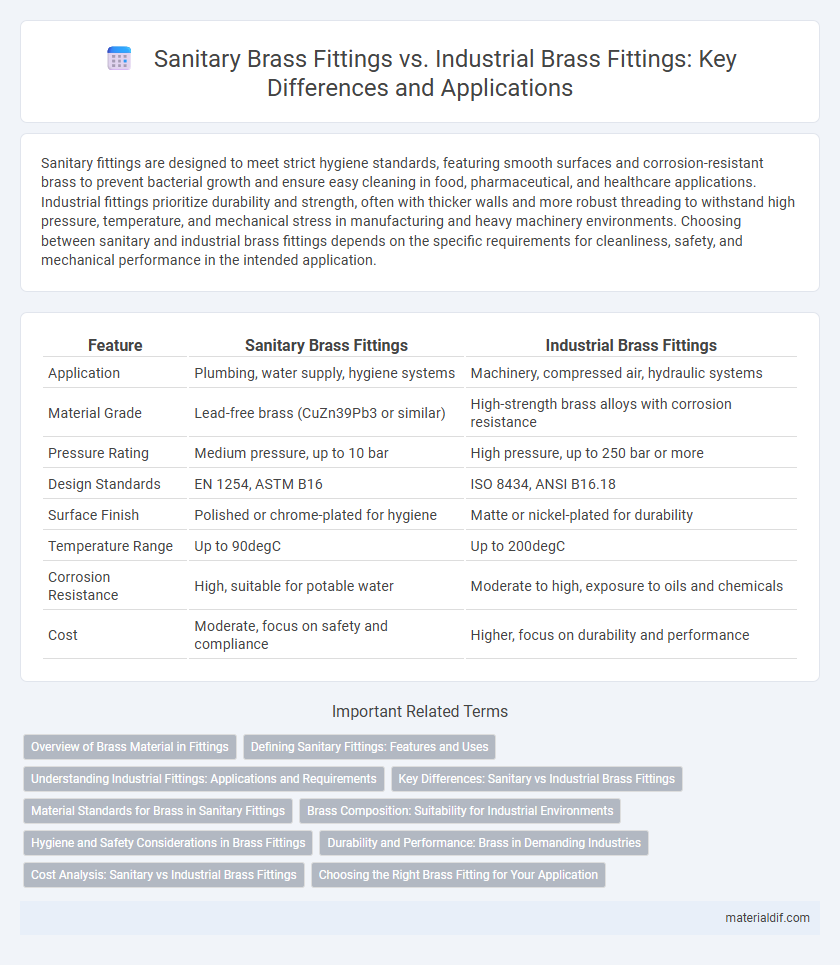
Sanitary fittings are designed to meet strict hygiene standards, featuring smooth surfaces and corrosion-resistant brass to prevent bacterial growth and ensure easy cleaning in food, pharmaceutical, and healthcare applications. Industrial fittings prioritize durability and strength, often with thicker walls and more robust threading to withstand high pressure, temperature, and mechanical stress in manufacturing and heavy machinery environments. Choosing between sanitary and industrial brass fittings depends on the specific requirements for cleanliness, safety, and mechanical performance in the intended application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sanitary Brass Fittings | Industrial Brass Fittings |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Plumbing, water supply, hygiene systems | Machinery, compressed air, hydraulic systems |
| Material Grade | Lead-free brass (CuZn39Pb3 or similar) | High-strength brass alloys with corrosion resistance |
| Pressure Rating | Medium pressure, up to 10 bar | High pressure, up to 250 bar or more |
| Design Standards | EN 1254, ASTM B16 | ISO 8434, ANSI B16.18 |
| Surface Finish | Polished or chrome-plated for hygiene | Matte or nickel-plated for durability |
| Temperature Range | Up to 90degC | Up to 200degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, suitable for potable water | Moderate to high, exposure to oils and chemicals |
| Cost | Moderate, focus on safety and compliance | Higher, focus on durability and performance |
Overview of Brass Material in Fittings
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is prized for its excellent corrosion resistance, machinability, and durability, making it ideal for both sanitary and industrial fittings. In sanitary fittings, brass ensures a hygienic, tarnish-free surface suitable for water supply and plumbing applications, while in industrial fittings, its strength and resistance to wear and high temperatures cater to demanding operational environments. The versatility of brass enables manufacturers to produce fittings that combine reliability with long-term performance across diverse sectors.
Defining Sanitary Fittings: Features and Uses
Sanitary fittings, primarily made from corrosion-resistant brass alloys, are designed for plumbing systems requiring hygiene and durability, such as in bathrooms and kitchens. These fittings focus on water-tight seals, smooth surfaces to prevent bacterial growth, and standards compliance like NSF/ANSI 61 for safe drinking water. Their applications include faucets, valves, and connectors where sanitary conditions are critical, contrasting with industrial fittings that prioritize pressure resistance and chemical compatibility.
Understanding Industrial Fittings: Applications and Requirements
Industrial fittings made from brass are engineered to endure high pressure, temperature, and corrosive environments typically found in manufacturing, chemical processing, and oil and gas industries. These fittings demand precise machining and robust design to ensure leak-proof connections and compatibility with various industrial piping systems. Unlike sanitary fittings designed for hygiene and easy cleaning in food or pharmaceutical applications, industrial fittings prioritize durability, strength, and resistance to wear for effective operation in harsh conditions.
Key Differences: Sanitary vs Industrial Brass Fittings
Sanitary brass fittings are designed for hygienic applications in plumbing and water systems, emphasizing corrosion resistance, smooth surfaces, and compliance with health standards. Industrial brass fittings prioritize strength, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures, suitable for heavy-duty machinery and fluid transport. Key differences include their material grades, surface finishes, and certifications tailored to either sanitary hygiene or industrial performance requirements.
Material Standards for Brass in Sanitary Fittings
Brass sanitary fittings must comply with stringent material standards such as ASTM B16 and NSF/ANSI 61, ensuring corrosion resistance, lead-free composition, and safe potable water contact. These standards emphasize low lead content (typically under 0.25%) and high copper alloy purity to prevent contamination and maintain durability. Industrial fittings, by contrast, may adhere to broader standards allowing higher lead content and varying alloy compositions suited for mechanical performance over health safety.
Brass Composition: Suitability for Industrial Environments
Brass used in sanitary fittings typically contains higher levels of copper and zinc, providing excellent corrosion resistance and antimicrobial properties essential for plumbing applications. Industrial fittings require brass alloys with enhanced strength and durability, often incorporating elements like lead or tin to withstand high pressure, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to harsh chemicals. The specific brass composition directly influences the fitting's performance, making tailored alloy formulations crucial for ensuring longevity and reliability in demanding industrial environments.
Hygiene and Safety Considerations in Brass Fittings
Brass sanitary fittings are engineered with corrosion-resistant properties and smooth surfaces that minimize bacterial growth, ensuring high hygiene standards essential for potable water systems. Industrial fittings, while robust and durable for high-pressure applications, often lack the refined finishes required for sanitary environments, potentially harboring contaminants. Prioritizing hygiene and safety, sanitary brass fittings comply with strict certifications such as NSF/ANSI 61, making them the preferred choice in healthcare and food processing industries.
Durability and Performance: Brass in Demanding Industries
Brass sanitary fittings exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and maintain hygiene standards, making them ideal for water supply systems in residential and commercial applications. In contrast, industrial fittings crafted from brass are engineered to withstand high pressure, extreme temperatures, and aggressive chemicals, ensuring long-lasting durability and reliable performance in manufacturing and processing environments. The alloy's inherent strength and antimicrobial properties contribute significantly to sustained operational efficiency in both sanitary and industrial contexts.
Cost Analysis: Sanitary vs Industrial Brass Fittings
Sanitary brass fittings typically incur higher manufacturing costs due to stringent hygiene standards and the use of lead-free alloys, making them pricier than industrial brass fittings. Industrial brass fittings prioritize durability and pressure resistance, often utilizing standard compositions that reduce production expenses and overall cost. The cost analysis reveals that while sanitary fittings demand a premium for compliance and safety, industrial fittings offer budget-friendly options suited for heavy-duty applications.
Choosing the Right Brass Fitting for Your Application
Selecting the right brass fitting depends on the application requirements, with sanitary fittings designed for hygienic environments and industrial fittings built to withstand higher pressure and corrosive conditions. Brass sanitary fittings offer corrosion resistance, smooth surfaces, and compliance with health standards, making them ideal for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical use. Industrial brass fittings prioritize durability, leak-proof performance, and compatibility with diverse chemicals, ensuring reliability in manufacturing, oil, and gas sectors.
Sanitary Fittings vs Industrial Fittings Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com