Glazed ceramic features a smooth, glass-like coating that enhances durability and provides water resistance, making it ideal for kitchenware and decorative tiles. Unglazed ceramic retains a porous, matte finish that offers better slip resistance and breathability, often used in pottery and flooring applications. Choosing between glazed and unglazed ceramic depends on the desired aesthetic, functionality, and maintenance requirements.
Table of Comparison
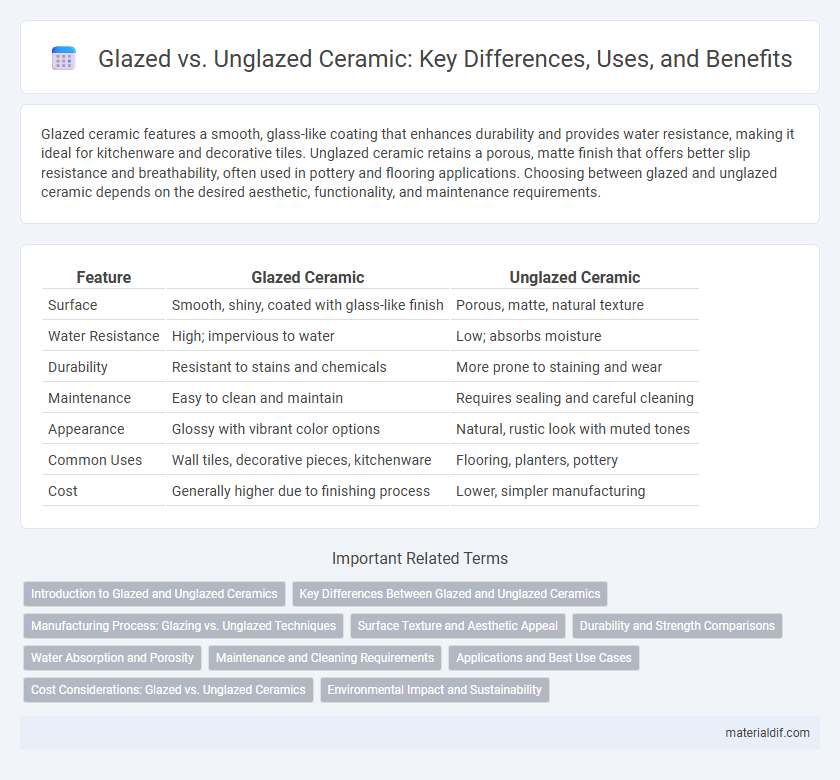
| Feature | Glazed Ceramic | Unglazed Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Surface | Smooth, shiny, coated with glass-like finish | Porous, matte, natural texture |
| Water Resistance | High; impervious to water | Low; absorbs moisture |
| Durability | Resistant to stains and chemicals | More prone to staining and wear |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and maintain | Requires sealing and careful cleaning |
| Appearance | Glossy with vibrant color options | Natural, rustic look with muted tones |
| Common Uses | Wall tiles, decorative pieces, kitchenware | Flooring, planters, pottery |
| Cost | Generally higher due to finishing process | Lower, simpler manufacturing |
Introduction to Glazed and Unglazed Ceramics
Glazed ceramics feature a glassy coating that enhances durability, water resistance, and aesthetic appeal through various colors and finishes. Unglazed ceramics maintain a porous surface that absorbs moisture and offers a natural, matte texture, often preferred for rustic or functional uses like terracotta pots. Understanding the differences in surface treatment and functionality is essential for selecting ceramics in applications ranging from cookware to tiles.
Key Differences Between Glazed and Unglazed Ceramics
Glazed ceramics feature a glass-like coating that enhances durability, water resistance, and color vibrancy, making them ideal for decorative and functional uses. Unglazed ceramics retain a porous surface, offering a natural, matte finish that provides better grip and breathability but requires more maintenance to prevent staining. Differences in finish, porosity, and maintenance define the primary contrasts between glazed and unglazed ceramic materials.
Manufacturing Process: Glazing vs. Unglazed Techniques
The manufacturing process of glazed ceramic involves applying a liquid glaze coating to the clay body before firing, which vitrifies into a smooth, glass-like surface that enhances durability and aesthetic appeal. Unglazed ceramic is fired without this additional coating, resulting in a porous, matte finish that allows for better breathability and slip resistance. Variations in kiln temperature and firing duration critically influence the final texture and strength of both glazed and unglazed ceramic products.
Surface Texture and Aesthetic Appeal
Glazed ceramic features a smooth, glossy surface created by a glass-like coating that enhances its vibrant colors and intricate patterns, making it ideal for decorative applications and easy cleaning. Unglazed ceramic has a porous, matte texture that offers a natural, rustic look, favored for its tactile feel and slip-resistant properties. The choice between glazed and unglazed ceramics significantly impacts the surface texture and aesthetic appeal, influencing functionality and design preferences in both interior and exterior environments.
Durability and Strength Comparisons
Glazed ceramic exhibits enhanced durability due to its glass-like coating, which provides superior resistance against moisture, stains, and surface wear compared to unglazed ceramic. Unglazed ceramic, while often more porous and susceptible to chipping, typically offers higher slip resistance and can withstand thermal shock better than some glazed varieties. Strength varies based on the ceramic composition, but glazed surfaces generally benefit from added protection, making them more suitable for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas.
Water Absorption and Porosity
Glazed ceramic features a glass-like coating that significantly reduces water absorption by sealing its porous surface, making it highly resistant to moisture and stains. Unglazed ceramic retains its natural porosity, resulting in higher water absorption rates that can lead to increased susceptibility to damage and staining. Porosity directly impacts durability and maintenance, with glazed ceramics offering a more impervious barrier compared to the porous structure of unglazed ceramics.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Glazed ceramic surfaces require minimal maintenance as their glass-like coating resists stains, moisture, and dirt, allowing for easy cleaning with mild detergents and water. Unglazed ceramic is more porous, making it prone to absorbing liquids and stains, necessitating more frequent sealing and specialized cleaners to prevent damage and maintain appearance. Regular sealing of unglazed ceramics enhances durability and reduces the risk of discoloration compared to the low-maintenance upkeep of glazed ceramics.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Glazed ceramic offers a smooth, non-porous surface ideal for applications requiring water resistance and easy cleaning, such as kitchen tiles, sanitary ware, and decorative pottery. Unglazed ceramic, with its porous and textured finish, excels in applications needing high slip resistance and breathability, making it suitable for outdoor flooring, terracotta pots, and industrial uses. Choosing between glazed and unglazed ceramics depends on factors like moisture exposure, durability requirements, and aesthetic preferences in specific environments.
Cost Considerations: Glazed vs. Unglazed Ceramics
Glazed ceramics typically incur higher costs due to additional materials and labor required for glazing and firing processes, enhancing surface durability and aesthetic appeal. Unglazed ceramics are generally more affordable, as they skip the glazing step, resulting in a more porous and matte finish but lower production complexity. Budget-conscious projects often choose unglazed ceramics for cost savings, while glazed options are preferred for their longevity and ease of maintenance despite the higher price.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glazed ceramic involves a glass-like coating that often requires higher kiln temperatures and additional raw materials, which can increase energy consumption and environmental footprint compared to unglazed ceramic. Unglazed ceramic is typically more sustainable due to its simpler production process, lower energy requirements, and better biodegradability, reducing waste impact. Both types have long lifespans, but unglazed ceramics often offer easier recyclability and less chemical run-off, making them preferable for eco-conscious applications.
Glazed Ceramic vs Unglazed Ceramic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com