Flooring cork offers a durable, warm surface ideal for reducing noise and providing comfort underfoot in homes. Insulation cork excels at thermal and acoustic insulation, making it a sustainable choice for regulating indoor temperatures and energy efficiency. Choosing between flooring and insulation cork depends on whether the priority is surface comfort or enhancing building insulation.
Table of Comparison
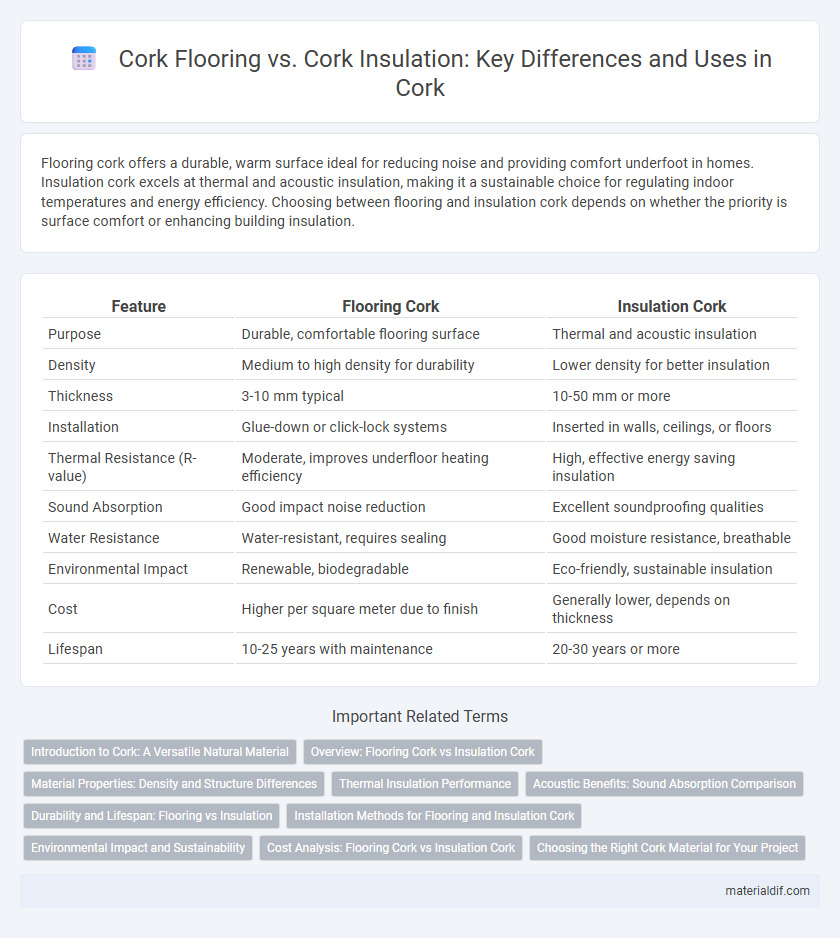
| Feature | Flooring Cork | Insulation Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Durable, comfortable flooring surface | Thermal and acoustic insulation |
| Density | Medium to high density for durability | Lower density for better insulation |
| Thickness | 3-10 mm typical | 10-50 mm or more |
| Installation | Glue-down or click-lock systems | Inserted in walls, ceilings, or floors |
| Thermal Resistance (R-value) | Moderate, improves underfloor heating efficiency | High, effective energy saving insulation |
| Sound Absorption | Good impact noise reduction | Excellent soundproofing qualities |
| Water Resistance | Water-resistant, requires sealing | Good moisture resistance, breathable |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable | Eco-friendly, sustainable insulation |
| Cost | Higher per square meter due to finish | Generally lower, depends on thickness |
| Lifespan | 10-25 years with maintenance | 20-30 years or more |
Introduction to Cork: A Versatile Natural Material
Cork, harvested from the bark of the Quercus suber tree, serves dual purposes in flooring and insulation applications due to its unique cellular structure. Flooring cork offers durability, thermal comfort, and sound absorption, making it ideal for residential and commercial spaces. Insulation cork efficiently reduces heat transfer and moisture penetration, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings while remaining eco-friendly and renewable.
Overview: Flooring Cork vs Insulation Cork
Flooring cork is designed for durability, comfort, and aesthetic appeal, commonly used in residential and commercial interiors to provide a warm, resilient surface. Insulation cork, on the other hand, focuses on thermal and acoustic insulation properties, often applied in building construction to improve energy efficiency and soundproofing. Both types leverage cork's natural cellular structure but serve distinct functions based on density, thickness, and treatment.
Material Properties: Density and Structure Differences
Flooring cork typically features a higher density and a more compact cellular structure, providing durability and resistance to wear in high-traffic areas. Insulation cork, on the other hand, has a lower density with a more open cellular matrix, enhancing its thermal and acoustic insulating properties. These differences in material density and microstructure directly influence performance, making flooring cork ideal for surface hardness and insulation cork suited for energy efficiency.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Cork used for insulation offers superior thermal insulation performance compared to flooring cork due to its higher density and cellular structure designed to minimize heat transfer. Insulation cork panels typically have a thermal conductivity as low as 0.040 W/mK, significantly reducing energy loss in buildings. Flooring cork, while providing some insulation benefits, prioritizes durability and comfort, resulting in a slightly higher thermal conductivity around 0.060 W/mK.
Acoustic Benefits: Sound Absorption Comparison
Cork flooring offers superior sound absorption due to its density and cellular structure, reducing impact noise and echo within indoor spaces effectively. Insulation cork primarily targets thermal performance but also provides moderate acoustic properties by dampening airborne sound transmission between rooms. Comparing both, cork flooring delivers enhanced acoustic comfort in living areas, while insulation cork serves as a supplemental sound barrier combined with its insulating benefits.
Durability and Lifespan: Flooring vs Insulation
Flooring cork is engineered to withstand heavy foot traffic and daily wear, offering durability that ranges from 10 to 30 years depending on maintenance and finish quality. Insulation cork, mainly used in building envelopes, exhibits exceptional longevity often exceeding 50 years due to its resistance to moisture, mold, and thermal degradation. The lifespan disparity between flooring and insulation cork is influenced by their functional roles, with insulation cork benefiting from minimal mechanical stress and stable environmental conditions.
Installation Methods for Flooring and Insulation Cork
Flooring cork installation typically involves laying cork tiles or planks with an adhesive or using a floating floor method over a subfloor, ensuring expansion gaps to accommodate natural cork movement. Insulation cork is often applied as cork boards or panels, fixed with specialized adhesives or mechanical fasteners to walls, roofs, or floors, creating a continuous thermal barrier. Proper moisture barriers and surface preparation are critical in both applications to enhance durability and performance of cork materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Flooring cork and insulation cork both offer eco-friendly benefits, but flooring cork primarily contributes through its renewable harvesting from cork oak trees without harming them, promoting biodiversity. Insulation cork excels in sustainability by improving building energy efficiency, reducing heating and cooling demands, and lowering carbon footprints over time. Both types are biodegradable and recyclable, supporting circular economy principles and minimizing landfill waste.
Cost Analysis: Flooring Cork vs Insulation Cork
Flooring cork typically costs between $3 to $8 per square foot, reflecting its durability, aesthetic appeal, and ease of installation in residential and commercial spaces. Insulation cork, priced around $5 to $12 per square foot, offers superior thermal and acoustic properties essential for energy efficiency and soundproofing in building construction. When conducting a cost analysis, insulation cork demands a higher initial investment but delivers long-term savings through energy conservation, while flooring cork combines moderate upfront costs with added comfort and style benefits.
Choosing the Right Cork Material for Your Project
Flooring cork offers natural durability, comfort underfoot, and thermal insulation, ideal for residential and commercial spaces seeking eco-friendly, sound-absorbing surfaces. Insulation cork provides superior thermal and acoustic resistance with moisture-repellent properties, making it perfect for walls, roofs, and industrial applications where energy efficiency is critical. Selecting the right cork type depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, exposure to moisture, and desired thermal performance.
flooring cork vs insulation cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com