Duralumin is a high-strength aluminum alloy mainly composed of aluminum, copper, manganese, and magnesium, prized for its excellent mechanical properties and lightweight nature. Alclad consists of a core aluminum alloy, often duralumin, coated with a thin layer of pure aluminum to enhance corrosion resistance without sacrificing strength. Choosing between Duralumin and Alclad depends on the application's need for strength versus corrosion protection, with Duralumin favored for structural integrity and Alclad for environments prone to oxidation.
Table of Comparison
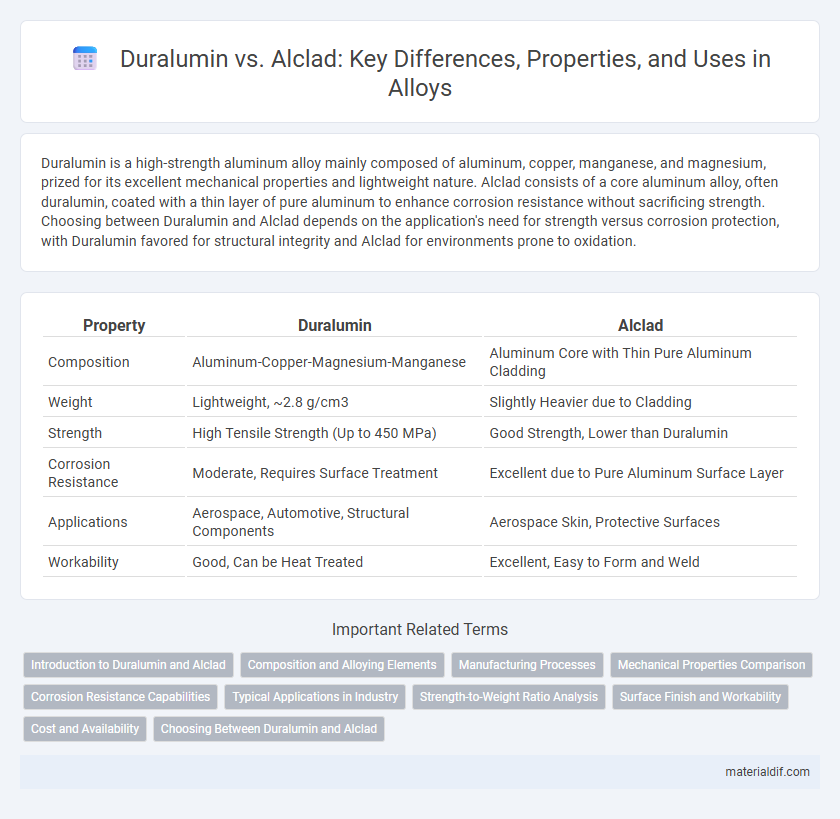
| Property | Duralumin | Alclad |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminum-Copper-Magnesium-Manganese | Aluminum Core with Thin Pure Aluminum Cladding |
| Weight | Lightweight, ~2.8 g/cm3 | Slightly Heavier due to Cladding |
| Strength | High Tensile Strength (Up to 450 MPa) | Good Strength, Lower than Duralumin |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, Requires Surface Treatment | Excellent due to Pure Aluminum Surface Layer |
| Applications | Aerospace, Automotive, Structural Components | Aerospace Skin, Protective Surfaces |
| Workability | Good, Can be Heat Treated | Excellent, Easy to Form and Weld |
Introduction to Duralumin and Alclad
Duralumin is a high-strength aluminum alloy primarily composed of aluminum, copper, manganese, and magnesium, favored for its lightweight and excellent mechanical properties in aerospace applications. Alclad is an aluminum sheet coated with a thin layer of pure aluminum to enhance corrosion resistance while maintaining the strength of the underlying alloy. Both materials balance strength and durability, with Duralumin offering superior structural performance and Alclad providing enhanced surface protection.
Composition and Alloying Elements
Duralumin is an aluminum alloy primarily composed of about 95% aluminum, with copper as the main alloying element at approximately 4%, along with trace amounts of magnesium and manganese to enhance strength and hardness. Alclad consists of a high-strength aluminum alloy core, often 2024 or 7075, coated with a thin layer of pure aluminum to improve corrosion resistance without compromising mechanical properties. The key difference lies in Duralumin's emphasis on copper content for improved tensile strength, whereas Alclad balances alloy core strength with surface protection via its pure aluminum cladding.
Manufacturing Processes
Duralumin manufacturing involves casting followed by extensive heat treatment and cold working to enhance its strength and corrosion resistance. Alclad production includes bonding a pure aluminum layer to an aluminum alloy core through rolling, creating a corrosion-resistant surface without compromising structural integrity. Both processes optimize the alloy's performance for aerospace and automotive applications, balancing durability with lightweight characteristics.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Duralumin exhibits higher tensile strength and better fatigue resistance due to its aluminum-copper alloy composition, making it ideal for structural applications requiring durability. Alclad, featuring an aluminum core with a pure aluminum cladding, offers superior corrosion resistance but generally lower mechanical strength compared to Duralumin. The choice between Duralumin and Alclad depends on balancing mechanical performance with environmental durability in aerospace and automotive industries.
Corrosion Resistance Capabilities
Duralumin, an aluminum-copper alloy, offers high strength but has moderate corrosion resistance due to its copper content, making it susceptible to oxidation and pitting. Alclad, on the other hand, consists of a high-strength aluminum alloy core coated with a pure aluminum layer, providing superior corrosion resistance by protecting the underlying metal from environmental damage. This cladding process enhances Alclad's durability in harsh atmospheric conditions, making it ideal for aerospace applications requiring both strength and corrosion protection.
Typical Applications in Industry
Duralumin, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, is commonly used in aerospace and automotive industries for structural components and aircraft manufacturing. Alclad, featuring a corrosion-resistant aluminum layer bonded to a high-strength core, is preferred in marine and aviation applications where enhanced durability and corrosion protection are critical. Both alloys serve specialized roles, with Duralumin excelling in load-bearing parts and Alclad dominating in environments exposed to harsh weather conditions.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio Analysis
Duralumin exhibits a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to Alclad, making it ideal for aerospace applications where lightweight durability is critical. This alloy combines aluminum with copper, magnesium, and manganese to enhance tensile strength while maintaining low density. Alclad, though corrosion-resistant due to its pure aluminum cladding, offers a slightly lower strength-to-weight ratio, prioritizing surface protection over maximum structural performance.
Surface Finish and Workability
Duralumin offers a strong yet lightweight aluminum alloy with a rougher surface finish due to its higher copper content, which can affect corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Alclad features a pure aluminum cladding over a strong core, providing excellent corrosion resistance and a smooth, bright surface finish ideal for applications requiring enhanced workability and appearance. The workability of Alclad is generally superior because the softer outer layer allows easier forming and machining compared to the harder, more brittle Duralumin core.
Cost and Availability
Duralumin, an aluminum-copper alloy, offers high strength and good machinability but tends to be more expensive due to its specialized composition and manufacturing process. Alclad, featuring a core of duralumin clad with pure aluminum, provides enhanced corrosion resistance at a lower cost, making it more readily available for aerospace and marine applications. The availability of Alclad is higher due to its widespread use and economical production, while Duralumin's cost and availability depend on demand for high-strength aluminum alloys.
Choosing Between Duralumin and Alclad
Choosing between Duralumin and Alclad depends on factors like strength, corrosion resistance, and application requirements. Duralumin, an aluminum-copper alloy, offers high tensile strength suitable for structural components, while Alclad combines high-strength aluminum alloys with a corrosion-resistant pure aluminum layer to enhance durability. Evaluating environmental exposure and mechanical stress helps determine if the superior strength of Duralumin or the protective coating of Alclad better fits specific aerospace or automotive uses.
Duralumin vs Alclad Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com