Copper conductors offer superior electrical conductivity and durability compared to aluminum conductors, making them ideal for applications requiring high performance and reliability. Copper's resistance to corrosion and better tensile strength reduces the risk of breakage and power loss, ensuring safer and more efficient electrical systems. Although aluminum conductors are lighter and more cost-effective, copper remains the preferred choice for critical wiring due to its enhanced conductivity and longevity.
Table of Comparison
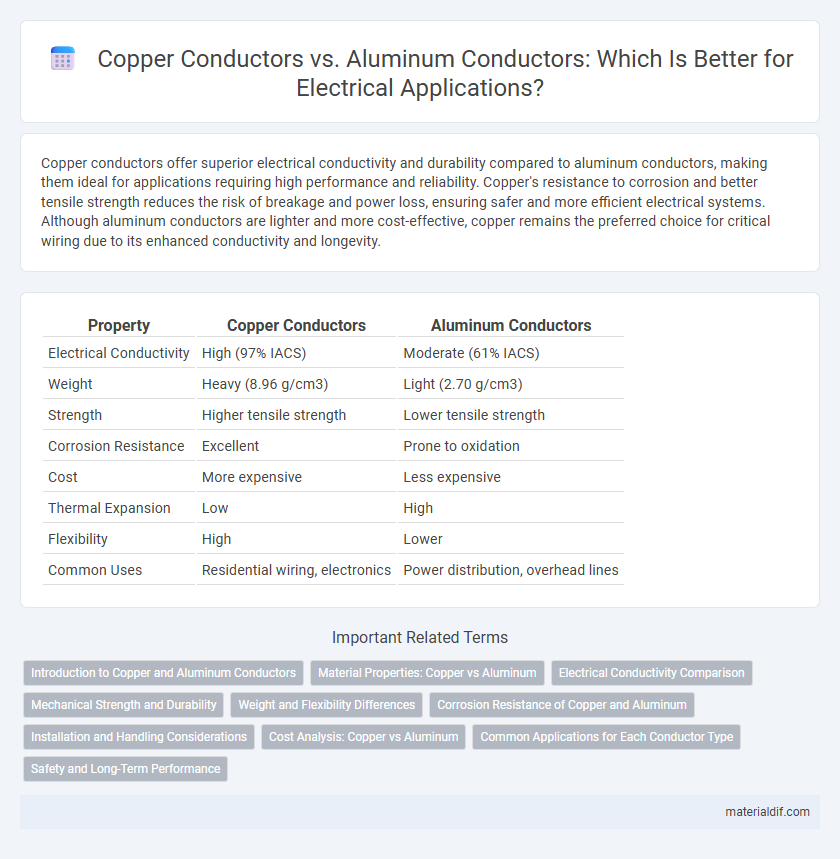
| Property | Copper Conductors | Aluminum Conductors |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High (97% IACS) | Moderate (61% IACS) |
| Weight | Heavy (8.96 g/cm3) | Light (2.70 g/cm3) |
| Strength | Higher tensile strength | Lower tensile strength |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Prone to oxidation |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
| Thermal Expansion | Low | High |
| Flexibility | High | Lower |
| Common Uses | Residential wiring, electronics | Power distribution, overhead lines |
Introduction to Copper and Aluminum Conductors
Copper conductors exhibit superior electrical conductivity, approximately 59.6 million siemens per meter, compared to aluminum's 37.8 million siemens per meter, making copper the preferred choice for high-performance electrical applications. Aluminum conductors offer advantages in weight and cost, weighing about 30% less and generally costing less per meter, which is beneficial for large-scale power distribution systems where weight and budget constraints are critical. Both materials have unique thermal expansion and mechanical properties, with copper demonstrating higher tensile strength and aluminum requiring anti-oxidation coatings to maintain reliability in electrical connections.
Material Properties: Copper vs Aluminum
Copper conductors exhibit higher electrical conductivity, approximately 59.6 MS/m, compared to aluminum's 36 MS/m, enabling more efficient current flow with less energy loss. Copper's superior mechanical strength and ductility enhance durability and resistance to fatigue, while aluminum's lower density provides a weight advantage in large-scale applications. Thermal conductivity of copper is nearly twice that of aluminum, improving heat dissipation and overall performance in electrical systems.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper conductors exhibit superior electrical conductivity, typically around 5.96 x 10^7 S/m at 20degC, compared to aluminum conductors, which have about 3.5 x 10^7 S/m. This higher conductivity means copper can carry more current with less energy loss, making it ideal for high-performance electrical systems. Despite aluminum's lighter weight and cost advantages, copper's efficiency in conducting electricity is unmatched for critical applications requiring minimal resistance and heat generation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Copper conductors exhibit significantly higher mechanical strength and durability compared to aluminum conductors, making them less prone to breaking or deformation under tensile stress. Copper's superior tensile strength and fatigue resistance ensure longer lifespan and reliable performance in demanding electrical installations. Aluminum conductors, while lighter and more cost-effective, require additional considerations for mechanical support and protection due to their lower strength and higher susceptibility to cracking or fatigue.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Copper conductors exhibit higher density than aluminum, resulting in increased weight but superior conductivity for electrical applications. Aluminum conductors are significantly lighter, making them advantageous for installations requiring reduced structural load and easier handling. Copper's intrinsic flexibility allows for better bending and fitting in tight spaces, whereas aluminum's rigidity can pose challenges in complex conduit layouts.
Corrosion Resistance of Copper and Aluminum
Copper conductors exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, maintaining conductivity and structural integrity over longer periods in harsh environments. Aluminum conductors are more prone to oxidation, forming an insulating oxide layer that can degrade performance and increase maintenance needs. This inherent difference makes copper the preferred choice for applications demanding high reliability and minimal corrosion-related issues.
Installation and Handling Considerations
Copper conductors offer superior tensile strength and flexibility, making them easier to handle and install in complex wiring configurations compared to aluminum conductors. Aluminum conductors require special connectors and anti-oxidation compounds to prevent corrosion and ensure secure electrical connections during installation. The weight advantage of aluminum reduces overall conductor mass, but its increased fragility necessitates careful handling to avoid damage and maintain system reliability.
Cost Analysis: Copper vs Aluminum
Copper conductors typically exhibit higher material costs than aluminum due to copper's greater market price and density, impacting overall project budgets. Aluminum conductors provide significant cost savings by offering lower initial investment and lighter weight, which reduces installation labor and structural support expenses. Despite aluminum's lower upfront costs, copper's superior conductivity and durability often result in lower lifecycle costs, especially in applications requiring long-term reliability and minimal maintenance.
Common Applications for Each Conductor Type
Copper conductors are widely used in residential wiring, electrical motors, and telecommunications due to their superior conductivity and durability. Aluminum conductors are commonly found in power distribution systems and overhead transmission lines, benefiting from their lighter weight and cost-effectiveness. Both conductor types are essential in electrical infrastructure, with copper preferred for smaller-scale, high-performance applications and aluminum favored for large-scale, budget-sensitive projects.
Safety and Long-Term Performance
Copper conductors offer superior safety due to their higher conductivity and lower resistance, which minimizes heat buildup and reduces fire risks compared to aluminum conductors. Copper's robust mechanical properties ensure better long-term performance, resisting corrosion and fatigue that commonly affect aluminum, especially in high-demand electrical systems. Choosing copper conductors enhances overall electrical reliability and decreases maintenance needs, making them a safer investment for critical infrastructure.
Copper Conductors vs Aluminum Conductors Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com