Aluminum foil is thin, flexible, and commonly used for packaging, insulation, and cooking applications due to its excellent heat resistance and barrier properties. Aluminum strips are thicker, rigid, and primarily utilized in industrial applications such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive components where strength and durability are essential. Choosing between aluminum foil and aluminum strip depends on the specific requirements for thickness, flexibility, and mechanical strength in the intended use.
Table of Comparison
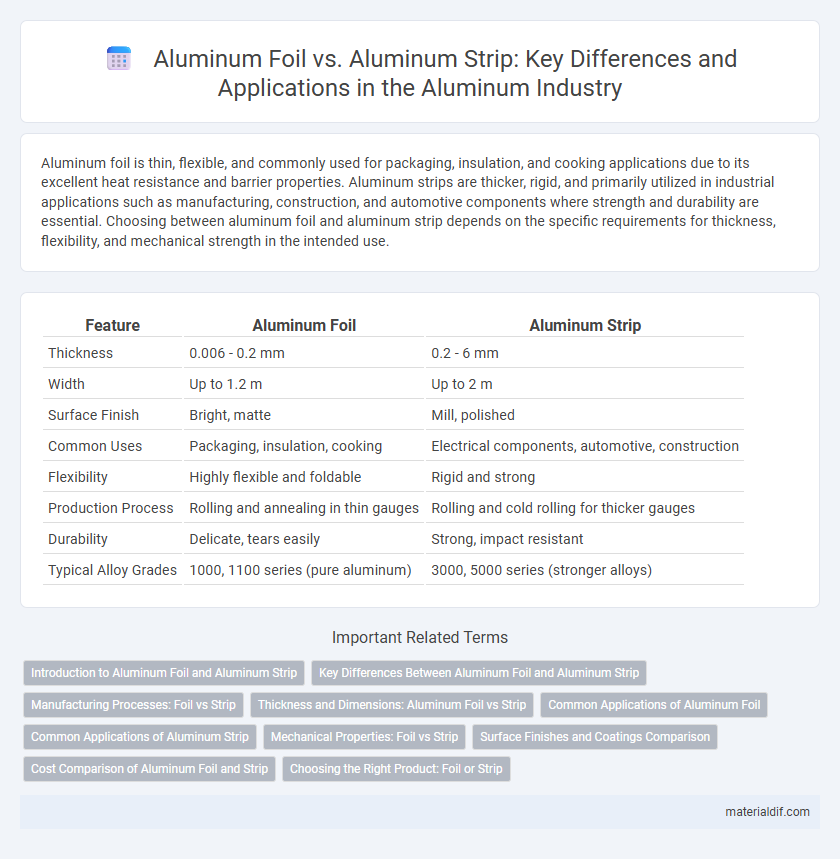
| Feature | Aluminum Foil | Aluminum Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.006 - 0.2 mm | 0.2 - 6 mm |
| Width | Up to 1.2 m | Up to 2 m |
| Surface Finish | Bright, matte | Mill, polished |
| Common Uses | Packaging, insulation, cooking | Electrical components, automotive, construction |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and foldable | Rigid and strong |
| Production Process | Rolling and annealing in thin gauges | Rolling and cold rolling for thicker gauges |
| Durability | Delicate, tears easily | Strong, impact resistant |
| Typical Alloy Grades | 1000, 1100 series (pure aluminum) | 3000, 5000 series (stronger alloys) |
Introduction to Aluminum Foil and Aluminum Strip
Aluminum foil is a thin, flexible sheet typically less than 0.2 millimeters thick, widely used for packaging, insulation, and cooking due to its lightweight and excellent barrier properties. Aluminum strips are thicker and narrower metal pieces, often utilized in industrial applications such as construction, electronics, and automotive manufacturing for their strength and durability. Both materials are manufactured from high-purity aluminum alloys, offering corrosion resistance and versatility across various sectors.
Key Differences Between Aluminum Foil and Aluminum Strip
Aluminum foil is a thin, flexible sheet typically less than 0.2 millimeters thick, used primarily for packaging, insulation, and cooking applications due to its malleability and barrier properties. Aluminum strip, on the other hand, is thicker, ranging from 0.2 to 6 millimeters, offering higher strength and structural applications in automotive, construction, and manufacturing industries. The key differences lie in thickness, mechanical strength, and typical usage, with foil optimized for flexibility and barrier functions, while strips are designed for durability and structural integrity.
Manufacturing Processes: Foil vs Strip
Aluminum foil is manufactured through a process called rolling, where hot or cold rolling machines reduce aluminum slabs into extremely thin sheets, typically less than 0.2 mm thick, achieving high flexibility and superior barrier properties. In contrast, aluminum strips undergo a cold rolling and annealing process to produce thicker sheets ranging from 0.2 mm to 6 mm, ensuring enhanced mechanical strength and dimensional stability ideal for structural applications. The precise control in foil manufacturing emphasizes thinness and uniformity, while strip production prioritizes thickness consistency and robustness for industrial uses.
Thickness and Dimensions: Aluminum Foil vs Strip
Aluminum foil typically ranges from 0.006 mm to 0.2 mm in thickness, making it extremely thin and flexible for packaging and insulation applications. In contrast, aluminum strips have a thickness range from 0.2 mm up to several millimeters, providing greater rigidity and structural strength for industrial and construction uses. Dimensions of aluminum strips are generally wider and longer than foil, allowing for diverse fabrication possibilities such as metal stamping and component manufacturing.
Common Applications of Aluminum Foil
Aluminum foil is widely used in food packaging, insulation, and pharmaceutical applications due to its excellent barrier properties against light, moisture, and bacteria. Unlike aluminum strips, which are primarily used in construction, automotive, and electrical industries, aluminum foil is preferred for its flexibility and ability to be easily molded around objects. This makes aluminum foil essential in household kitchen uses, medical packaging, and heat insulation products.
Common Applications of Aluminum Strip
Aluminum strips are widely used in automotive manufacturing for heat exchangers and radiator fins due to their excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion. In construction, aluminum strips serve as roofing materials and window frames, offering durability and lightweight benefits. They also play a critical role in electrical industries, where they are utilized for busbars and connectors because of their high electrical conductivity and malleability.
Mechanical Properties: Foil vs Strip
Aluminum foil exhibits higher flexibility and lower tensile strength compared to aluminum strip, making it ideal for packaging and insulation applications. Aluminum strip offers superior mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to deformation, suitable for structural and industrial uses. The difference in thickness between foil (typically less than 0.2 mm) and strip (0.2 mm to 6 mm) directly influences their mechanical properties, with strip providing enhanced load-bearing capacity.
Surface Finishes and Coatings Comparison
Aluminum foil typically features a smooth, shiny surface finish created by rolling between polished steel rolls, enhancing its reflective properties and making it ideal for packaging and insulation. In contrast, aluminum strips often undergo anodizing or coating processes to improve corrosion resistance and wear durability, suitable for structural and industrial applications. The choice of surface finish or coating depends on the end-use requirements, balancing factors like appearance, protection, and conductivity.
Cost Comparison of Aluminum Foil and Strip
Aluminum foil generally costs more per unit weight compared to aluminum strip due to its thinness and specialized manufacturing processes like rolling and annealing. Aluminum strip, being thicker and easier to produce in bulk, typically offers lower material costs and better structural strength for industrial applications. When selecting between aluminum foil and strip, factors such as thickness, production process, application requirements, and efficiency impact the overall cost-effectiveness of each material.
Choosing the Right Product: Foil or Strip
Choosing between aluminum foil and aluminum strip depends on the application-specific requirements such as thickness, strength, and flexibility. Aluminum foil, with its thin gauge typically under 0.2 mm, excels in packaging, insulation, and heat retention due to its lightweight and malleability. Aluminum strip, thicker and more durable, is preferred for industrial uses like manufacturing, electrical components, and construction where enhanced mechanical properties and structural integrity are essential.
Aluminum foil vs Aluminum strip Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com