Bronze alloy primarily consists of copper and tin, offering excellent corrosion resistance and strength, often used in marine and industrial applications. Phosphor bronze, a variant of bronze alloy, includes a small percentage of phosphorus, which enhances its wear resistance, stiffness, and fatigue durability, making it ideal for electrical connectors and springs. Both alloys provide robust mechanical properties, but phosphor bronze delivers superior performance in applications requiring higher strength and resistance to deformation.
Table of Comparison
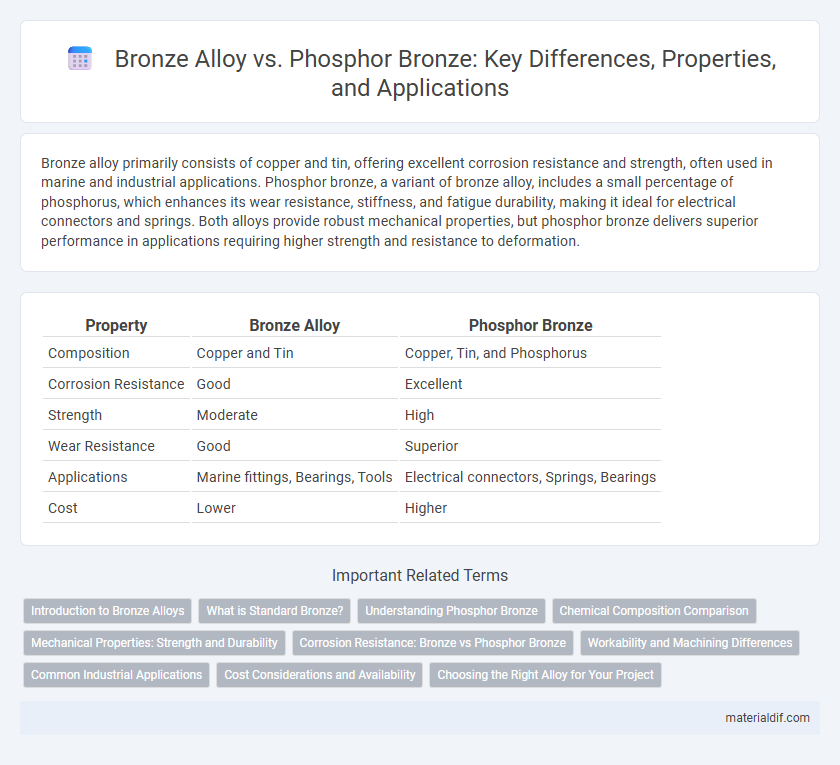
| Property | Bronze Alloy | Phosphor Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and Tin | Copper, Tin, and Phosphorus |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Strength | Moderate | High |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Applications | Marine fittings, Bearings, Tools | Electrical connectors, Springs, Bearings |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Bronze Alloys
Bronze alloys consist primarily of copper combined with tin, offering improved strength and corrosion resistance compared to pure copper. Phosphor bronze is a specialized bronze alloy that includes a small percentage of phosphorus, enhancing wear resistance, stiffness, and fatigue properties. These variations in composition make bronze alloys suitable for diverse applications such as bearings, springs, and electrical components.
What is Standard Bronze?
Standard bronze is primarily an alloy of copper and tin, typically containing about 88% copper and 12% tin, valued for its strength and corrosion resistance. Phosphor bronze differs by including a small percentage of phosphorus, usually around 0.01% to 0.35%, which enhances wear resistance, stiffness, and fatigue durability. Both alloys are widely used in manufacturing applications requiring reliable mechanical performance and resistance to environmental degradation.
Understanding Phosphor Bronze
Phosphor bronze, an advanced variant of bronze alloy, incorporates phosphorus to enhance wear resistance, stiffness, and fatigue resistance compared to traditional bronze alloys. This alloy's superior strength and corrosion resistance make it ideal for applications in springs, bearings, and electrical components where durability is critical. Understanding phosphor bronze's composition and properties helps optimize its use in high-performance industrial and mechanical environments.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Bronze alloy primarily consists of copper (Cu) and tin (Sn), with tin content typically ranging from 5% to 20%, which enhances hardness and corrosion resistance. Phosphor bronze further includes a small percentage (0.01% to 0.35%) of phosphorus (P), which improves wear resistance, stiffness, and fatigue durability. The presence of phosphorus in phosphor bronze distinguishes its chemical composition and performance characteristics from standard bronze alloys.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Bronze alloy typically offers good strength and moderate durability, making it suitable for general applications requiring corrosion resistance and wear properties. Phosphor bronze, an alloy of copper with tin and phosphorus, exhibits higher tensile strength and superior fatigue resistance, enhancing its mechanical durability under repeated stress conditions. The presence of phosphorus in phosphor bronze increases hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for demanding mechanical components.
Corrosion Resistance: Bronze vs Phosphor Bronze
Phosphor bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional bronze due to its higher phosphorus content, which enhances its ability to withstand oxidation and chemical exposure. This makes phosphor bronze ideal for marine and electrical applications where long-term durability against environmental factors is critical. Traditional bronze, while corrosion-resistant, is more susceptible to dezincification and surface degradation in aggressive environments.
Workability and Machining Differences
Bronze alloy primarily consists of copper and tin, while phosphor bronze additionally contains phosphorus, which significantly improves its wear resistance and stiffness. Phosphor bronze offers superior workability due to its enhanced strength and reduced friction, making it more suitable for high-precision applications. Machining phosphor bronze requires specialized tools and techniques because of its hardness, whereas standard bronze alloy is easier to machine but lacks the durability of phosphor bronze.
Common Industrial Applications
Bronze alloy and phosphor bronze are widely used in industrial applications due to their unique properties; bronze alloy is commonly employed in marine hardware, sculptures, and bearings for its corrosion resistance and durability. Phosphor bronze, containing a small amount of phosphorus, excels in electrical connectors, springs, and musical instruments because of its enhanced strength, elasticity, and wear resistance. Both materials are chosen based on specific mechanical and environmental requirements in manufacturing and engineering.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Bronze alloy generally offers lower cost options due to its simpler copper-tin composition and widespread availability of raw materials. Phosphor bronze, with added phosphorus enhancing strength and corrosion resistance, tends to be more expensive and less readily available due to specialized manufacturing processes. Cost considerations often drive the choice between standard bronze alloy for budget-sensitive projects and phosphor bronze where durability and performance justify higher investment.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Project
Bronze alloy, primarily composed of copper and tin, offers superior corrosion resistance and a classic appearance ideal for decorative and structural applications. Phosphor bronze, enhanced with phosphorus, provides increased strength, stiffness, and wear resistance, making it suitable for precision components like springs and bearings. Selecting the right alloy depends on balancing durability needs, mechanical properties, and environmental exposure specific to your project's requirements.
Bronze Alloy vs Phosphor Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com