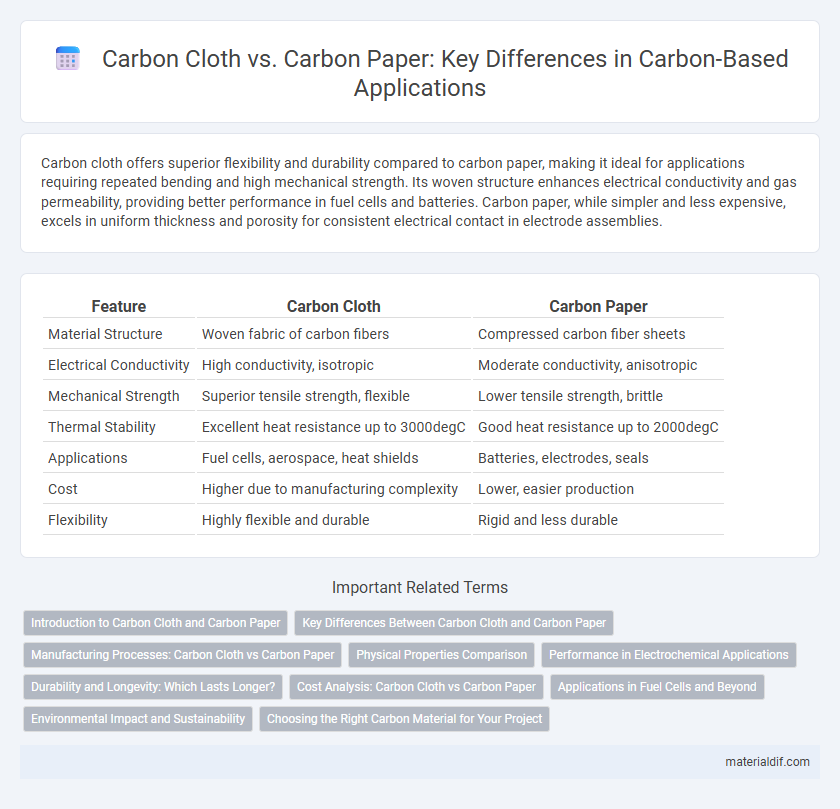
Carbon cloth offers superior flexibility and durability compared to carbon paper, making it ideal for applications requiring repeated bending and high mechanical strength. Its woven structure enhances electrical conductivity and gas permeability, providing better performance in fuel cells and batteries. Carbon paper, while simpler and less expensive, excels in uniform thickness and porosity for consistent electrical contact in electrode assemblies.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Carbon Cloth | Carbon Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Structure | Woven fabric of carbon fibers | Compressed carbon fiber sheets |
| Electrical Conductivity | High conductivity, isotropic | Moderate conductivity, anisotropic |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior tensile strength, flexible | Lower tensile strength, brittle |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent heat resistance up to 3000degC | Good heat resistance up to 2000degC |
| Applications | Fuel cells, aerospace, heat shields | Batteries, electrodes, seals |
| Cost | Higher due to manufacturing complexity | Lower, easier production |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and durable | Rigid and less durable |
Introduction to Carbon Cloth and Carbon Paper
Carbon cloth is a woven material composed of carbon fibers that offers high tensile strength, excellent electrical conductivity, and thermal resistance, making it ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and energy storage industries. Carbon paper consists of a non-woven mat of carbon fibers bonded with a polymer, providing flexibility, lightweight properties, and superior electrical conductivity for use in batteries, fuel cells, and electrochemical sensors. Both materials serve as key components in electrochemical applications but differ in structure, mechanical strength, and suitability for specific technical requirements.
Key Differences Between Carbon Cloth and Carbon Paper
Carbon cloth offers superior flexibility and durability due to its woven fiber structure, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength and repeated bending. In contrast, carbon paper is a thin, non-woven sheet primarily used for conductivity and transfer purposes, lacking the mechanical robustness of carbon cloth. The porosity and surface area of carbon cloth enable enhanced electrochemical performance, whereas carbon paper provides a consistent, smooth surface better suited for uniform current distribution.
Manufacturing Processes: Carbon Cloth vs Carbon Paper
Carbon cloth is produced through a weaving process that interlaces carbon fibers into a flexible textile, enhancing mechanical strength and durability. Carbon paper, manufactured by binding short carbon fibers with a resin and pressing them into thin sheets, tends to have a denser, less flexible structure. Differences in fiber arrangement and binder use directly influence the thermal conductivity and structural integrity of these carbon materials.
Physical Properties Comparison
Carbon cloth exhibits superior tensile strength and flexibility compared to carbon paper, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and conformability. Carbon paper has a more uniform thickness and higher surface area, which enhances its conductivity and reaction efficiency in electrochemical cells. Both materials are lightweight and chemically stable, but carbon cloth offers better mechanical resilience under stress.
Performance in Electrochemical Applications
Carbon cloth exhibits superior electrochemical performance compared to carbon paper due to its higher porosity and larger surface area, enabling enhanced reactant diffusion and electron transfer. Its flexible, woven structure improves mechanical durability and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for fuel cells and batteries. Carbon paper, while offering a more uniform surface, often suffers from lower permeability and limited mass transport, reducing its efficiency in high-demand electrochemical applications.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Carbon cloth offers superior durability compared to carbon paper due to its woven fiber structure, which provides enhanced tear resistance and flexibility under mechanical stress. The longevity of carbon cloth is significantly higher, making it ideal for repeated use in applications such as battery electrodes and fuel cells. In contrast, carbon paper tends to degrade faster because of its non-woven, brittle composition, resulting in limited lifespan when exposed to harsh operational conditions.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Cloth vs Carbon Paper
Carbon cloth generally incurs higher upfront costs compared to carbon paper due to its woven structure and enhanced durability, making it suitable for long-term applications in fuel cells and batteries. Carbon paper offers a cost-effective alternative with lower initial expenses, but it may require more frequent replacement and can lead to higher lifecycle costs. Evaluating total ownership cost highlights carbon cloth as more economical for high-performance, extended-use scenarios, while carbon paper suits budget-conscious, short-term projects.
Applications in Fuel Cells and Beyond
Carbon cloth exhibits superior flexibility and durability compared to carbon paper, making it ideal for fuel cell gas diffusion layers where efficient reactant transport and water management are critical. Its woven structure enhances mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, supporting longer fuel cell lifespan and performance stability. Beyond fuel cells, carbon cloth is increasingly utilized in wearable electronics, energy storage devices, and flexible sensors due to its lightweight, porous nature, and high surface area.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon cloth offers superior environmental benefits compared to carbon paper due to its reusable and durable nature, reducing waste generation significantly. Its production involves fewer chemical treatments and lower energy consumption, enhancing overall sustainability. Carbon paper, typically single-use, contributes to higher landfill accumulation and requires more frequent replacement, increasing its ecological footprint.
Choosing the Right Carbon Material for Your Project
Carbon cloth offers superior flexibility and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent bending or high mechanical strength, such as aerospace and automotive components. Carbon paper, known for its affordability and easier handling, suits projects involving electrical conductivity and electrode fabrication in fuel cells or batteries. Selecting the appropriate carbon material depends on factors like mechanical stress, conductivity requirements, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance.
Carbon Cloth vs Carbon Paper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com