Vitrified ceramic tiles undergo a high-temperature fusion process that makes them dense, non-porous, and highly durable, ideal for heavy-traffic areas and outdoor use. Non-vitrified ceramic tiles retain some porosity, making them more absorbent and less resistant to stains and moisture, often preferred for indoor, low-traffic settings. The choice between vitrified and non-vitrified tiles hinges on factors like durability requirements, moisture exposure, and maintenance preferences.
Table of Comparison
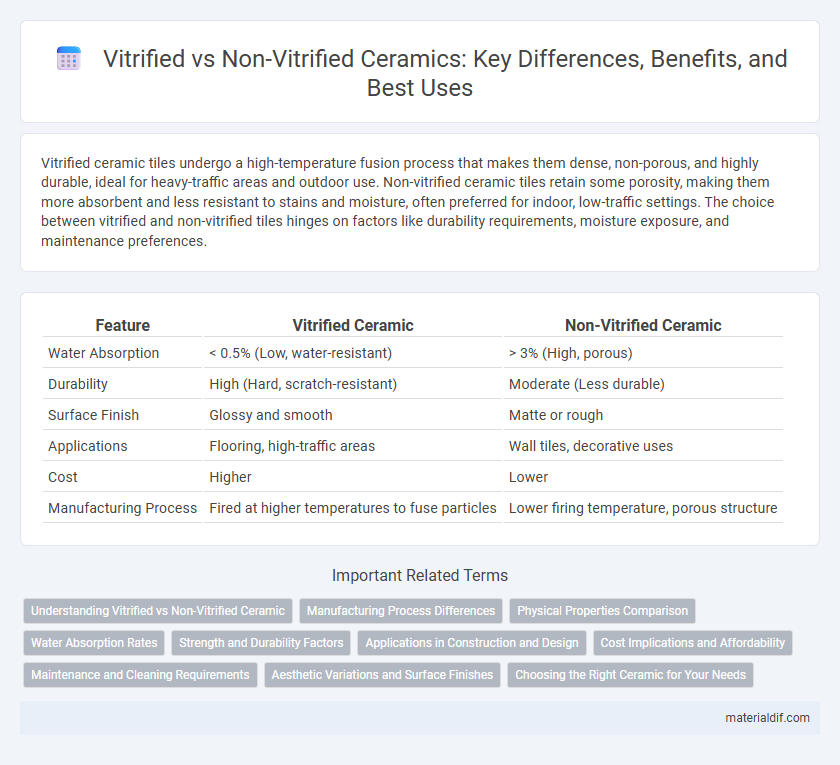
| Feature | Vitrified Ceramic | Non-Vitrified Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Water Absorption | < 0.5% (Low, water-resistant) | > 3% (High, porous) |
| Durability | High (Hard, scratch-resistant) | Moderate (Less durable) |
| Surface Finish | Glossy and smooth | Matte or rough |
| Applications | Flooring, high-traffic areas | Wall tiles, decorative uses |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Manufacturing Process | Fired at higher temperatures to fuse particles | Lower firing temperature, porous structure |
Understanding Vitrified vs Non-Vitrified Ceramic
Vitrified ceramic tiles are created by fusing natural materials at high temperatures, resulting in a dense, non-porous surface that provides enhanced durability and water resistance compared to non-vitrified tiles. Non-vitrified ceramics retain a porous structure, making them more absorbent and less resistant to wear, which suits indoor, low-traffic areas. Understanding the key differences in manufacturing and properties helps in selecting the appropriate ceramic type for specific applications based on factors like moisture exposure and foot traffic.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Vitrified ceramics undergo a manufacturing process involving high-temperature firing that fuses the particles, resulting in a dense, non-porous surface with low water absorption. Non-vitrified ceramics are fired at lower temperatures, leading to a more porous and less dense structure that retains moisture. The key manufacturing difference lies in the firing temperature and the level of vitrification, which directly impacts the ceramic's durability, strength, and water resistance.
Physical Properties Comparison
Vitrified ceramic tiles exhibit low porosity, increased density, and high resistance to water absorption, making them highly durable and suitable for heavy traffic areas. Non-vitrified tiles have higher porosity, resulting in greater water absorption and lower mechanical strength, which makes them more prone to wear and staining. The enhanced hardness and non-porous nature of vitrified ceramics contribute to superior physical properties compared to non-vitrified variants.
Water Absorption Rates
Vitrified ceramic tiles exhibit extremely low water absorption rates, typically less than 0.5%, making them highly resistant to moisture and ideal for areas prone to water exposure. Non-vitrified tiles absorb more water, often exceeding 3%, which can lead to increased susceptibility to stains and damage in wet environments. This difference in water absorption significantly impacts their durability and suitability for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Strength and Durability Factors
Vitrified ceramic tiles exhibit superior strength and durability due to their low porosity and dense composition, making them highly resistant to cracking and wear. Non-vitrified tiles, having higher porosity, absorb more water, which weakens their structure and reduces longevity under heavy use. The vitrification process enhances mechanical strength, making vitrified ceramics ideal for high-traffic areas and demanding environments.
Applications in Construction and Design
Vitrified tiles, known for their low porosity and high durability, are ideal for high-traffic commercial spaces, outdoor flooring, and wet areas due to their resistance to water and stains. Non-vitrified tiles, with higher porosity and a more natural texture, are preferred for interior walls, decorative accents, and low-moisture residential areas where cost-effectiveness and aesthetic variety are prioritized. Architects and designers select vitrified tiles for strength and maintenance ease, while non-vitrified tiles offer versatility and a rustic appearance suited to traditional or artistic designs.
Cost Implications and Affordability
Vitrified ceramic tiles, known for their low porosity and durability, typically come at a higher initial cost compared to non-vitrified tiles, which are more affordable but less resistant to water and wear. Non-vitrified tiles offer budget-friendly options suitable for low-traffic areas, while vitrified tiles justify their price with long-term cost savings due to reduced maintenance and replacement needs. Choosing between vitrified and non-vitrified ceramics largely depends on balancing upfront affordability with the anticipated lifecycle expenses.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Vitrified ceramic tiles are highly resistant to stains, water, and scratches due to their low porosity, making them easier to clean and maintain with just regular sweeping and mopping using mild detergents. Non-vitrified ceramic tiles are more porous and prone to absorbing spills and stains, requiring more frequent sealing and intense cleaning to prevent discoloration and damage. Regular maintenance of vitrified tiles reduces the risk of surface degradation, while non-vitrified tiles demand ongoing care to protect their appearance and longevity.
Aesthetic Variations and Surface Finishes
Vitrified ceramics exhibit a glass-like, non-porous surface with a smooth, glossy finish that enhances color richness and pattern clarity, making them ideal for premium aesthetic applications. Non-vitrified ceramics have a more porous texture and matte or semi-matte finishes, offering rustic, natural looks with greater variation in surface texture and tone. The choice between vitrified and non-vitrified affects design versatility, as vitrified tiles provide uniformity and durability, while non-vitrified tiles present diverse textures and organic visual appeal.
Choosing the Right Ceramic for Your Needs
Vitrified ceramics are dense, durable, and water-resistant due to their low porosity, making them ideal for high-traffic and moisture-prone areas. Non-vitrified ceramics offer more design flexibility and color options but are more porous and less resistant to wear, suitable for decorative and low-traffic spaces. Selecting the right ceramic depends on balancing durability, maintenance, and aesthetic requirements for your specific application.
Vitrified vs Non-Vitrified Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com