Wheel throwing offers artisans precise control and creative freedom to shape unique ceramic pieces through manual rotation and hand-building techniques. Slip casting enables efficient mass production by pouring liquid clay into molds, ensuring uniformity and intricate detail replication. Each method caters to different artistic and manufacturing needs, balancing craftsmanship with scalability.
Table of Comparison
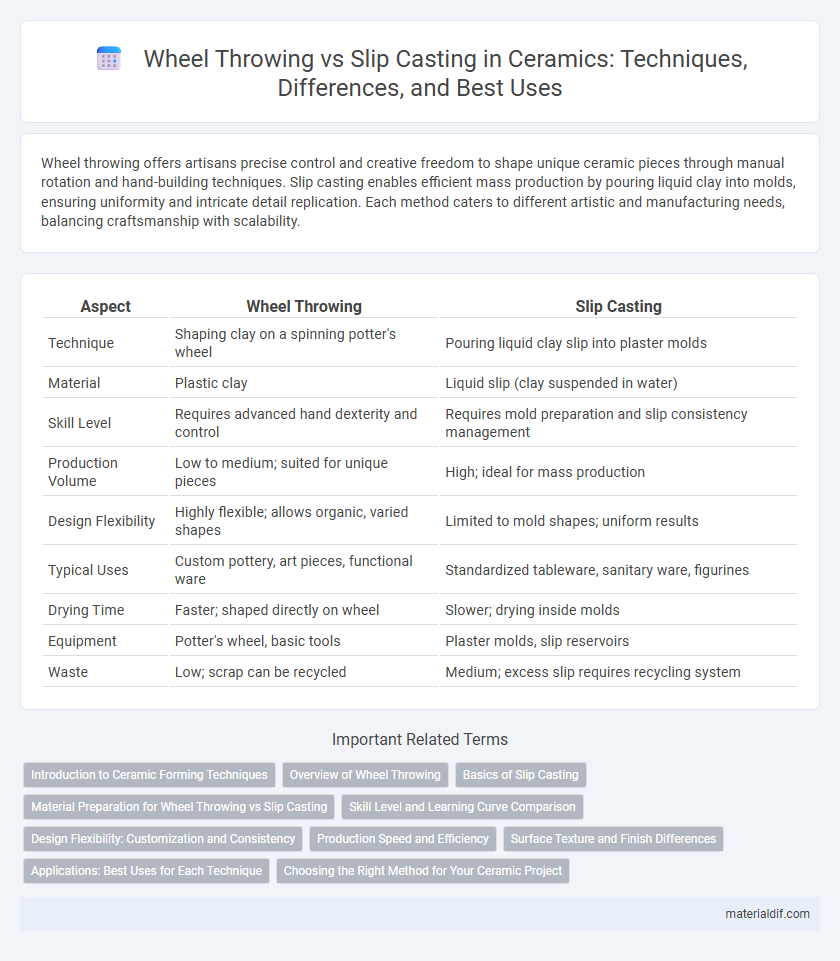
| Aspect | Wheel Throwing | Slip Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Shaping clay on a spinning potter's wheel | Pouring liquid clay slip into plaster molds |
| Material | Plastic clay | Liquid slip (clay suspended in water) |
| Skill Level | Requires advanced hand dexterity and control | Requires mold preparation and slip consistency management |
| Production Volume | Low to medium; suited for unique pieces | High; ideal for mass production |
| Design Flexibility | Highly flexible; allows organic, varied shapes | Limited to mold shapes; uniform results |
| Typical Uses | Custom pottery, art pieces, functional ware | Standardized tableware, sanitary ware, figurines |
| Drying Time | Faster; shaped directly on wheel | Slower; drying inside molds |
| Equipment | Potter's wheel, basic tools | Plaster molds, slip reservoirs |
| Waste | Low; scrap can be recycled | Medium; excess slip requires recycling system |
Introduction to Ceramic Forming Techniques
Wheel throwing involves shaping clay on a rotating pottery wheel, allowing for precise control and symmetrical forms, making it ideal for creating functional vessels. Slip casting uses liquid clay slip poured into plaster molds, enabling mass production of complex shapes with consistent detail and minimal manual intervention. Both techniques are fundamental ceramic forming methods, each suited for different artistic and industrial applications.
Overview of Wheel Throwing
Wheel throwing is a traditional ceramic technique where clay is shaped on a rotating potter's wheel using the hands and basic tools. This method allows for precise control over the form and thickness of the piece, enabling the creation of symmetrical objects like bowls, vases, and mugs. Skilled artisans can achieve unique textures and intricate details, making wheel throwing ideal for custom, handcrafted pottery.
Basics of Slip Casting
Slip casting involves pouring liquid clay slip into plaster molds, where the plaster absorbs water, forming a solid clay layer along the mold walls. This technique allows for precise replication of intricate shapes and fine surface details, making it ideal for mass production of ceramic pieces. Unlike wheel throwing, slip casting requires minimal hands-on shaping, relying instead on mold design and controlled drying processes.
Material Preparation for Wheel Throwing vs Slip Casting
Wheel throwing requires well-kneaded, plastic clay with consistent moisture content to ensure elasticity and workability on the potter's wheel. Slip casting uses a liquid clay body called slip, which must be thoroughly sieved and deflocculated to achieve a fine, homogeneous suspension for even casting in molds. Proper material preparation in wheel throwing emphasizes clay wedging to eliminate air pockets, while slip casting focuses on controlling slip viscosity and particle dispersion.
Skill Level and Learning Curve Comparison
Wheel throwing demands a higher initial skill level and a steeper learning curve, requiring fine motor control and hand-eye coordination to shape clay on a spinning wheel. Slip casting, on the other hand, involves pouring liquid clay into molds, making it more accessible to beginners with less manual dexterity. Mastery in wheel throwing typically takes longer due to the development of tactile sensitivity and rhythm, while slip casting emphasizes mold preparation and timing over hand skills.
Design Flexibility: Customization and Consistency
Wheel throwing offers exceptional design flexibility, allowing artisans to create unique, customizable shapes with subtle variations in texture and form. Slip casting provides high consistency and precision, producing uniform pieces ideal for mass production with intricate details replicated across batches. Combining wheel throwing's artistic expression with slip casting's repeatability can optimize both customization and consistency in ceramic design.
Production Speed and Efficiency
Wheel throwing offers greater control and customization but is generally slower due to manual shaping, making it ideal for artisanal or small-batch ceramic production. Slip casting excels in production speed and efficiency by using liquid clay poured into molds for rapid, consistent replication of complex shapes, well-suited for mass manufacturing. Factories favor slip casting when high volume and uniformity are priorities, while wheel throwing is preferred for unique, handcrafted pieces.
Surface Texture and Finish Differences
Wheel throwing produces ceramics with a distinctive tactile surface texture marked by subtle concentric ridges and variations due to hand shaping, offering a more organic and raw finish. Slip casting yields smoother surfaces with uniform, fine textures since the liquid clay (slip) conforms precisely to the mold's interior, ideal for consistent and detailed finishes. Artists often select wheel throwing for expressive texture and slip casting for sleek, flawless ceramic pieces.
Applications: Best Uses for Each Technique
Wheel throwing excels in creating unique, handcrafted pottery with organic shapes, ideal for artisanal cups, bowls, and vases requiring individual attention and subtle variations. Slip casting suits mass production of complex forms, such as detailed figurines, tableware sets, and intricate ceramics that demand precision and consistency. Each method's application depends on the desired volume, detail intricacy, and artistic expression in ceramic production.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Ceramic Project
Wheel throwing offers precise control and unique, handcrafted aesthetics ideal for small-batch or custom ceramic pieces, appealing to artists prioritizing technique and individual expression. Slip casting excels in producing consistent, complex shapes with high efficiency, making it suitable for large-scale production or intricate designs where uniformity is crucial. Selecting the appropriate method depends on project scale, design complexity, and desired artistic outcome, with wheel throwing favored for artisanal quality and slip casting preferred for repeatability.
Wheel Throwing vs Slip Casting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com