Billet aluminum is machined from a solid block of pure aluminum, offering superior strength, precision, and uniformity compared to cast aluminum, which is formed by pouring molten metal into molds. The denser, grain-aligned structure of billet aluminum enhances durability and performance in high-stress applications, while cast aluminum provides cost-effective production with more design flexibility but lower mechanical properties. Choosing between billet and cast aluminum depends on balancing the need for structural integrity and manufacturing efficiency in specific projects.
Table of Comparison
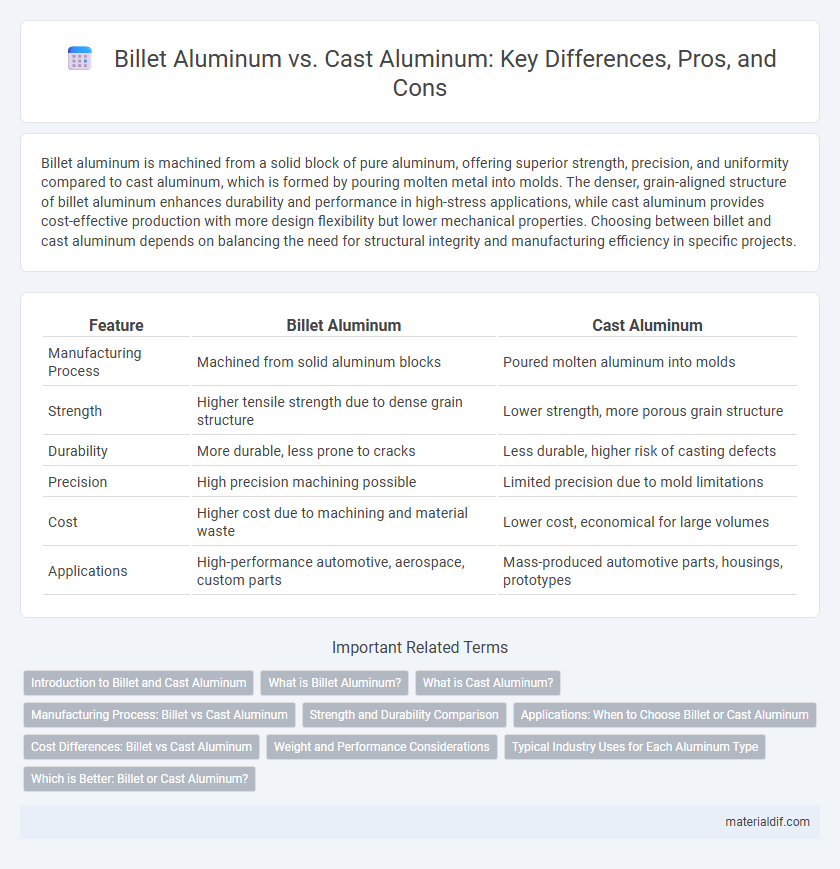
| Feature | Billet Aluminum | Cast Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Machined from solid aluminum blocks | Poured molten aluminum into molds |
| Strength | Higher tensile strength due to dense grain structure | Lower strength, more porous grain structure |
| Durability | More durable, less prone to cracks | Less durable, higher risk of casting defects |
| Precision | High precision machining possible | Limited precision due to mold limitations |
| Cost | Higher cost due to machining and material waste | Lower cost, economical for large volumes |
| Applications | High-performance automotive, aerospace, custom parts | Mass-produced automotive parts, housings, prototypes |
Introduction to Billet and Cast Aluminum
Billet aluminum is a solid piece of high-quality aluminum that is precisely machined from a single block, offering superior strength, uniform grain structure, and excellent durability for critical applications. Cast aluminum is created by pouring molten aluminum into a mold, allowing for complex shapes and cost-effective production, although it tends to have lower strength and less consistent microstructures compared to billet aluminum. Both materials are widely used in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing industries, with billet aluminum preferred for performance parts and cast aluminum selected for intricate components.
What is Billet Aluminum?
Billet aluminum is a solid piece of aluminum formed through the process of extrusion or forging, offering superior strength and uniformity compared to cast aluminum. It is manufactured by cutting a large, precisely controlled aluminum ingot into specific shapes, resulting in a dense, high-quality material with enhanced mechanical properties. This makes billet aluminum ideal for applications requiring high durability, such as aerospace, automotive, and industrial components.
What is Cast Aluminum?
Cast aluminum is a metal alloy shaped by pouring molten aluminum into molds, allowing for complex geometries and intricate designs that are difficult to achieve with other manufacturing methods. It typically exhibits a coarser grain structure compared to billet aluminum, which affects its mechanical properties such as strength and durability. Cast aluminum is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries where lightweight components with specific shapes are essential.
Manufacturing Process: Billet vs Cast Aluminum
Billet aluminum undergoes a manufacturing process where solid aluminum ingots are extruded or machined into precise shapes, resulting in denser and stronger components with improved structural integrity. Cast aluminum is produced by pouring molten aluminum into molds, allowing for complex shapes but often introducing porosity and reduced mechanical properties. The choice between billet and cast aluminum depends on the required strength, dimensional accuracy, and production volume for specific applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Billet aluminum exhibits superior strength and durability compared to cast aluminum due to its dense, uniform grain structure achieved through precision machining from a solid block. Cast aluminum, formed by pouring molten metal into molds, tends to have a more porous microstructure leading to lower tensile strength and increased susceptibility to cracking under stress. For applications demanding high mechanical performance and resistance to fatigue, billet aluminum is the preferred material.
Applications: When to Choose Billet or Cast Aluminum
Billet aluminum is ideal for applications requiring exceptional strength, precision, and uniformity, such as aerospace components, automotive performance parts, and high-stress structural elements. Cast aluminum suits complex shapes and cost-effective mass production, often used in engine blocks, housings, and intricate machinery parts. Choose billet aluminum for durability and high performance, while cast aluminum fits better for versatile designs and lower manufacturing costs.
Cost Differences: Billet vs Cast Aluminum
Billet aluminum often incurs higher production costs due to its manufacturing process, which involves machining from a solid block, resulting in greater material waste and longer production times. Cast aluminum is generally more cost-effective as it utilizes molten metal poured into molds, allowing for complex shapes with less waste and faster production cycles. For applications where budget is a priority, cast aluminum offers significant cost advantages over billet aluminum without compromising essential performance characteristics.
Weight and Performance Considerations
Billet aluminum offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to cast aluminum, making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring lightweight durability. Cast aluminum, while generally heavier due to its porosity and grain structure, provides excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness for less demanding uses. Weight-conscious industries, such as aerospace and automotive racing, often prefer billet aluminum to optimize performance without compromising structural integrity.
Typical Industry Uses for Each Aluminum Type
Billet aluminum is predominantly used in high-performance applications such as aerospace components, automotive parts, and precision machinery due to its superior strength and machinability. Cast aluminum is commonly utilized for complex shapes in automotive engine blocks, housings, and consumer goods where cost-effectiveness and design flexibility are critical. Both materials serve distinct industry needs based on structural requirements and production volume, optimizing performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Which is Better: Billet or Cast Aluminum?
Billet aluminum offers superior strength and precision due to its solid block manufacturing process, making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability and exact tolerances. Cast aluminum, produced by pouring molten metal into molds, provides cost-effective complex shapes but often lacks the mechanical strength and uniformity of billet. Choosing between billet and cast aluminum depends on prioritizing either mechanical properties and accuracy or manufacturing complexity and budget constraints.
Billet Aluminum vs Cast Aluminum Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com