Copper-nickel alloys offer superior corrosion resistance and excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for marine and industrial applications. Nickel-silver alloys, while lacking actual silver content, provide better machinability and aesthetic appeal due to their bright, silvery finish. Both alloys balance cost and performance, with copper-nickel excelling in durability and nickel-silver favored for decorative and precision components.
Table of Comparison
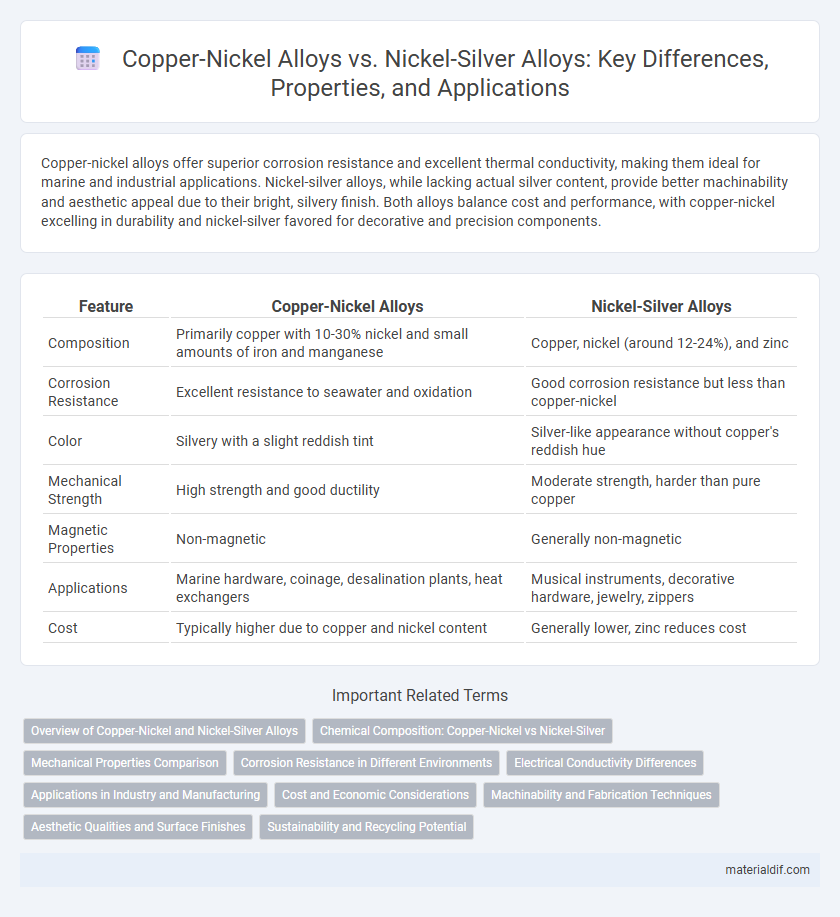
| Feature | Copper-Nickel Alloys | Nickel-Silver Alloys |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Primarily copper with 10-30% nickel and small amounts of iron and manganese | Copper, nickel (around 12-24%), and zinc |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance to seawater and oxidation | Good corrosion resistance but less than copper-nickel |
| Color | Silvery with a slight reddish tint | Silver-like appearance without copper's reddish hue |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and good ductility | Moderate strength, harder than pure copper |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic | Generally non-magnetic |
| Applications | Marine hardware, coinage, desalination plants, heat exchangers | Musical instruments, decorative hardware, jewelry, zippers |
| Cost | Typically higher due to copper and nickel content | Generally lower, zinc reduces cost |
Overview of Copper-Nickel and Nickel-Silver Alloys
Copper-nickel alloys, primarily composed of copper and nickel with minor additions of iron and manganese, exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and superb thermal stability, making them ideal for marine and coinage applications. Nickel-silver alloys, also known as German silver, consist of copper, nickel, and zinc, offering good corrosion resistance and a silver-like appearance, commonly used in musical instruments, jewelry, and decorative items. The key differences lie in their composition and applications, with copper-nickel alloys favored for durability and conductivity, while nickel-silver alloys are prized for aesthetic appeal and moderate mechanical properties.
Chemical Composition: Copper-Nickel vs Nickel-Silver
Copper-nickel alloys typically contain 60-90% copper with 10-40% nickel, often including trace amounts of iron and manganese, providing excellent corrosion resistance and thermal stability. Nickel-silver alloys consist mainly of copper, 10-30% nickel, and 5-20% zinc, which results in a silvery appearance without actual silver content and enhanced machinability. The distinct chemical compositions influence their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and applications in marine engineering and musical instruments.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Copper-nickel alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance and excellent tensile strength, making them ideal for marine and industrial applications. Nickel-silver alloys offer higher hardness and better wear resistance but typically have lower tensile strength compared to copper-nickel alloys. The mechanical performance of copper-nickel alloys supports enhanced durability under stress, whereas nickel-silver alloys excel in scenarios requiring abrasion resistance.
Corrosion Resistance in Different Environments
Copper-nickel alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance in marine and acidic environments due to their high copper content and protective oxide layers. Nickel-silver alloys, containing higher nickel and zinc concentrations, perform well in atmospheric conditions but are less resistant to seawater corrosion. The enhanced durability of copper-nickel alloys makes them preferable for applications exposed to harsh saline and chemical conditions.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Copper-nickel alloys exhibit significantly higher electrical conductivity than nickel-silver alloys due to their higher copper content, which enhances electron mobility. Nickel-silver alloys, containing a higher proportion of nickel and often zinc, have lower conductivity but superior corrosion resistance and strength. For applications requiring efficient electricity transfer, copper-nickel alloys dominate, while nickel-silver alloys are preferred for durability and aesthetic qualities.
Applications in Industry and Manufacturing
Copper-nickel alloys are widely used in marine engineering, desalination plants, and coinage due to their excellent corrosion resistance and antimicrobial properties. Nickel-silver alloys find extensive application in musical instruments, electrical connectors, and decorative hardware because of their attractive appearance and good mechanical strength. Both alloys serve critical roles in industrial manufacturing where durability and aesthetic appeal are essential.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Copper-nickel alloys typically offer a lower cost solution due to their higher availability and simpler refining processes compared to nickel-silver alloys, which contain higher percentages of nickel and often incur premium pricing. The economic considerations for choosing copper-nickel alloys include reduced raw material expenses and better corrosion resistance, leading to longer lifecycle and maintenance savings. Nickel-silver alloys, while aesthetically preferred in some applications, involve higher initial investment and processing costs that impact overall project budgets.
Machinability and Fabrication Techniques
Copper-nickel alloys exhibit superior machinability compared to nickel-silver alloys due to their lower work-hardening rate and better chip control during cutting processes. Fabrication techniques for copper-nickel alloys typically include cold forming, machining, and welding, benefiting from their excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. Nickel-silver alloys require more careful machining parameters to avoid tool wear and often involve specialized fabrication methods like precision stamping and grinding to maintain surface finish quality.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finishes
Copper-nickel alloys exhibit a warm, reddish hue with excellent resistance to tarnishing, making them ideal for applications requiring a rich, natural metallic appearance. Nickel-silver alloys display a bright, silvery-white finish with superior smoothness and polishability, resulting in a lustrous, reflective surface prized in decorative and musical instruments. Both alloys offer durable surface finishes, but copper-nickel's patina evolves over time, while nickel-silver maintains a consistent, shiny aesthetic without significant discoloration.
Sustainability and Recycling Potential
Copper-nickel alloys exhibit superior sustainability due to their high corrosion resistance and longer lifecycle, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing environmental impact. These alloys have well-established recycling processes, allowing metals to be efficiently recovered and reused with minimal loss in quality, thereby conserving raw materials. In contrast, nickel-silver alloys, while also recyclable, often contain higher amounts of zinc, which can complicate recycling streams and reduce overall material recovery efficiency.
Copper-nickel alloys vs Nickel-silver alloys Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com