Super Duplex stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and higher strength compared to Duplex stainless steel, making it ideal for harsh environments such as offshore oil and gas applications. Duplex stainless steel provides a balanced combination of austenitic and ferritic properties, suitable for moderate conditions with good toughness and weldability. Choosing between Super Duplex and Duplex depends on the specific demands of the application, including pressure, temperature, and exposure to corrosive elements.
Table of Comparison
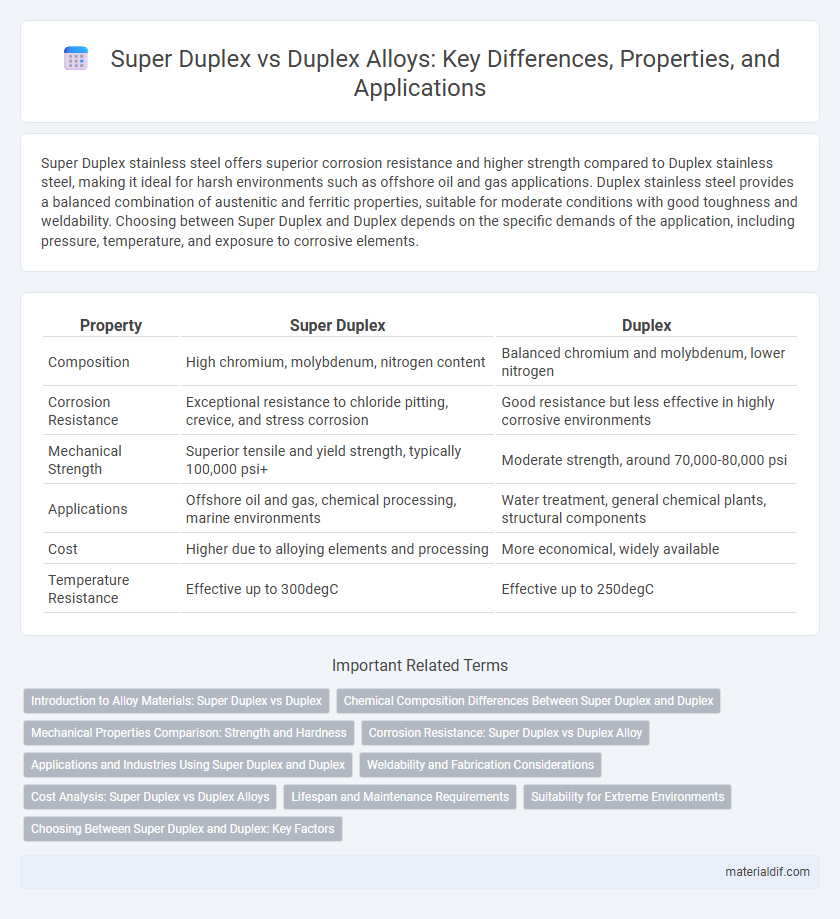
| Property | Super Duplex | Duplex |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High chromium, molybdenum, nitrogen content | Balanced chromium and molybdenum, lower nitrogen |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceptional resistance to chloride pitting, crevice, and stress corrosion | Good resistance but less effective in highly corrosive environments |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior tensile and yield strength, typically 100,000 psi+ | Moderate strength, around 70,000-80,000 psi |
| Applications | Offshore oil and gas, chemical processing, marine environments | Water treatment, general chemical plants, structural components |
| Cost | Higher due to alloying elements and processing | More economical, widely available |
| Temperature Resistance | Effective up to 300degC | Effective up to 250degC |
Introduction to Alloy Materials: Super Duplex vs Duplex
Super Duplex stainless steel offers higher strength and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to Duplex alloys, making it ideal for aggressive environments such as chemical processing and offshore applications. Composed of roughly 25-30% chromium, 6-8% nickel, and 3-5% molybdenum, Super Duplex boasts improved pitting and stress corrosion cracking resistance over Duplex steel, which contains lower concentrations of these elements. The microstructure of Super Duplex features a balanced ferritic-austenitic phase mix that contributes to its superior mechanical properties and durability in harsh conditions.
Chemical Composition Differences Between Super Duplex and Duplex
Super Duplex stainless steel contains higher levels of chromium (25-26%), molybdenum (3-5%), and nitrogen (0.24-0.32%) compared to Duplex, which typically has chromium (22-23%), molybdenum (3-4%), and nitrogen (0.08-0.20%). The increased nitrogen and molybdenum in Super Duplex enhance corrosion resistance and strength, especially in chloride-rich environments. Differences in nickel content also influence the microstructure, with Super Duplex having slightly lower nickel (6-8%) relative to Duplex (5-7%).
Mechanical Properties Comparison: Strength and Hardness
Super Duplex stainless steel exhibits higher tensile strength ranging from 75,000 to 105,000 psi compared to Duplex, which typically ranges between 60,000 to 85,000 psi, making it suitable for more demanding structural applications. In terms of hardness, Super Duplex alloys achieve values around 270-300 HV, significantly outperforming Duplex alloys that generally exhibit hardness in the 220-270 HV range. The enhanced mechanical properties of Super Duplex result from its higher alloy content and balanced microstructure, providing superior resistance to deformation under stress.
Corrosion Resistance: Super Duplex vs Duplex Alloy
Super Duplex alloys exhibit significantly higher corrosion resistance compared to standard Duplex alloys due to their increased chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen content, which enhances resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking. The microstructure of Super Duplex, consisting of approximately equal parts austenite and ferrite, provides superior protection in chloride-rich and harsh chemical environments, making it ideal for offshore oil and gas, chemical processing, and seawater applications. Duplex alloys offer good corrosion resistance but are less effective than Super Duplex in highly aggressive environments, limiting their use where maximum durability and longevity are critical.
Applications and Industries Using Super Duplex and Duplex
Super Duplex stainless steel is extensively used in offshore oil and gas platforms, chemical processing, and marine applications due to its superior corrosion resistance and high strength, outperforming standard Duplex alloys. Duplex stainless steel finds application in water treatment, pulp and paper, and food processing industries where moderate strength and corrosion resistance are sufficient. Both alloys serve critical roles in environments requiring resistance to stress corrosion cracking and pitting, but Super Duplex is preferred in more aggressive conditions such as seawater and chloride-rich environments.
Weldability and Fabrication Considerations
Super duplex stainless steel offers superior weldability compared to duplex grades due to its higher alloy content, requiring precise control of heat input and cooling rates to avoid sensitization and maintain mechanical properties. Fabrication of super duplex alloys demands advanced techniques such as controlled heat treatment and post-weld heat treatment to prevent intermetallic phase formation, enhancing corrosion resistance and structural integrity. Duplex stainless steel, while easier to weld and fabricate, requires careful attention to thermal cycles to prevent phase imbalance that can reduce toughness and corrosion performance.
Cost Analysis: Super Duplex vs Duplex Alloys
Super duplex alloys typically cost 30-50% more than standard duplex alloys due to higher alloying elements like nickel, molybdenum, and chromium, which enhance corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. Despite the initial higher investment, super duplex alloys offer longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in aggressive environments, providing better total cost of ownership over time. Duplex alloys remain a cost-effective choice for less corrosive conditions but may incur higher replacement and downtime expenses in highly corrosive or high-pressure applications.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Super Duplex alloys offer a significantly longer lifespan compared to standard Duplex due to superior corrosion resistance and enhanced mechanical strength in aggressive environments. Maintenance requirements for Super Duplex are generally lower, as its high resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking reduces the frequency of inspections and repairs. Duplex alloys, while cost-effective, require more frequent maintenance to address corrosion-related degradation, particularly in chloride-rich or high-temperature conditions.
Suitability for Extreme Environments
Super Duplex alloys offer superior resistance to corrosion, especially in chloride-rich and highly corrosive environments, outperforming standard Duplex alloys. Their enhanced mechanical properties, including higher tensile strength and toughness, make them ideal for extreme temperature and pressure conditions commonly found in offshore oil and gas and chemical processing industries. Super Duplex's microstructure, combining balanced ferrite and austenite phases, ensures exceptional durability and reliability in the most demanding environments.
Choosing Between Super Duplex and Duplex: Key Factors
Super Duplex stainless steel offers higher corrosion resistance and strength compared to Duplex, making it ideal for harsh environments and aggressive chemicals. Duplex alloys typically provide a cost-effective solution with excellent toughness and good resistance to stress corrosion cracking in less extreme conditions. Selecting between Super Duplex and Duplex hinges on factors such as expected operating temperature, chloride concentration, mechanical stress, and budget constraints.
Super Duplex vs Duplex Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com