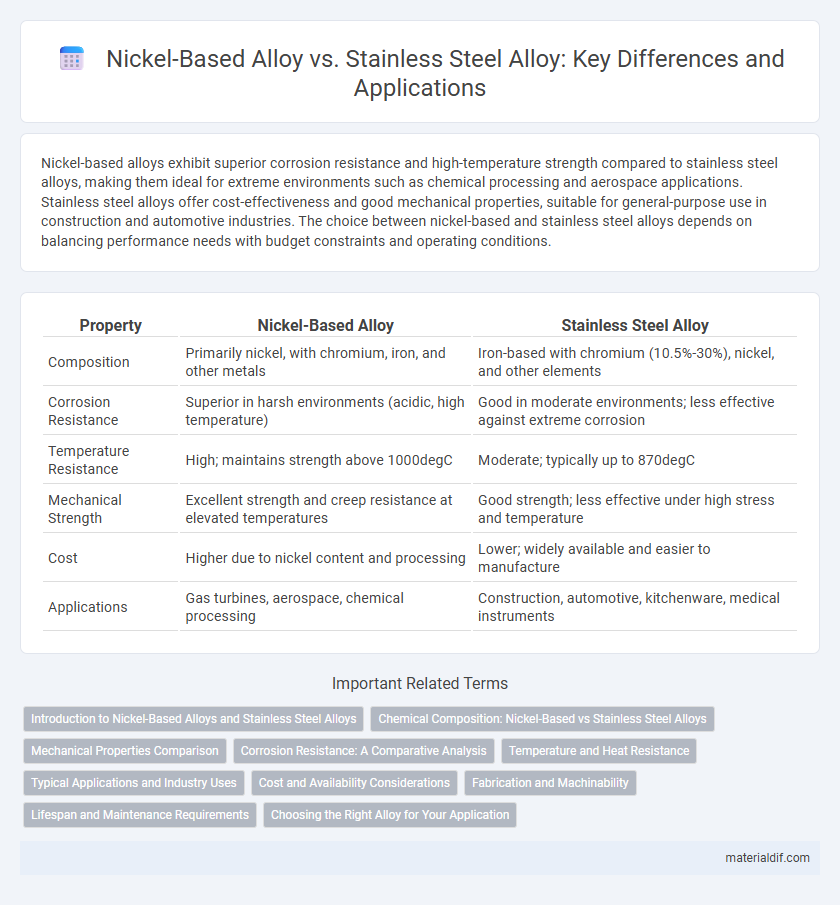
Nickel-based alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to stainless steel alloys, making them ideal for extreme environments such as chemical processing and aerospace applications. Stainless steel alloys offer cost-effectiveness and good mechanical properties, suitable for general-purpose use in construction and automotive industries. The choice between nickel-based and stainless steel alloys depends on balancing performance needs with budget constraints and operating conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nickel-Based Alloy | Stainless Steel Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Primarily nickel, with chromium, iron, and other metals | Iron-based with chromium (10.5%-30%), nickel, and other elements |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior in harsh environments (acidic, high temperature) | Good in moderate environments; less effective against extreme corrosion |
| Temperature Resistance | High; maintains strength above 1000degC | Moderate; typically up to 870degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent strength and creep resistance at elevated temperatures | Good strength; less effective under high stress and temperature |
| Cost | Higher due to nickel content and processing | Lower; widely available and easier to manufacture |
| Applications | Gas turbines, aerospace, chemical processing | Construction, automotive, kitchenware, medical instruments |
Introduction to Nickel-Based Alloys and Stainless Steel Alloys
Nickel-based alloys exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and excellent oxidation resistance, making them ideal for harsh environments such as aerospace, chemical processing, and power generation. Stainless steel alloys, primarily composed of iron, chromium, and varying amounts of nickel and other elements, offer strong corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties, commonly used in construction, automotive, and food processing industries. The distinct microstructures and elemental compositions in nickel-based alloys and stainless steel alloys determine their specific performance characteristics and application suitability.
Chemical Composition: Nickel-Based vs Stainless Steel Alloys
Nickel-based alloys typically contain 50% to 70% nickel, combined with elements like chromium, iron, molybdenum, and copper, providing superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. Stainless steel alloys, primarily composed of iron with 10% to 30% chromium and varying amounts of nickel, manganese, and carbon, offer excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties at moderate temperatures. The higher nickel content in nickel-based alloys enhances resistance to acidic environments and thermal stability compared to stainless steel alloys.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nickel-based alloys exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to stainless steel alloys, including higher tensile strength and excellent fatigue resistance at elevated temperatures. These alloys maintain hardness and creep resistance under extreme thermal conditions, making them ideal for high-stress applications in aerospace and power generation. Stainless steel alloys offer good corrosion resistance and mechanical performance but generally lack the high-temperature strength and durability of nickel-based alloys.
Corrosion Resistance: A Comparative Analysis
Nickel-based alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel alloys, particularly in harsh environments such as acidic or high-temperature conditions. Their high nickel content enhances resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, making them ideal for chemical processing and marine applications. Stainless steel alloys, while offering good general corrosion resistance, are more susceptible to localized attack in chloride-rich environments.
Temperature and Heat Resistance
Nickel-based alloys exhibit superior temperature and heat resistance compared to stainless steel alloys, maintaining strength and corrosion resistance at temperatures exceeding 1000degC. Stainless steel alloys typically withstand temperatures up to 870degC but may experience scaling and reduced mechanical properties beyond this range. The high nickel content in nickel-based alloys enhances their stability in extreme thermal environments, making them ideal for aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing applications.
Typical Applications and Industry Uses
Nickel-based alloys are extensively used in aerospace, chemical processing, and power generation industries due to their exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. Stainless steel alloys find widespread application in food processing, medical instruments, and construction, benefiting from their balanced corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Industries that require extreme heat and corrosive environment resilience typically prefer nickel-based alloys, while stainless steels are favored for general-purpose durability and cost-effectiveness.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Nickel-based alloys generally incur higher costs than stainless steel alloys due to the expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes involved. Stainless steel alloys benefit from broader availability and established supply chains, making them more cost-effective for large-scale applications. The price volatility of nickel can lead to fluctuating costs for nickel-based alloys, whereas stainless steel prices remain relatively stable.
Fabrication and Machinability
Nickel-based alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability compared to stainless steel alloys, making them ideal for demanding fabrication processes such as welding and forming. Their machinability is generally lower due to higher strength and work-hardening tendencies, requiring specialized tooling and cutting parameters. Stainless steel alloys, while easier to machine with conventional tools, may face limitations in extreme environments where nickel-based alloys excel.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Nickel-based alloys typically offer superior corrosion resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to stainless steel alloys, resulting in extended lifespan in harsh environments. These alloys require less frequent maintenance due to their enhanced durability and resistance to oxidation and chemical degradation. Stainless steel alloys, while more cost-effective, generally demand more regular inspections and preventative upkeep to maintain performance and prevent corrosion-related failures.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Application
Nickel-based alloys offer superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to stainless steel alloys, making them ideal for harsh environments such as chemical processing and aerospace applications. Stainless steel alloys provide excellent corrosion resistance and affordability, suitable for everyday use in construction, food processing, and medical instruments. Selecting the right alloy depends on factors like operating temperature, exposure to corrosive substances, mechanical stress, and budget constraints.
Nickel-based alloy vs Stainless steel alloy Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com