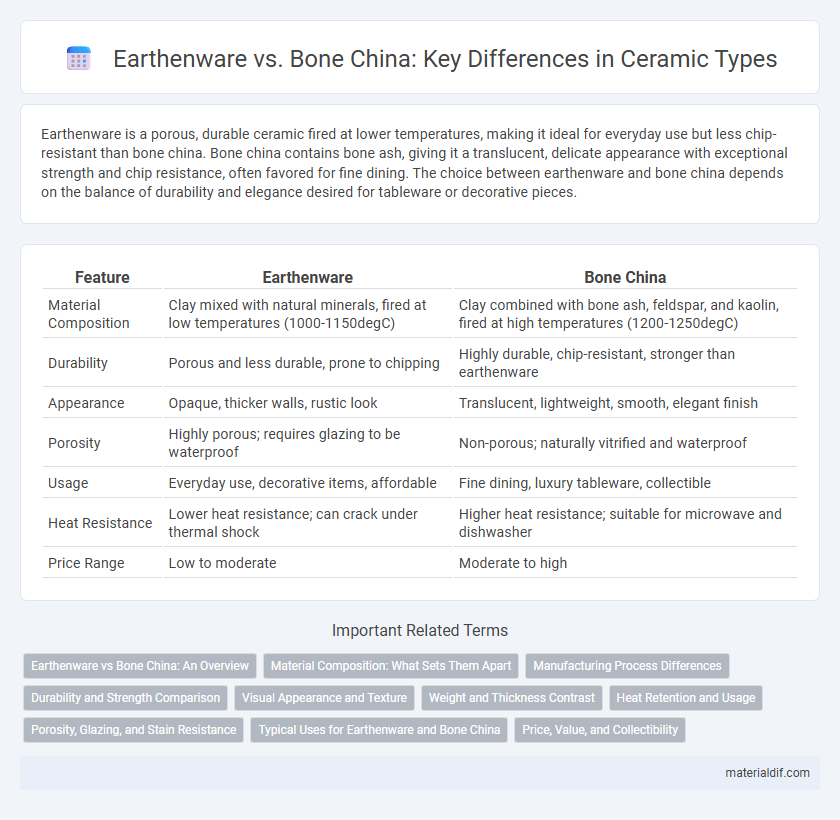
Earthenware is a porous, durable ceramic fired at lower temperatures, making it ideal for everyday use but less chip-resistant than bone china. Bone china contains bone ash, giving it a translucent, delicate appearance with exceptional strength and chip resistance, often favored for fine dining. The choice between earthenware and bone china depends on the balance of durability and elegance desired for tableware or decorative pieces.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Earthenware | Bone China |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay mixed with natural minerals, fired at low temperatures (1000-1150degC) | Clay combined with bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin, fired at high temperatures (1200-1250degC) |
| Durability | Porous and less durable, prone to chipping | Highly durable, chip-resistant, stronger than earthenware |
| Appearance | Opaque, thicker walls, rustic look | Translucent, lightweight, smooth, elegant finish |
| Porosity | Highly porous; requires glazing to be waterproof | Non-porous; naturally vitrified and waterproof |
| Usage | Everyday use, decorative items, affordable | Fine dining, luxury tableware, collectible |
| Heat Resistance | Lower heat resistance; can crack under thermal shock | Higher heat resistance; suitable for microwave and dishwasher |
| Price Range | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
Earthenware vs Bone China: An Overview
Earthenware is a porous, coarse ceramic fired at lower temperatures, making it more fragile and less translucent compared to bone china. Bone china incorporates bone ash, resulting in higher strength, whiteness, and translucency, ideal for fine tableware. Both materials offer unique aesthetic and functional qualities, with earthenware favored for rustic appeal and bone china valued for elegance and durability.
Material Composition: What Sets Them Apart
Earthenware is primarily composed of natural clay mixed with water and fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous and less durable material. Bone china distinguishes itself by incorporating bone ash into the porcelain mix, enhancing its strength, translucency, and whiteness. This critical difference in material composition defines the distinct properties and uses of each ceramic type.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Earthenware is made from coarse clay fired at lower temperatures, typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a porous and less durable material. Bone china incorporates bone ash with fine clays and feldspar, fired at higher temperatures around 1,200degC to 1,300degC, producing a strong, translucent, and non-porous ceramic. The inclusion of bone ash in bone china enhances vitrification during firing, differentiating its manufacturing process and final physical properties from earthenware.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Earthenware, characterized by its porous and less vitrified structure, demonstrates lower durability and strength compared to bone china, which boasts a higher density and remarkable toughness due to its bone ash content. Bone china's exceptional mechanical strength allows it to resist chipping and cracking under daily use, whereas earthenware is more prone to breakage and wear over time. The superior hardness and resilience of bone china make it ideal for fine dining and long-term use, contrasting with earthenware's suitability for decorative or low-impact applications.
Visual Appearance and Texture
Earthenware exhibits a rustic, porous texture with a matte or slightly glossy finish, often showcasing earthy tones and visible inclusions, giving it a handcrafted appeal. Bone China displays a translucent, smooth surface with a high-gloss, almost glass-like finish, characterized by its delicate whiteness and fine, refined texture. The visual contrast is marked by Earthenware's robust, opaque look versus Bone China's elegant, luminous quality.
Weight and Thickness Contrast
Earthenware is generally heavier and thicker compared to the delicate, lightweight structure of bone china, which contains bone ash for added strength. The porous nature of earthenware requires greater thickness for durability, while bone china achieves thinness without compromising toughness. This weight and thickness contrast directly impacts the aesthetic and functional qualities of each ceramic type.
Heat Retention and Usage
Earthenware, with its porous structure, retains heat moderately but cools faster than bone china, making it suitable for everyday use and casual dining. Bone china features a denser composition and higher thermal insulation, allowing it to maintain heat longer and excel in serving hot beverages or fine dining settings. The choice between earthenware and bone china depends on heat retention needs and the intended use environment, balancing durability and elegance.
Porosity, Glazing, and Stain Resistance
Earthenware is more porous than bone china, leading to greater absorption of liquids unless thoroughly glazed. Bone china features a highly vitrified body with low porosity, providing superior durability and stain resistance. The glazing on bone china is smoother and less prone to crazing, enhancing its longevity compared to the typically thicker, more porous glaze found on earthenware.
Typical Uses for Earthenware and Bone China
Earthenware is commonly used for rustic tableware, decorative pottery, and plant pots due to its porous nature and durability at lower firing temperatures. Bone china, prized for its high strength and translucent quality, is typically used in fine dining settings for elegant dinnerware, tea sets, and collectible porcelain items. The distinction in typical uses highlights earthenware's practicality and bone china's luxury appeal in ceramics.
Price, Value, and Collectibility
Earthenware offers an affordable price point and durable everyday use, making it a popular choice for casual dining, while bone china commands higher prices due to its refined translucency, strength, and craftsmanship. Bone china holds greater collectible value, with its historical significance and manufacturer marks attracting enthusiasts and investors alike. The intrinsic differences in material composition and production methods create distinct markets for both ceramics, impacting their long-term desirability and price appreciation.
Earthenware vs Bone China Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com