Aluminum profiles offer greater design flexibility and precision compared to aluminum bars, making them ideal for complex structural applications in the PET industry. They provide enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and can be extruded into custom shapes that aluminum bars cannot achieve efficiently. This specificity improves assembly efficiency and reduces material waste, maximizing performance in PET manufacturing processes.
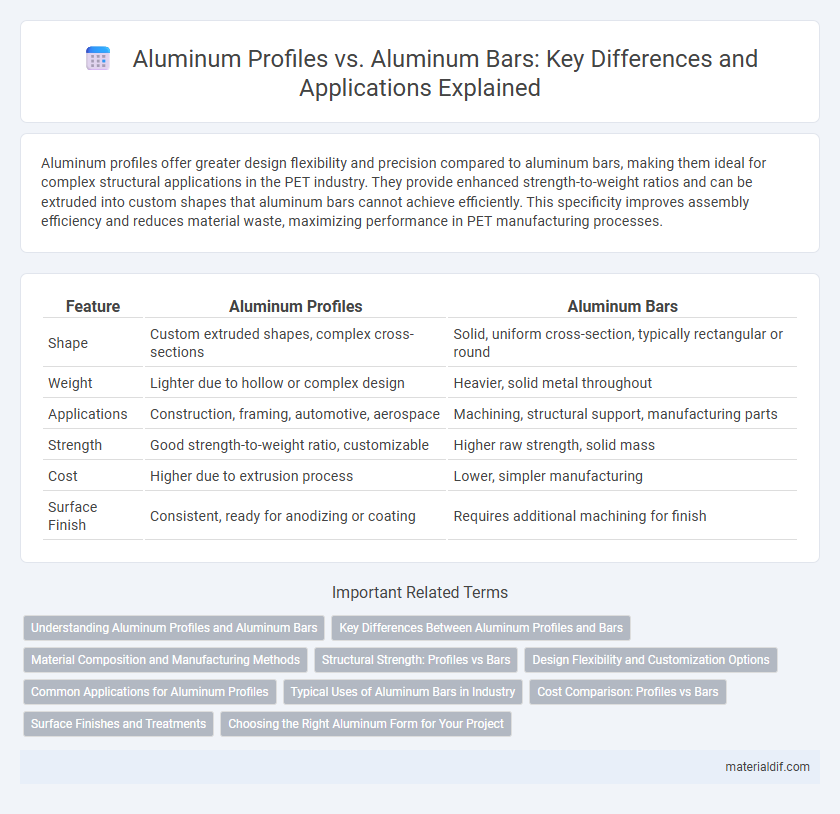
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aluminum Profiles | Aluminum Bars |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Custom extruded shapes, complex cross-sections | Solid, uniform cross-section, typically rectangular or round |
| Weight | Lighter due to hollow or complex design | Heavier, solid metal throughout |
| Applications | Construction, framing, automotive, aerospace | Machining, structural support, manufacturing parts |
| Strength | Good strength-to-weight ratio, customizable | Higher raw strength, solid mass |
| Cost | Higher due to extrusion process | Lower, simpler manufacturing |
| Surface Finish | Consistent, ready for anodizing or coating | Requires additional machining for finish |
Understanding Aluminum Profiles and Aluminum Bars
Aluminum profiles are extruded shapes designed for specific structural or architectural purposes, offering customized cross-sections for applications such as window frames and industrial frameworks. Aluminum bars, typically solid and uniform in shape like square or round, are raw materials used for machining, fabrication, or further processing. Understanding the distinction highlights aluminum profiles' versatility in tailored applications versus the foundational role of aluminum bars in manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Aluminum Profiles and Bars
Aluminum profiles are extruded shapes with complex cross-sections designed for specific applications like window frames and heat sinks, while aluminum bars are solid, uniform shapes such as rounds, squares, or rectangles used for machining and structural purposes. Profiles offer greater design flexibility and lightweight properties due to their hollow or intricate constructions, whereas bars provide higher strength and are easier to machine or fabricate. The choice depends on application requirements, balancing structural integrity, weight, and manufacturing complexity.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Methods
Aluminum profiles are typically extruded shapes made by forcing aluminum alloy billets through custom-designed dies, allowing complex cross-sections with precise dimensional control. In contrast, aluminum bars are generally produced by hot rolling or continuous casting, resulting in solid rectangular or square forms with uniform material composition. Both products commonly use alloys like 6061 or 6063, but profiles benefit from specialized extrusion alloys tailored for strength and corrosion resistance while bars emphasize machinability and structural integrity.
Structural Strength: Profiles vs Bars
Aluminum profiles offer enhanced structural strength due to their engineered cross-sectional shapes, which distribute loads efficiently and resist bending better than solid aluminum bars. These profiles, such as T-slots and I-beams, provide optimized weight-to-strength ratios ideal for frameworks and construction applications. In contrast, aluminum bars deliver uniform strength in all directions but generally require more material to achieve comparable rigidity, making profiles a more material-efficient choice in structural use.
Design Flexibility and Customization Options
Aluminum profiles offer superior design flexibility compared to aluminum bars due to their ability to be extruded into complex cross-sectional shapes tailored to specific applications, enabling precise customization. Unlike solid aluminum bars, profiles can incorporate channels, slots, and various geometric features during the manufacturing process, reducing the need for secondary machining. This intrinsic versatility makes aluminum profiles ideal for industries requiring bespoke components, such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Common Applications for Aluminum Profiles
Aluminum profiles are extensively used in construction for window frames, door frames, and curtain walls due to their customizable shapes and excellent corrosion resistance. They are preferred in automotive and aerospace industries where lightweight structural components with precise dimensions enhance performance. Unlike aluminum bars, which are solid and typically used for machining and fabrication, profiles enable efficient assembly in modular systems and architectural designs.
Typical Uses of Aluminum Bars in Industry
Aluminum bars are commonly used in industrial applications requiring high strength and precise machining, such as manufacturing machinery parts, automotive components, and structural frameworks. Their solid form allows for extensive customization through processes like milling, drilling, and turning, making them ideal for complex, load-bearing parts. Compared to aluminum profiles, bars offer superior versatility for producing custom-engineered solutions in aerospace, construction, and transportation industries.
Cost Comparison: Profiles vs Bars
Aluminum profiles generally cost more than aluminum bars due to the added manufacturing processes such as extrusion and shaping, which increase production expenses. Bars are simpler, solid shapes often produced by casting or rolling, making them cheaper and suitable for applications requiring less complex geometries. The choice between aluminum profiles and bars depends on balancing the budget with the need for customized shapes and mechanical properties in specific projects.
Surface Finishes and Treatments
Aluminum profiles offer a wide variety of surface finishes, including anodizing, powder coating, and brushing, which enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Aluminum bars typically have simpler surface treatments, often limited to mill finishes or basic anodizing for protection. The choice of profiles allows for more complex and durable surface treatments tailored to specific applications, making them more versatile in industries like construction and automotive.
Choosing the Right Aluminum Form for Your Project
Aluminum profiles offer precise shapes and customizable cross-sections, making them ideal for architectural frameworks and intricate designs where specific dimensions and structural support are crucial. Aluminum bars provide solid, uniform material, suitable for machining, fabrication, or applications requiring robust strength and durability. Selecting the right aluminum form depends on project needs, such as complexity, load-bearing requirements, and machining capabilities, ensuring efficiency and performance.
Aluminum Profiles vs Aluminum Bars Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com