Alloy scrap and virgin alloy differ significantly in composition and cost, with alloy scrap containing recycled metal fragments that may include impurities affecting performance. Virgin alloy consists of newly extracted and refined metals, offering consistent quality and higher purity ideal for critical applications. Choosing alloy scrap can reduce material costs and support sustainability efforts, while virgin alloy ensures optimal mechanical properties and durability.
Table of Comparison
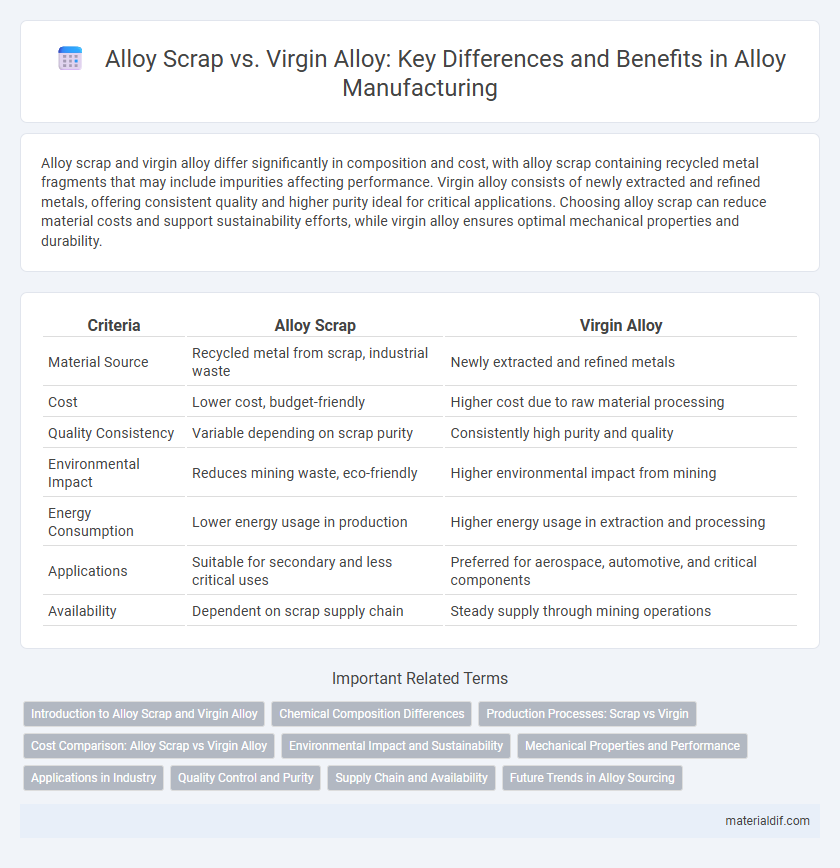
| Criteria | Alloy Scrap | Virgin Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Recycled metal from scrap, industrial waste | Newly extracted and refined metals |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost due to raw material processing |
| Quality Consistency | Variable depending on scrap purity | Consistently high purity and quality |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces mining waste, eco-friendly | Higher environmental impact from mining |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy usage in production | Higher energy usage in extraction and processing |
| Applications | Suitable for secondary and less critical uses | Preferred for aerospace, automotive, and critical components |
| Availability | Dependent on scrap supply chain | Steady supply through mining operations |
Introduction to Alloy Scrap and Virgin Alloy
Alloy scrap consists of recycled metal materials recovered from manufacturing processes or end-of-life products, retaining valuable alloying elements essential for remelting and reuse. Virgin alloy refers to newly produced metal made from raw ores, offering high purity and consistent mechanical properties ideal for critical industrial applications. Understanding the balance between alloy scrap and virgin alloy usage is crucial for cost-effective and sustainable metal production.
Chemical Composition Differences
Alloy scrap typically contains a more variable and less controlled chemical composition compared to virgin alloy, which is produced to meet strict industry standards and specifications. The presence of impurities and mixed alloy grades in alloy scrap can alter the elemental balance, affecting elements such as carbon, manganese, and chromium concentrations. Virgin alloys maintain uniformity in key components like nickel, molybdenum, and vanadium, ensuring predictable mechanical and corrosion-resistant properties essential for high-performance applications.
Production Processes: Scrap vs Virgin
Alloy scrap undergoes processes such as collection, sorting, and remelting, which require less energy compared to producing virgin alloy from raw materials involving mining, refining, and smelting. Using scrap significantly reduces carbon emissions and conserves natural resources by recycling existing metals instead of extracting new ores. Production with virgin alloy is more resource-intensive, relying on primary extraction and complex purification to achieve desired metal compositions.
Cost Comparison: Alloy Scrap vs Virgin Alloy
Alloy scrap significantly reduces material costs compared to virgin alloy due to lower raw material acquisition expenses and decreased energy consumption in processing. Virgin alloy requires extensive mining, refining, and alloying, leading to higher production costs and environmental impact. Utilizing alloy scrap not only cuts costs by up to 30-50% but also supports sustainable manufacturing practices through resource conservation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alloy scrap significantly reduces environmental impact compared to virgin alloy production by lowering energy consumption and minimizing mining-related habitat destruction. Recycling alloy scrap decreases greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% and reduces the need for raw material extraction, contributing to resource conservation and sustainable manufacturing. Utilizing alloy scrap supports circular economy principles, enhancing material efficiency and reducing industrial waste in metal production processes.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Alloy scrap often contains trace impurities that can slightly reduce tensile strength and elongation compared to virgin alloy, which is produced with controlled chemical compositions ensuring consistent mechanical properties. Virgin alloy typically exhibits superior fatigue resistance and corrosion performance due to its homogeneous microstructure, whereas alloy scrap might introduce variability affecting durability. Selecting virgin alloy maximizes reliability in critical applications requiring high mechanical performance and predictable behavior.
Applications in Industry
Alloy scrap finds extensive application in industries such as automotive manufacturing, construction, and aerospace, where recycled materials reduce production costs and environmental impact. Virgin alloy, characterized by its higher purity and controlled composition, is preferred in critical sectors like electronics and medical devices that demand superior mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The choice between alloy scrap and virgin alloy hinges on balancing performance requirements, cost efficiency, and sustainability goals within industrial applications.
Quality Control and Purity
Alloy scrap often requires intensive quality control measures to ensure consistency and reliability, as impurities and contaminants can vary significantly between batches. Virgin alloy, produced directly from raw materials, typically offers higher purity levels and more predictable chemical properties, reducing the need for extensive purification processes. The stringent quality control protocols applied to virgin alloy result in superior mechanical performance and enhanced material integrity in critical applications.
Supply Chain and Availability
Alloy scrap offers a more reliable supply chain due to its widespread availability and lower dependency on mining operations compared to virgin alloy. Recycled alloy scrap reduces lead times and mitigates risks associated with raw material extraction, transportation, and geopolitical factors. Supply chain resilience is improved as scrap metal can be sourced locally or regionally, enhancing availability and reducing cost volatility.
Future Trends in Alloy Sourcing
Future trends in alloy sourcing emphasize increased reliance on alloy scrap due to its cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits, driving demand for advanced recycling technologies. Innovations in sorting and processing alloy scrap enhance material quality, narrowing the performance gap with virgin alloy and promoting circular economy principles. Market forecasts predict alloy scrap will constitute a larger proportion of raw materials, supported by regulatory pressures and sustainability goals across manufacturing industries.
Alloy Scrap vs Virgin Alloy Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com