Sand cast bronze offers a rougher surface finish and is typically used for larger, less detailed components due to its lower tooling costs and flexibility in casting size. Investment cast bronze provides higher precision, smoother surfaces, and intricate detail, making it ideal for complex, smaller parts where dimensional accuracy is critical. The choice between sand cast and investment cast bronze depends on the specific application requirements, balancing cost, detail, and mechanical properties.
Table of Comparison
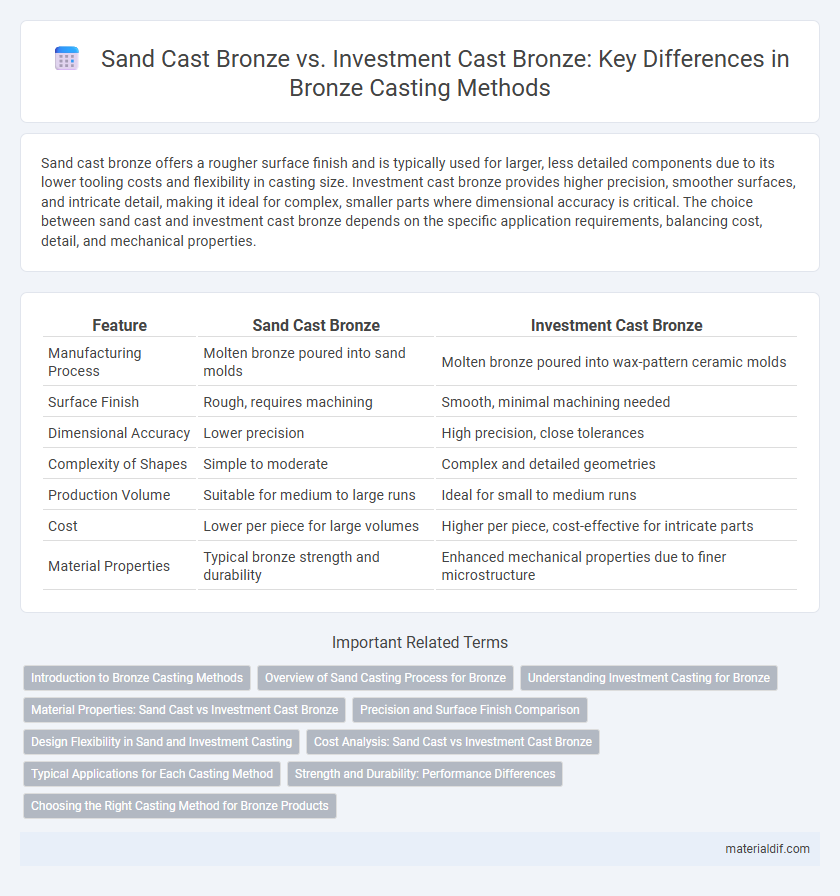
| Feature | Sand Cast Bronze | Investment Cast Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Molten bronze poured into sand molds | Molten bronze poured into wax-pattern ceramic molds |
| Surface Finish | Rough, requires machining | Smooth, minimal machining needed |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Lower precision | High precision, close tolerances |
| Complexity of Shapes | Simple to moderate | Complex and detailed geometries |
| Production Volume | Suitable for medium to large runs | Ideal for small to medium runs |
| Cost | Lower per piece for large volumes | Higher per piece, cost-effective for intricate parts |
| Material Properties | Typical bronze strength and durability | Enhanced mechanical properties due to finer microstructure |
Introduction to Bronze Casting Methods
Sand cast bronze offers cost-effective production with a rougher surface finish and is ideal for large, simple shapes, while investment cast bronze provides superior precision and intricate detail suitable for complex designs. Sand casting involves packing sand around a pattern to form a mold, whereas investment casting uses a wax model coated in ceramic for high accuracy. Both methods are essential in bronze casting, each optimized for specific applications based on dimensional tolerance and surface quality.
Overview of Sand Casting Process for Bronze
Sand casting for bronze involves creating a mold by compacting sand around a pattern, which shapes the cavity for molten bronze to be poured into. This method allows for the production of large, complex bronze components with relatively low tooling costs and is highly adaptable to custom designs and sizes. Cooling and solidification times vary based on part thickness, impacting the final microstructure and mechanical properties of the cast bronze.
Understanding Investment Casting for Bronze
Investment cast bronze offers superior precision and intricate detail compared to sand cast bronze, making it ideal for complex components with tight tolerances. This process involves creating a wax pattern coated with ceramic material to form a mold, ensuring high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes. The ability to produce consistent, repeatable parts with minimal post-processing enhances the value of investment cast bronze in aerospace, automotive, and artistic applications.
Material Properties: Sand Cast vs Investment Cast Bronze
Sand cast bronze typically exhibits a coarser grain structure, resulting in lower tensile strength and surface finish quality compared to investment cast bronze. Investment cast bronze offers superior dimensional accuracy, smoother surfaces, and enhanced mechanical properties due to its fine microstructure and controlled cooling process. These differences make investment cast bronze ideal for intricate components requiring high durability and precision, while sand cast bronze suits less detailed, larger parts where strength demands are moderate.
Precision and Surface Finish Comparison
Sand cast bronze typically exhibits a rougher surface finish and lower dimensional precision due to the nature of the sand mold, which can cause slight irregularities and porosity. Investment cast bronze offers superior precision and a smoother surface finish, as the wax mold process allows for intricate details and tighter tolerances. This makes investment cast bronze ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and fine surface details.
Design Flexibility in Sand and Investment Casting
Sand cast bronze offers greater design flexibility for large, simple shapes due to the mold's adaptability and lower tooling costs, allowing for easier modifications during production. Investment cast bronze excels in producing intricate, detailed designs with tight tolerances, ideal for complex geometries and thin walls that are difficult to achieve with sand casting. The choice between sand and investment casting depends largely on the required part complexity and production volume, balancing design freedom and manufacturing precision.
Cost Analysis: Sand Cast vs Investment Cast Bronze
Sand cast bronze typically offers lower production costs due to simpler mold-making processes and shorter setup times, making it ideal for larger, less detailed components. Investment cast bronze involves higher expenses related to wax pattern creation and ceramic shell molds but provides superior precision and surface finish, which can reduce machining costs in intricate parts. Cost analysis should consider not only initial casting expenses but also post-casting machining requirements and production volume to determine the most economical choice.
Typical Applications for Each Casting Method
Sand cast bronze is typically used for large, heavy-duty components such as pumps, valves, and marine hardware due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to produce complex shapes. Investment cast bronze excels in applications requiring high precision and fine detail, including small intricate parts like sculptures, jewelry, and aerospace components. The choice between sand casting and investment casting depends largely on the required dimensional accuracy and production volume of the bronze parts.
Strength and Durability: Performance Differences
Sand cast bronze exhibits robust mechanical strength due to its coarse-grained structure, making it well-suited for heavy-duty applications requiring high durability. Investment cast bronze offers superior dimensional accuracy and a finer grain structure, resulting in improved strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced resistance to stress and fatigue. The choice between these casting methods impacts performance, with investment cast bronze often preferred for intricate designs necessitating greater durability and precise tolerances.
Choosing the Right Casting Method for Bronze Products
Sand cast bronze offers cost-effective production for large, simple shapes with good mechanical properties and surface finish, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications like marine and industrial components. Investment cast bronze provides superior dimensional accuracy and intricate detail, suitable for complex, precision parts such as decorative hardware and aerospace components. Selecting the right casting method depends on balancing factors like production volume, complexity, tolerance requirements, and surface quality for optimal bronze product performance.
Sand Cast Bronze vs Investment Cast Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com