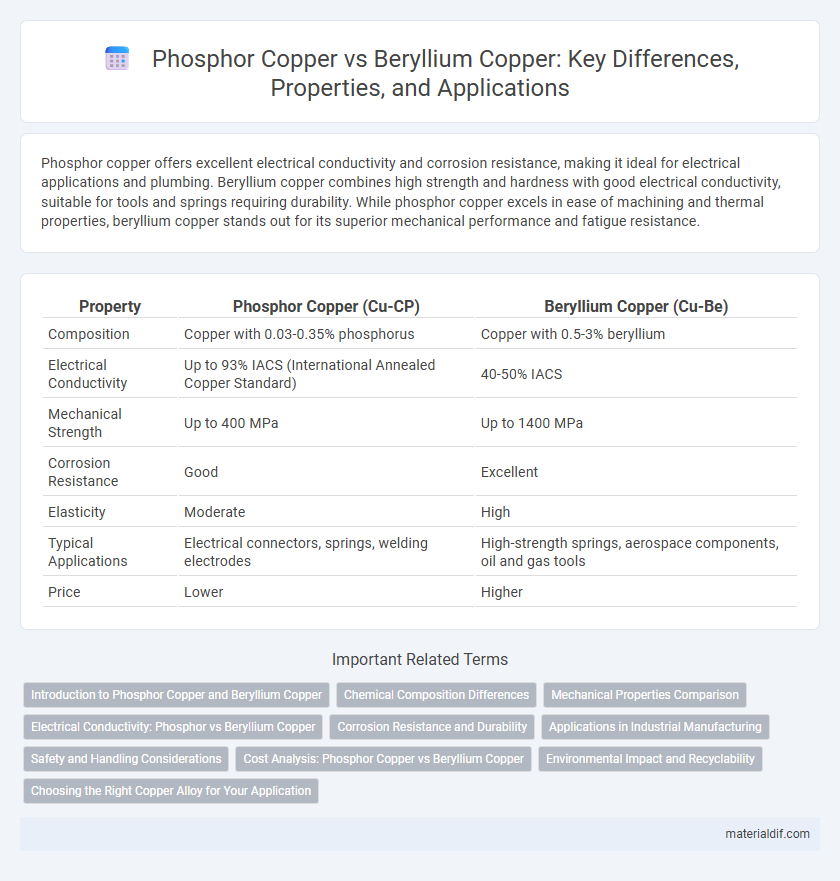
Phosphor copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical applications and plumbing. Beryllium copper combines high strength and hardness with good electrical conductivity, suitable for tools and springs requiring durability. While phosphor copper excels in ease of machining and thermal properties, beryllium copper stands out for its superior mechanical performance and fatigue resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phosphor Copper (Cu-CP) | Beryllium Copper (Cu-Be) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper with 0.03-0.35% phosphorus | Copper with 0.5-3% beryllium |
| Electrical Conductivity | Up to 93% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) | 40-50% IACS |
| Mechanical Strength | Up to 400 MPa | Up to 1400 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Elasticity | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Electrical connectors, springs, welding electrodes | High-strength springs, aerospace components, oil and gas tools |
| Price | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Phosphor Copper and Beryllium Copper
Phosphor copper, an alloy of copper with a small percentage of phosphorus, is valued for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and superior wear resistance, making it ideal for electrical connectors, springs, and marine hardware. Beryllium copper, containing 0.5 to 3% beryllium, offers exceptional hardness, tensile strength, and non-magnetic properties, widely used in aerospace, telecommunications, and precision tools. Both alloys enhance copper's base properties but serve distinct industrial applications depending on mechanical and electrical performance requirements.
Chemical Composition Differences
Phosphor copper primarily consists of about 99.9% copper with a small addition of 0.01-0.35% phosphorus, enhancing its wear resistance and stiffness. Beryllium copper contains approximately 0.5-3% beryllium alongside copper, significantly increasing its hardness, strength, and electrical conductivity. The absence of beryllium in phosphor copper makes it less toxic and more suitable for applications where biocompatibility is essential.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Phosphor copper exhibits excellent electrical conductivity combined with moderate strength and good wear resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring good ductility and corrosion resistance. Beryllium copper offers superior mechanical properties, including higher tensile strength, hardness, and fatigue resistance, due to its age-hardening capability, making it ideal for demanding environments requiring exceptional toughness and durability. The distinct difference in mechanical properties positions phosphor copper for electrical connectors and beryllium copper for high-performance springs and precision instruments.
Electrical Conductivity: Phosphor vs Beryllium Copper
Phosphor copper exhibits electrical conductivity around 88-95% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), making it highly efficient for electrical applications requiring low resistance. Beryllium copper, while known for superior strength and hardness, typically has lower conductivity, ranging from 20-65% IACS depending on heat treatment and alloy composition. The trade-off between conductivity and mechanical properties makes phosphor copper preferable in circuits where optimal electrical performance is critical.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Phosphor copper exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, especially in freshwater and mildly acidic environments, making it ideal for plumbing and marine applications. Beryllium copper, while slightly less resistant to corrosion, offers superior durability and mechanical strength, particularly in high-stress and high-wear settings such as aerospace and industrial tooling. Both alloys provide specific advantages, with phosphor copper excelling in corrosion resistance and beryllium copper leading in durability and hardness.
Applications in Industrial Manufacturing
Phosphor copper is widely used in industrial manufacturing for electrical connectors, springs, and resistance welding electrodes due to its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Beryllium copper, known for its superior strength, hardness, and fatigue resistance, is preferred in precision instruments, aerospace components, and high-stress mechanical parts. Both materials offer unique benefits, with phosphor copper maximizing electrical performance and beryllium copper excelling in structural durability.
Safety and Handling Considerations
Phosphor copper offers excellent corrosion resistance and conductivity with minimal toxicity, making it safer to handle with standard precautions such as gloves and eye protection. Beryllium copper poses significant health risks due to beryllium dust and fumes, requiring stringent safety protocols like specialized ventilation and respiratory protection during machining or welding. Proper training and monitoring are essential to prevent chronic beryllium disease when working with beryllium copper alloys.
Cost Analysis: Phosphor Copper vs Beryllium Copper
Phosphor copper offers a lower cost option compared to beryllium copper, making it more suitable for budget-sensitive applications. Beryllium copper, despite its higher price, provides superior strength, conductivity, and corrosion resistance, often justifying the investment in high-performance environments. Cost analysis must weigh initial material expenses against long-term benefits such as durability and reduced maintenance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Phosphor copper features high recyclability due to its minimal use of hazardous substances, resulting in a lower environmental impact compared to beryllium copper. Beryllium copper contains toxic beryllium, posing significant health and environmental risks during mining, processing, and recycling. Recycling phosphor copper reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions more effectively than beryllium copper, making it a more sustainable choice for various industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Copper Alloy for Your Application
Phosphor copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical and plumbing applications requiring high ductility. Beryllium copper provides superior strength, hardness, and fatigue resistance, suited for demanding mechanical and aerospace components. Selecting between phosphor and beryllium copper depends on balancing conductivity needs against mechanical performance and cost considerations.
Phosphor Copper vs Beryllium Copper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com