maximize aesthetic value and sheets provide cost-effective bulk coverage.
Choosing the Right Cork Material for Your Project
Choosing between cork veneer and cork sheet depends on the project's surface and application requirements. Cork veneer, being thinner and more flexible, is ideal for decorative finishes and lightweight coverings, offering easy adhesion to curved surfaces. Cork sheets provide greater thickness and durability, making them suitable for insulation, soundproofing, and impact-resistant applications where robust material performance is essential.
cork veneer vs cork sheet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com