Bio-based HDPE is derived from renewable resources like sugarcane, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions compared to conventional HDPE made from petroleum. Both types maintain identical physical properties, ensuring durability and versatility for packaging and manufacturing applications. The shift to bio-based HDPE supports sustainability goals while preserving performance standards.
Table of Comparison
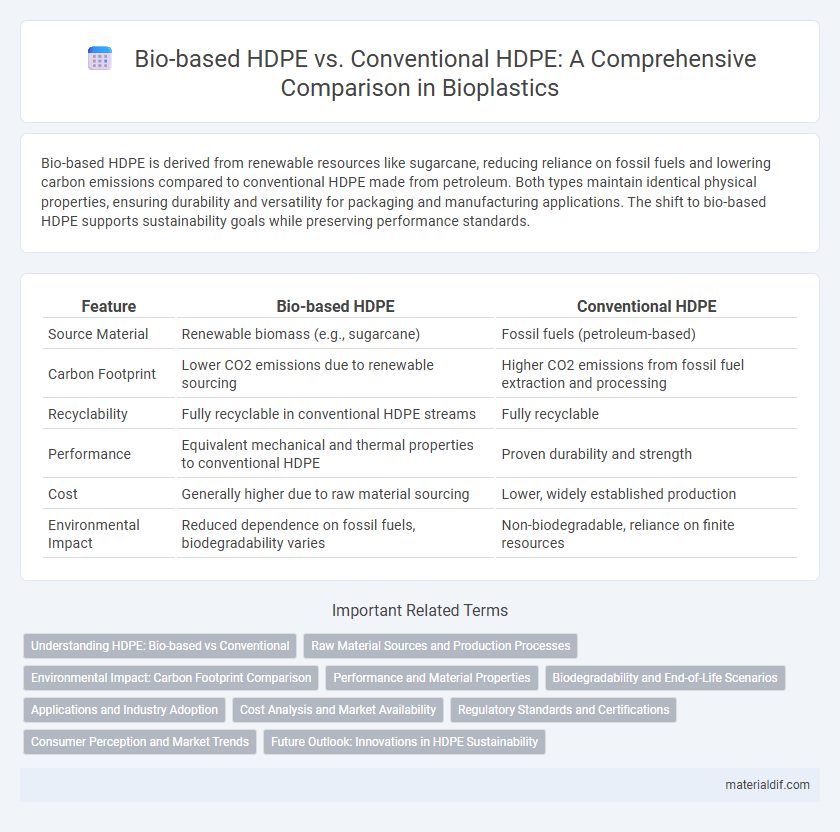
| Feature | Bio-based HDPE | Conventional HDPE |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Renewable biomass (e.g., sugarcane) | Fossil fuels (petroleum-based) |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower CO2 emissions due to renewable sourcing | Higher CO2 emissions from fossil fuel extraction and processing |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable in conventional HDPE streams | Fully recyclable |
| Performance | Equivalent mechanical and thermal properties to conventional HDPE | Proven durability and strength |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw material sourcing | Lower, widely established production |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced dependence on fossil fuels, biodegradability varies | Non-biodegradable, reliance on finite resources |
Understanding HDPE: Bio-based vs Conventional
Bio-based HDPE is derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane ethanol, reducing reliance on fossil fuels compared to conventional HDPE, which is primarily produced from petrochemical feedstocks. Both bio-based and conventional HDPE share identical chemical structures and physical properties, ensuring compatibility with existing manufacturing processes and applications. The shift toward bio-based HDPE supports lower carbon footprints and sustainable material cycles while maintaining the performance standards expected from high-density polyethylene products.
Raw Material Sources and Production Processes
Bio-based HDPE is derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, utilizing plant-based feedstocks that reduce reliance on fossil fuels compared to conventional HDPE, which is produced from petrochemical hydrocarbons through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene derived from crude oil or natural gas. The production process of bio-based HDPE involves fermentation and refining of biomass into bio-ethylene before polymerization, whereas conventional HDPE relies on steam cracking and catalytic conversion of fossil feedstocks. This shift in raw material source results in bio-based HDPE having a lower carbon footprint and enhanced sustainability in polymer synthesis.
Environmental Impact: Carbon Footprint Comparison
Bio-based HDPE significantly reduces the carbon footprint compared to conventional HDPE by utilizing renewable biomass feedstocks instead of fossil fuels, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions during production. Lifecycle analyses reveal bio-based HDPE can cut carbon emissions by up to 70%, contributing substantially to climate change mitigation. Despite comparable material properties, the environmental impact advantage makes bio-based HDPE a more sustainable choice for packaging and manufacturing applications.
Performance and Material Properties
Bio-based HDPE matches conventional HDPE in tensile strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for packaging and automotive components. Both materials exhibit excellent impact resistance and thermal stability, with bio-based HDPE offering a reduced carbon footprint. Material properties such as melt flow index and density remain consistent, ensuring compatibility with existing manufacturing processes.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Scenarios
Bio-based HDPE is chemically identical to conventional HDPE, resulting in similar non-biodegradability profiles and requiring comparable waste management processes such as recycling or landfilling. Both materials do not readily biodegrade under natural conditions, limiting their environmental benefit if not properly processed at end-of-life. Effective recycling infrastructure and advanced thermal recovery methods are critical to minimize environmental impact for both bio-based and fossil-derived HDPE.
Applications and Industry Adoption
Bio-based HDPE, derived from renewable resources, offers comparable performance to conventional HDPE, making it suitable for packaging, automotive components, and consumer goods. Industries such as packaging and agriculture are increasingly adopting bio-based HDPE to meet sustainability goals and reduce carbon footprints. Growing regulatory support and consumer demand drive wider incorporation of bio-based HDPE in applications traditionally dominated by conventional HDPE.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Bio-based High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) typically incurs higher production costs than conventional HDPE due to the reliance on renewable feedstocks and more complex manufacturing processes, impacting its market pricing. Despite premium pricing, bio-based HDPE is gaining traction in sustainable packaging sectors, supported by increasing consumer demand and regulatory incentives promoting eco-friendly materials. Conventional HDPE dominates the market with widespread availability and lower costs, but the growing shift toward carbon footprint reduction is gradually expanding bio-based HDPE's market share.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Bio-based HDPE complies with stringent regulatory standards such as ASTM D7611 and ISO 16620-2, ensuring its renewable carbon content and environmental performance are certified. Conventional HDPE typically meets general ISO 9001 quality management standards but lacks renewable content verification. Certifications like the USDA BioPreferred Program and certification from the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) distinguish bio-based HDPE by guaranteeing sustainable sourcing and biodegradability criteria absent in conventional HDPE products.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Bio-based HDPE is gaining consumer trust due to its reduced carbon footprint and renewable feedstock, fostering positive perceptions around sustainability compared to conventional HDPE made from fossil fuels. Market trends indicate a rising demand for bio-based HDPE in packaging and consumer goods, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stricter regulations on plastic waste. Growth projections show bio-based HDPE capturing a growing share of the HDPE market as brands prioritize eco-friendly materials to meet consumer expectations.
Future Outlook: Innovations in HDPE Sustainability
Bio-based HDPE is evolving with advancements in renewable feedstocks, significantly reducing carbon footprints compared to conventional HDPE derived from fossil fuels. Innovations in catalyst technology and recycling methods enhance biodegradability and circularity, driving sustainable lifecycle management. Industry trends forecast increased adoption of bio-based HDPE in packaging and automotive sectors due to stringent environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly materials.
Bio-based HDPE vs Conventional HDPE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com