Chopped carbon fiber consists of short strands randomly oriented, offering isotropic strength and easier molding for complex shapes. Woven carbon fiber features interlaced fibers in a fabric pattern, providing higher tensile strength and stiffness primarily in the fiber directions. The choice between chopped and woven carbon fiber depends on the performance requirements and manufacturing processes of the carbon PET applications.
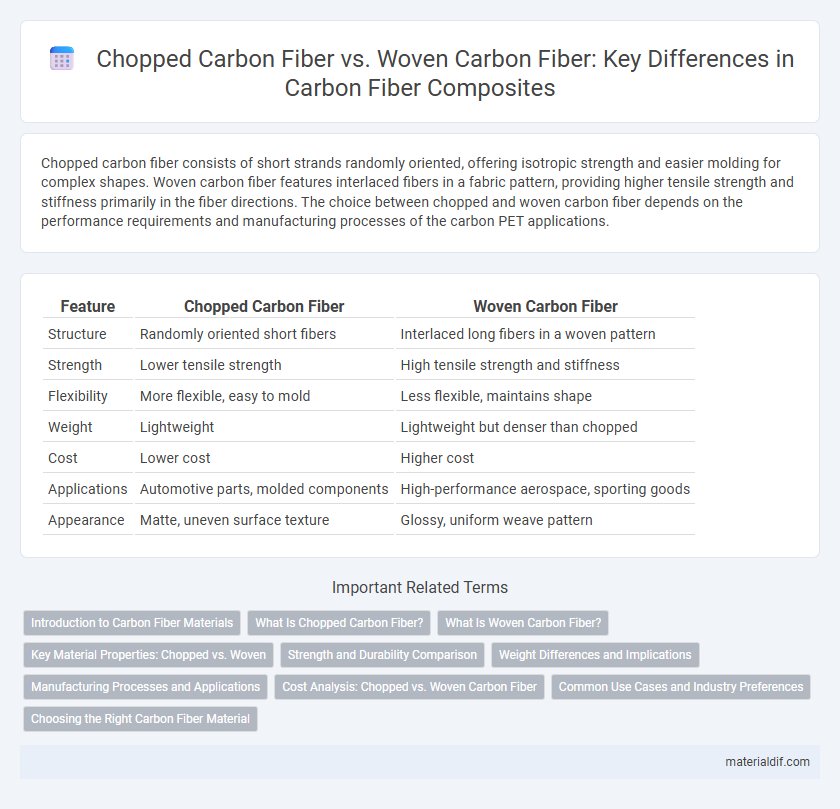
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Chopped Carbon Fiber | Woven Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Randomly oriented short fibers | Interlaced long fibers in a woven pattern |
| Strength | Lower tensile strength | High tensile strength and stiffness |
| Flexibility | More flexible, easy to mold | Less flexible, maintains shape |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but denser than chopped |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Automotive parts, molded components | High-performance aerospace, sporting goods |
| Appearance | Matte, uneven surface texture | Glossy, uniform weave pattern |
Introduction to Carbon Fiber Materials
Chopped carbon fiber consists of short strands randomly oriented, providing isotropic strength and enhanced molding flexibility for complex shapes, making it ideal for automotive parts and consumer goods. Woven carbon fiber features long continuous fibers woven into a fabric, offering superior strength, stiffness, and directional stability, commonly used in aerospace, high-performance sports equipment, and structural applications. Both forms retain carbon fiber's lightweight and high-strength characteristics but differ in mechanical properties and manufacturing processes tailored to specific engineering needs.
What Is Chopped Carbon Fiber?
Chopped carbon fiber consists of short strands of carbon fiber that are randomly arranged and bonded with a resin matrix, offering enhanced isotropic properties and consistent strength in multiple directions. This form is commonly used in injection molding and composite materials to improve impact resistance and reduce manufacturing costs compared to woven carbon fiber. Its versatility makes chopped carbon fiber ideal for applications requiring complex shapes and lightweight reinforcement without the need for directional strength.
What Is Woven Carbon Fiber?
Woven carbon fiber consists of interlaced carbon threads arranged in a crisscross pattern, providing enhanced strength and flexibility compared to chopped carbon fiber. This fabric-like structure allows for improved load distribution and resistance to impact, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods applications. Its high tensile strength and lightweight properties contribute to superior performance in composite materials and structural components.
Key Material Properties: Chopped vs. Woven
Chopped carbon fiber consists of short fiber segments that provide isotropic mechanical properties, enhancing impact resistance and formability in complex shapes. Woven carbon fiber features continuous fibers in a woven pattern, offering superior tensile strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability along fiber directions. The choice between chopped and woven carbon fiber depends on specific application requirements for strength, flexibility, and manufacturing complexity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Chopped carbon fiber consists of short, randomly oriented fibers that offer decent strength but lower tensile strength and impact resistance compared to woven carbon fiber. Woven carbon fiber features continuous, interlaced fibers that provide superior strength, improved durability, and enhanced resistance to fatigue and cracking under stress. This structural integrity makes woven carbon fiber the preferred choice for high-performance applications requiring maximum strength and long-term durability.
Weight Differences and Implications
Chopped carbon fiber typically weighs less than woven carbon fiber due to its shorter fiber lengths and fragmented structure, which reduces density and stiffness. The weight difference influences material selection, with chopped fibers preferred in applications requiring lightweight components but less mechanical strength. Woven carbon fiber, being heavier and mechanically more robust, suits high-performance uses demanding superior tensile strength and durability despite additional weight.
Manufacturing Processes and Applications
Chopped carbon fiber involves cutting continuous carbon fibers into short strands, which are then mixed with resin or thermoplastics for injection molding or compression molding, offering increased design flexibility and cost-efficiency. Woven carbon fiber is created by interlacing continuous fiber tows in a fabric form, enabling superior strength and stiffness, commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods where structural performance is critical. Manufacturing processes for woven carbon fiber include layup and curing, while chopped carbon fiber manufacturing emphasizes moldability and faster production cycles for complex geometries.
Cost Analysis: Chopped vs. Woven Carbon Fiber
Chopped carbon fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to woven carbon fiber due to lower manufacturing complexity and reduced labor requirements. Woven carbon fiber, while more expensive, provides superior strength and uniformity, justifying its higher price in high-performance applications. Cost analysis reveals that chopped fibers are ideal for budget-sensitive projects, whereas woven carbon fibers suit performance-critical designs demanding maximum structural integrity.
Common Use Cases and Industry Preferences
Chopped carbon fiber is commonly used in automotive and consumer electronics industries for molded parts requiring complex shapes and cost efficiency, offering enhanced strength and reduced weight in injection molding processes. Woven carbon fiber is preferred in aerospace, sporting goods, and high-performance sectors due to its superior tensile strength, impact resistance, and aesthetic appeal, ideal for structural components and visible surfaces. Industry preferences favor chopped carbon fiber for mass production and cost-sensitive applications, while woven carbon fiber dominates where mechanical performance and appearance are critical.
Choosing the Right Carbon Fiber Material
Chopped carbon fiber offers enhanced moldability and impact resistance, making it ideal for complex shapes and applications requiring durability. Woven carbon fiber provides superior strength and stiffness along specific fiber directions, benefiting structural components subjected to high loads. Selecting the right carbon fiber material depends on balancing fabrication complexity with mechanical performance requirements for the intended use.
Chopped Carbon Fiber vs Woven Carbon Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com