Cellophane lamination offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to plastic lamination, making it a preferred choice for sustainable packaging solutions. It provides a natural gloss and a smooth finish that enhances product appearance while allowing breathability, unlike plastic lamination which creates a completely airtight seal. The durability and moisture resistance of plastic lamination make it suitable for long-term protection, but cellophane lamination remains popular for its compostability and lower environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
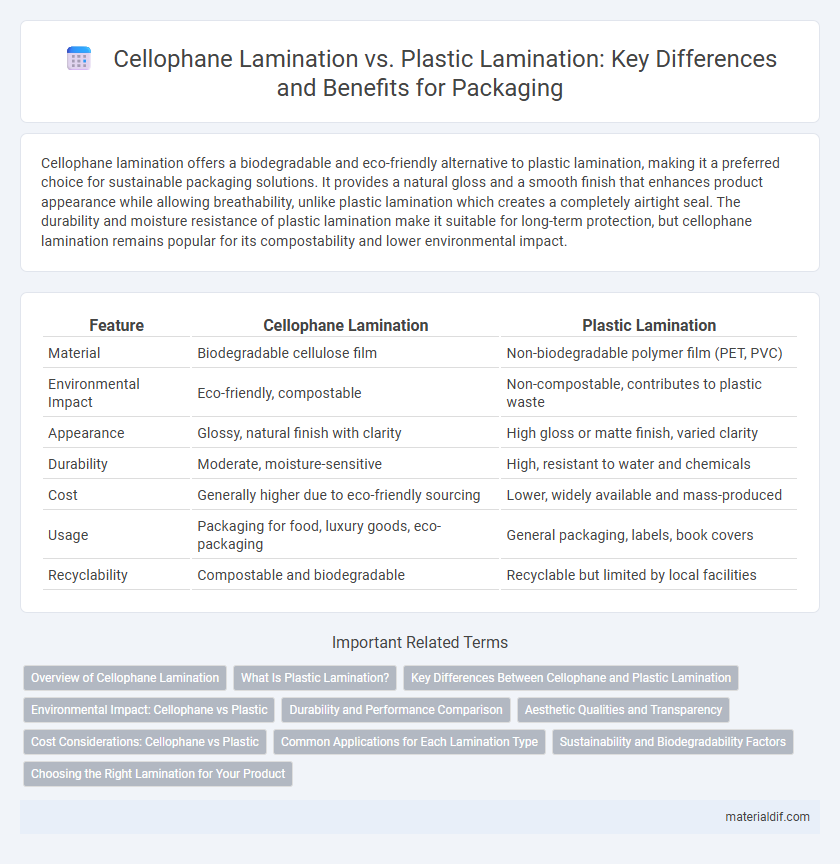
| Feature | Cellophane Lamination | Plastic Lamination |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Biodegradable cellulose film | Non-biodegradable polymer film (PET, PVC) |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, compostable | Non-compostable, contributes to plastic waste |
| Appearance | Glossy, natural finish with clarity | High gloss or matte finish, varied clarity |
| Durability | Moderate, moisture-sensitive | High, resistant to water and chemicals |
| Cost | Generally higher due to eco-friendly sourcing | Lower, widely available and mass-produced |
| Usage | Packaging for food, luxury goods, eco-packaging | General packaging, labels, book covers |
| Recyclability | Compostable and biodegradable | Recyclable but limited by local facilities |
Overview of Cellophane Lamination
Cellophane lamination involves applying a thin, transparent film made from cellulose to packaging materials, enhancing their moisture resistance and gloss while remaining biodegradable and eco-friendly. Unlike plastic lamination, which uses synthetic polymers like polypropylene or polyethylene, cellophane lamination offers superior breathability and recyclability, making it ideal for sustainable packaging solutions. This method improves product shelf life and visual appeal without compromising environmental impact, aligning with increasing demand for green packaging alternatives.
What Is Plastic Lamination?
Plastic lamination involves applying a thin plastic film, usually polyethylene or polypropylene, onto printed material to enhance durability, water resistance, and appearance. Unlike cellophane lamination, which uses a biodegradable cellulose film, plastic lamination offers stronger protection against moisture and mechanical wear. This method is widely used for packaging, book covers, and posters to extend product life and maintain print quality.
Key Differences Between Cellophane and Plastic Lamination
Cellophane lamination uses a biodegradable cellulose film derived from wood pulp, offering excellent breathability and a natural glossy finish, while plastic lamination employs synthetic polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene, providing superior water resistance and durability. Cellophane is favored for eco-friendly packaging due to its compostable nature, whereas plastic lamination is widely used for heavy-duty protection and moisture barriers. The environmental impact remains a key differentiator, with cellophane presenting a sustainable option compared to conventional plastic laminates.
Environmental Impact: Cellophane vs Plastic
Cellophane lamination is biodegradable and derived from renewable resources like cellulose, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic lamination, which relies on petroleum-based materials and contributes to long-term pollution. Unlike plastic lamination that can take hundreds of years to decompose and often ends up in landfills or oceans, cellophane breaks down naturally within a few months under composting conditions. The reduced carbon footprint and lower toxicity of cellophane lamination offer significant environmental benefits over plastic lamination in sustainable packaging solutions.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Cellophane lamination offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly barrier that provides moderate durability but is less resistant to moisture and heat compared to plastic lamination. Plastic lamination, typically made from polyethylene or polypropylene, delivers superior durability, enhanced moisture resistance, and higher performance in protecting printed materials under harsh conditions. For applications requiring long-term preservation and robust protection, plastic lamination outperforms cellophane in durability and overall protective performance.
Aesthetic Qualities and Transparency
Cellophane lamination offers superior clarity and a natural gloss that enhances product visibility, making packaging more visually appealing and eco-friendly. Unlike plastic lamination, cellophane maintains a high level of transparency without a plastic film's artificial sheen, preserving the original colors and textures beneath. This makes it ideal for premium packaging that requires both an attractive finish and clear product presentation.
Cost Considerations: Cellophane vs Plastic
Cellophane lamination generally incurs higher material costs compared to plastic lamination due to its biodegradable composition and manufacturing process. Plastic lamination, often made from polyethylene or polypropylene, offers a lower-cost alternative with greater durability and moisture resistance. Companies balancing budget and environmental impact frequently weigh these cost discrepancies when selecting packaging solutions.
Common Applications for Each Lamination Type
Cellophane lamination is commonly used for food packaging, gift wrap, and cosmetic product packaging due to its natural biodegradability and moisture resistance. Plastic lamination, often made from polyester or polypropylene, is preferred for heavy-duty packaging, printed materials, and industrial applications because of its superior durability and water resistance. Both lamination types enhance product protection and visual appeal but cater to different industry needs based on environmental impact and strength requirements.
Sustainability and Biodegradability Factors
Cellophane lamination offers superior sustainability due to its biodegradable and compostable nature, derived from cellulose, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastic lamination. Unlike plastic lamination, which often involves petroleum-based polymers that persist in the environment for centuries, cellophane breaks down naturally without leaving harmful residues. This biodegradability significantly reduces landfill waste and environmental pollution, highlighting cellophane lamination as a preferred choice for sustainable packaging solutions.
Choosing the Right Lamination for Your Product
Cellophane lamination offers a natural, biodegradable option that enhances product appearance with a glossy finish while maintaining breathability, making it ideal for food packaging and eco-conscious brands. Plastic lamination provides superior durability, moisture resistance, and a wider range of finishes, suitable for products requiring extended shelf life and heavy handling. Selecting the right lamination depends on balancing environmental impact with performance needs, product type, and customer preference for sustainability.
Cellophane Lamination vs Plastic Lamination Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com