Pultruded carbon fibers offer enhanced strength and stiffness due to continuous fiber alignment, making them ideal for structural applications requiring uniform load distribution. Woven carbon fibers provide greater flexibility and impact resistance, as their interlaced patterns absorb energy more effectively. Choosing between pultruded and woven carbon depends on whether rigidity or durability is the priority in the composite design.
Table of Comparison
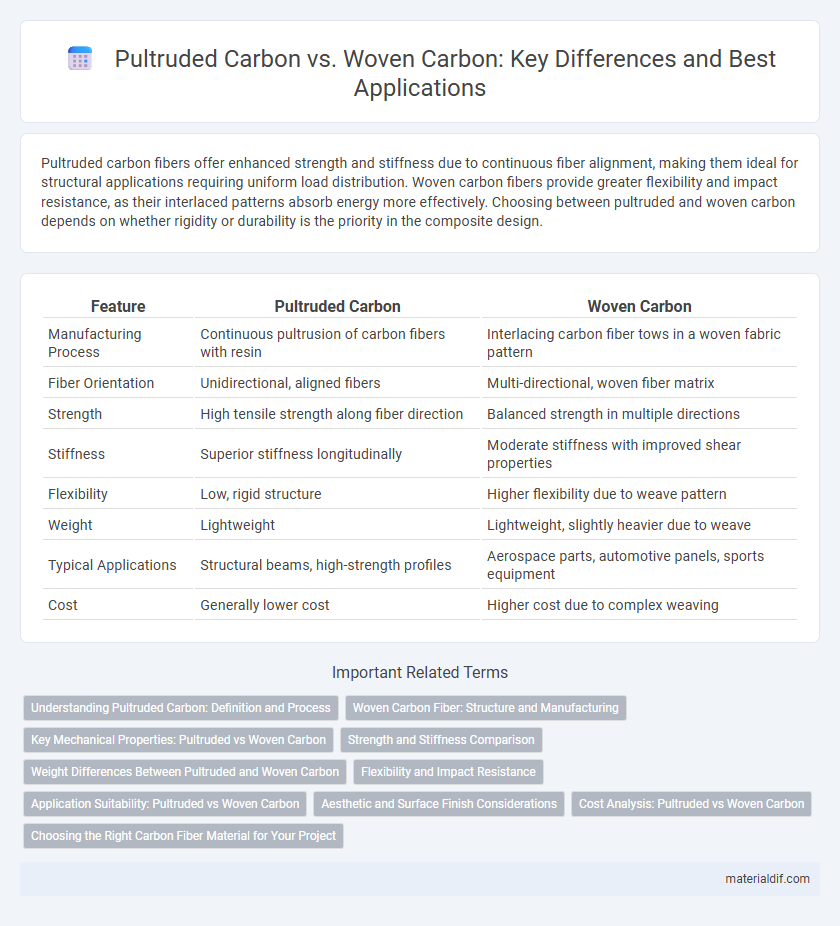
| Feature | Pultruded Carbon | Woven Carbon |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Continuous pultrusion of carbon fibers with resin | Interlacing carbon fiber tows in a woven fabric pattern |
| Fiber Orientation | Unidirectional, aligned fibers | Multi-directional, woven fiber matrix |
| Strength | High tensile strength along fiber direction | Balanced strength in multiple directions |
| Stiffness | Superior stiffness longitudinally | Moderate stiffness with improved shear properties |
| Flexibility | Low, rigid structure | Higher flexibility due to weave pattern |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight, slightly heavier due to weave |
| Typical Applications | Structural beams, high-strength profiles | Aerospace parts, automotive panels, sports equipment |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complex weaving |
Understanding Pultruded Carbon: Definition and Process
Pultruded carbon is a composite material created by continuously pulling carbon fibers through a resin bath and shaped die, resulting in strong, lightweight profiles with uniform cross-sections. This process enhances fiber alignment and resin impregnation, optimizing mechanical properties such as tensile strength and stiffness. Pultrusion differs from woven carbon by producing linear, anisotropic components rather than fabric-like sheets, making it ideal for structural applications requiring consistent performance.
Woven Carbon Fiber: Structure and Manufacturing
Woven carbon fiber features a fabric-like structure created by interlacing carbon fiber yarns in a crisscross pattern, enhancing its dimensional stability and impact resistance. The manufacturing process involves weaving carbon filaments into sheets, which are then impregnated with resin and cured to form strong, lightweight composite materials ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. This fabric structure allows for greater flexibility in shaping complex geometries compared to pultruded carbon products.
Key Mechanical Properties: Pultruded vs Woven Carbon
Pultruded carbon fibers exhibit higher tensile strength and stiffness due to their unidirectional fiber alignment, optimizing load-bearing capacity along the fiber axis. Woven carbon fibers offer enhanced impact resistance and improved multi-directional strength, resulting from their interlaced fiber architecture. The choice between pultruded and woven carbon significantly influences structural performance in aerospace, automotive, and sporting applications.
Strength and Stiffness Comparison
Pultruded carbon fibers exhibit higher tensile strength and stiffness due to their unidirectional fiber alignment, which efficiently bears load along the fiber length. Woven carbon fabrics offer multidirectional strength and improved impact resistance but generally have lower stiffness compared to pultruded counterparts. The anisotropic nature of pultruded carbon makes it ideal for applications requiring maximum rigidity, while woven carbon suits complex geometries needing flexibility and damage tolerance.
Weight Differences Between Pultruded and Woven Carbon
Pultruded carbon fibers exhibit a higher fiber alignment, resulting in a lighter composite material compared to woven carbon, which contains interlaced fibers that increase overall weight. The enhanced density control in pultrusion processes minimizes resin and void content, further reducing weight while maintaining strength. Woven carbon composites are typically heavier due to their fabric structure, which adds thickness and weight from overlapping fiber bundles.
Flexibility and Impact Resistance
Pultruded carbon offers superior rigidity and higher tensile strength due to its continuous fiber alignment, making it less flexible but excellent for structural applications requiring impact resistance. Woven carbon provides enhanced flexibility and better energy absorption upon impact, attributed to its interlaced fiber architecture that distributes stress more evenly. Choosing between pultruded and woven carbon depends on balancing the need for stiffness versus the ability to withstand dynamic forces without fracturing.
Application Suitability: Pultruded vs Woven Carbon
Pultruded carbon fiber offers high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent stiffness, making it ideal for structural components in aerospace, automotive, and construction where load-bearing efficiency is critical. Woven carbon fiber provides superior flexibility and impact resistance, suited for applications requiring complex shapes and enhanced surface finish, such as sports equipment and protective gear. Each material's application suitability hinges on the balance between structural rigidity and form adaptability, with pultruded carbon emphasizing mechanical performance and woven carbon favoring contour precision and toughness.
Aesthetic and Surface Finish Considerations
Pultruded carbon fibers offer a uniform, consistent surface finish ideal for applications requiring sleek, smooth aesthetics with minimal texture variation. Woven carbon fabrics provide a distinct, patterned appearance characterized by visible fiber interlacing that enhances visual depth and complexity. Surface finish considerations depend on the intended visual impact, with pultruded carbon emphasizing clean, glossy surfaces, while woven carbon highlights intricate textures and a more tactile appeal.
Cost Analysis: Pultruded vs Woven Carbon
Pultruded carbon materials typically offer lower production costs due to continuous fiber alignment and automated manufacturing processes, leading to reduced labor and material waste. Woven carbon fabrics often incur higher expenses because of complex weaving techniques and increased material usage to achieve multidirectional strength. Cost analysis reveals that pultruded carbon is preferable for budget-sensitive applications, whereas woven carbon justifies higher costs with superior structural versatility.
Choosing the Right Carbon Fiber Material for Your Project
Pultruded carbon fiber offers exceptional strength and stiffness, ideal for projects requiring consistent mechanical properties and streamlined manufacturing processes. Woven carbon fiber provides enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for complex shapes and applications demanding higher fatigue durability. Selecting the appropriate carbon fiber depends on specific project goals, load requirements, and desired performance characteristics.
Pultruded Carbon vs Woven Carbon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com