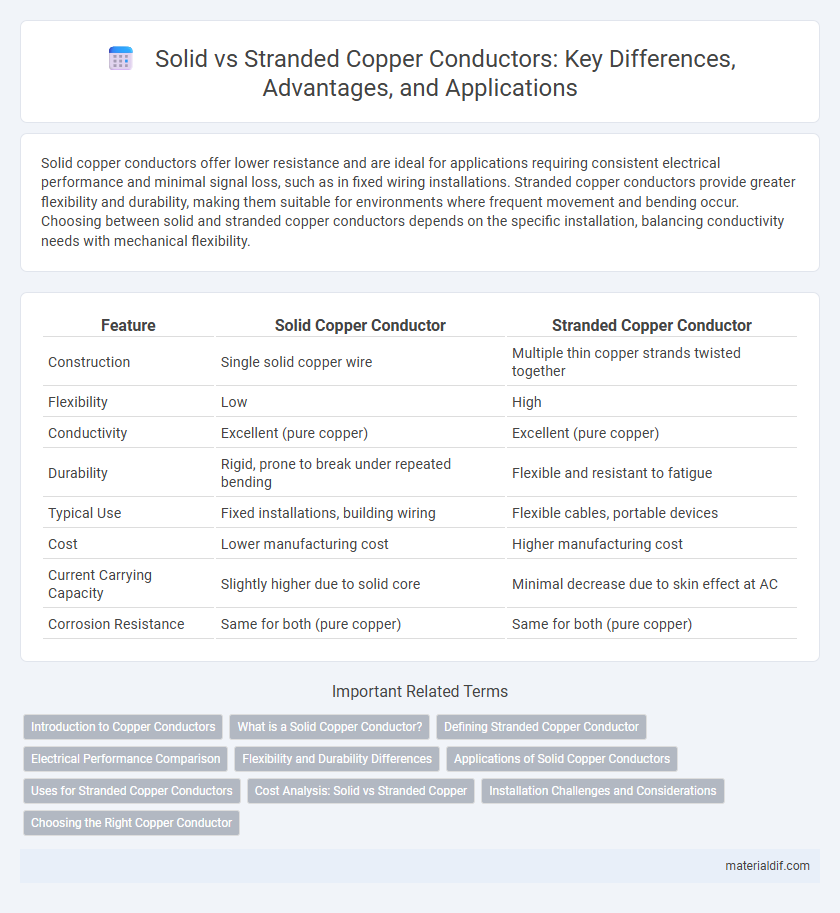
Solid copper conductors offer lower resistance and are ideal for applications requiring consistent electrical performance and minimal signal loss, such as in fixed wiring installations. Stranded copper conductors provide greater flexibility and durability, making them suitable for environments where frequent movement and bending occur. Choosing between solid and stranded copper conductors depends on the specific installation, balancing conductivity needs with mechanical flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solid Copper Conductor | Stranded Copper Conductor |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Single solid copper wire | Multiple thin copper strands twisted together |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Conductivity | Excellent (pure copper) | Excellent (pure copper) |
| Durability | Rigid, prone to break under repeated bending | Flexible and resistant to fatigue |
| Typical Use | Fixed installations, building wiring | Flexible cables, portable devices |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Current Carrying Capacity | Slightly higher due to solid core | Minimal decrease due to skin effect at AC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Same for both (pure copper) | Same for both (pure copper) |
Introduction to Copper Conductors
Solid copper conductors consist of a single, continuous copper wire, offering superior conductivity and minimal resistance, ideal for fixed installations and long-distance transmissions. Stranded copper conductors are made of multiple thin copper strands twisted together, enhancing flexibility and durability, making them suitable for applications requiring frequent movement or bending. Both types maintain excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance inherent to copper, influencing their selection based on mechanical and installation requirements.
What is a Solid Copper Conductor?
A solid copper conductor consists of a single, continuous copper wire, providing excellent conductivity and durability in electrical applications. It offers lower electrical resistance and is commonly used in residential wiring and grounding systems where rigidity and stability are essential. Solid copper conductors are less flexible than stranded conductors but are preferred for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness in fixed installations.
Defining Stranded Copper Conductor
Stranded copper conductor consists of multiple small copper wires twisted or braided together to form a single conductor, enhancing flexibility and durability compared to solid copper conductor. This construction reduces the risk of breakage under repeated bending or vibration, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent movement or complex routing. Stranded copper conductors maintain excellent electrical conductivity while offering superior mechanical strength and flexibility.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Solid copper conductors offer lower electrical resistance and consistent conductivity, making them ideal for applications requiring minimal signal loss. Stranded copper conductors, composed of multiple thin wires, provide greater flexibility but slightly higher resistance due to increased surface area and contact points. Both types maintain excellent conductivity, but solid conductors excel in long-distance and high-frequency electrical transmission where performance stability is crucial.
Flexibility and Durability Differences
Solid copper conductors feature a single, solid wire offering superior durability and consistent conductivity, making them ideal for fixed, inflexible installations. Stranded copper conductors consist of multiple thin wires twisted together, providing enhanced flexibility and resistance to metal fatigue, crucial for applications requiring frequent movement or bending. The choice between solid and stranded copper conductors depends on balancing the need for mechanical strength against flexibility in electrical wiring projects.
Applications of Solid Copper Conductors
Solid copper conductors are widely used in residential wiring, where their rigidity ensures stable connections in electrical outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures. These conductors provide lower resistance and better conductivity, making them preferable for fixed installations with minimal movement. Their durability and simplicity also make them ideal for circuit board grounding and low-frequency applications requiring less flexibility.
Uses for Stranded Copper Conductors
Stranded copper conductors offer enhanced flexibility compared to solid copper conductors, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent movement or bending, such as in automotive wiring, portable devices, and robotics. Their multiple small strands provide better resistance to metal fatigue and vibration, ensuring durability in dynamic environments. Stranded conductors also facilitate easier installation in tight spaces and complex routing paths where rigid solid conductors would be impractical.
Cost Analysis: Solid vs Stranded Copper
Solid copper conductors typically offer lower upfront costs due to simpler manufacturing processes and fewer materials compared to stranded copper conductors. Stranded copper conductors, while more expensive initially, provide enhanced flexibility and durability, potentially reducing replacement and maintenance expenses over time. Analyzing total lifecycle costs reveals that stranded conductors may deliver better long-term value despite higher initial investment, especially in applications requiring frequent movement or vibration resistance.
Installation Challenges and Considerations
Solid copper conductors offer ease of termination and lower electrical resistance but present challenges in bending and flexibility, making them less suitable for complex or tight installations. Stranded copper conductors, composed of multiple smaller wires, provide superior flexibility and resistance to fatigue from repeated movement, facilitating installation in confined spaces and dynamic environments. However, stranded conductors require careful termination techniques to ensure reliable connections and prevent fraying or poor contact.
Choosing the Right Copper Conductor
Choosing the right copper conductor between solid copper and stranded copper depends on the application and flexibility requirements. Solid copper conductors provide superior conductivity and durability, ideal for fixed installations with minimal movement. Stranded copper conductors offer enhanced flexibility and resist metal fatigue, making them suitable for applications involving frequent bending and vibrations.
Solid Copper Conductor vs Stranded Copper Conductor Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com