Copper wire offers superior electrical conductivity and durability compared to aluminum wire, making it a preferred choice for most electrical installations. While aluminum wire is lighter and less expensive, it is more prone to oxidation and requires special connectors to prevent safety hazards. Copper's reliability and ability to withstand higher temperatures make it ideal for long-term wiring solutions.
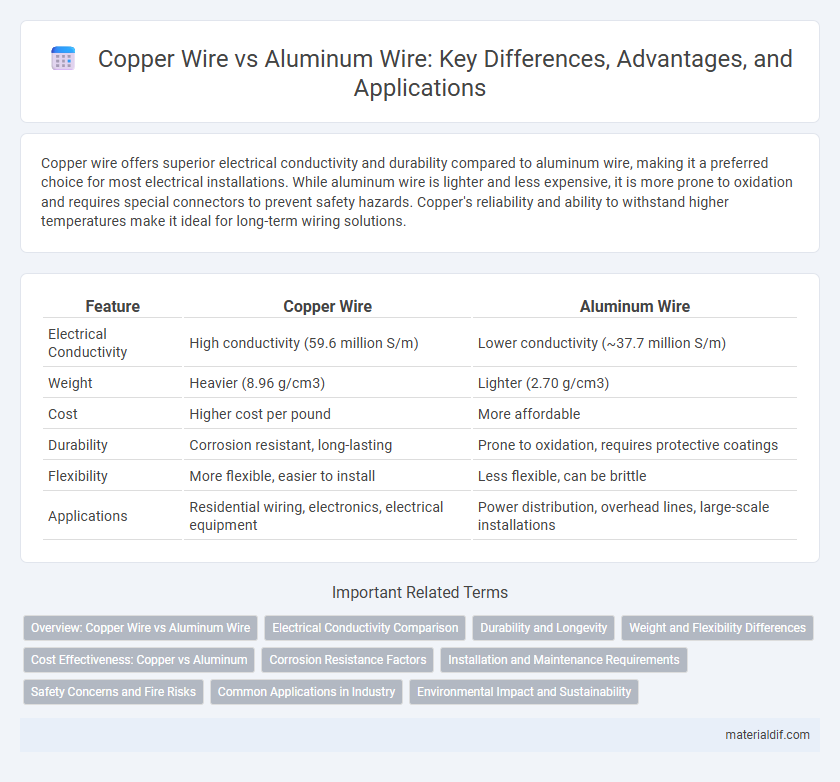
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Copper Wire | Aluminum Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High conductivity (59.6 million S/m) | Lower conductivity (~37.7 million S/m) |
| Weight | Heavier (8.96 g/cm3) | Lighter (2.70 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Higher cost per pound | More affordable |
| Durability | Corrosion resistant, long-lasting | Prone to oxidation, requires protective coatings |
| Flexibility | More flexible, easier to install | Less flexible, can be brittle |
| Applications | Residential wiring, electronics, electrical equipment | Power distribution, overhead lines, large-scale installations |
Overview: Copper Wire vs Aluminum Wire
Copper wire and aluminum wire differ significantly in conductivity, weight, and cost, with copper offering about 40% higher electrical conductivity and superior corrosion resistance. Aluminum wire, while lighter and more affordable, requires larger gauge sizes to match copper's capacity due to its lower conductivity and can be prone to oxidation and mechanical fatigue. These characteristics influence their applications in electrical wiring, where copper's durability favors residential and commercial use, while aluminum's cost-effectiveness finds preference in high-voltage overhead power lines.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper wire exhibits superior electrical conductivity, typically around 5.96 x 107 S/m, compared to aluminum wire's 3.5 x 107 S/m, making copper a more efficient conductor for electrical applications. This higher conductivity translates to lower resistance and reduced energy loss in copper wiring, enhancing overall system performance. Consequently, copper wiring is preferred in critical electrical installations where minimal voltage drop and high reliability are essential.
Durability and Longevity
Copper wire offers superior durability and longevity compared to aluminum wire due to its higher tensile strength and resistance to corrosion. Copper maintains stable electrical conductivity over time, reducing the risk of oxidation-related failures commonly seen in aluminum wiring. Its robust mechanical properties make copper wire the preferred choice for long-lasting and reliable electrical installations.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Copper wire is denser and heavier than aluminum wire, making it less suitable for applications requiring lightweight materials. Copper exhibits superior flexibility, allowing it to bend without breaking or damaging the conductor, whereas aluminum wire is stiffer and more prone to cracking under repeated bending. These differences impact installation ease and durability in electrical wiring projects.
Cost Effectiveness: Copper vs Aluminum
Copper wire typically costs more upfront than aluminum wire, but its superior conductivity and durability often result in lower maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Aluminum wire, while cheaper initially and lighter in weight, may require larger gauge sizes to match copper's performance, potentially offsetting initial savings. Long-term cost effectiveness favors copper in applications demanding high reliability and efficiency.
Corrosion Resistance Factors
Copper wire exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum wire due to its stable oxide layer, which prevents further degradation and maintains conductivity over time. Unlike aluminum, which forms a porous and less protective oxide layer prone to corrosion in moist or acidic environments, copper's tarnish layer acts as a strong barrier against oxidation. This enhanced durability makes copper wire ideal for long-term electrical applications in harsh environmental conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Copper wire offers superior flexibility and tensile strength, simplifying installation in complex electrical systems and reducing the risk of damage during handling. Its excellent conductivity requires fewer supports and connectors, leading to lower maintenance compared to aluminum wire, which is prone to oxidation and thermal expansion issues. Aluminum wire demands frequent inspections and specialized connectors to prevent loosening and ensure safety, increasing overall maintenance complexity.
Safety Concerns and Fire Risks
Copper wire offers higher conductivity and better resistance to corrosion, reducing the risk of overheating and electrical fires compared to aluminum wire. Aluminum wire, prone to oxidation and expansion, can loosen connections over time, increasing the chance of arcing and fire hazards. Electrical codes often favor copper wire for critical applications due to its superior safety performance in preventing fire risks.
Common Applications in Industry
Copper wire is extensively used in electrical wiring for residential, commercial, and industrial buildings due to its superior conductivity and durability. Aluminum wire is commonly applied in high-voltage power transmission lines and large-scale electrical distribution systems because of its lightweight property and cost-effectiveness. Both materials serve critical roles in the electrical industry, with copper preferred for low-voltage applications and aluminum dominating in overhead power cables.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper wire demonstrates a lower environmental impact due to its higher recyclability rate of about 95%, which reduces the need for mining new raw materials, unlike aluminum wire that requires more energy-intensive extraction processes. Aluminum wire, while lighter and less expensive, has a higher carbon footprint owing to the significant electricity consumption in its production phase, primarily from bauxite mining and smelting. Sustainable wiring solutions prioritize copper for its durability and longer lifecycle, minimizing waste and promoting circular economy practices in electrical infrastructure.
Copper Wire vs Aluminum Wire Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com