Acrylic PMMA offers superior clarity and UV resistance compared to ABS plastic, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and outdoor durability. While ABS plastic provides better impact resistance and is more cost-effective, it lacks the optical qualities and weatherability of Acrylic PMMA. Choosing between Acrylic PMMA and ABS plastic depends on the specific needs for strength, appearance, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
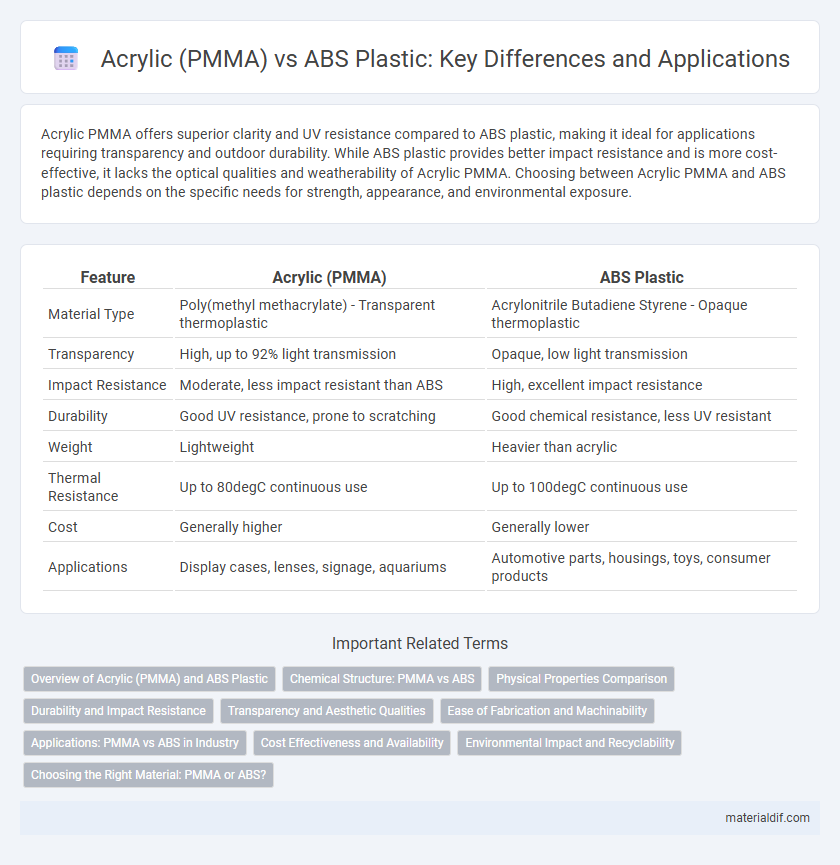
| Feature | Acrylic (PMMA) | ABS Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Poly(methyl methacrylate) - Transparent thermoplastic | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene - Opaque thermoplastic |
| Transparency | High, up to 92% light transmission | Opaque, low light transmission |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, less impact resistant than ABS | High, excellent impact resistance |
| Durability | Good UV resistance, prone to scratching | Good chemical resistance, less UV resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than acrylic |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 80degC continuous use | Up to 100degC continuous use |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Applications | Display cases, lenses, signage, aquariums | Automotive parts, housings, toys, consumer products |
Overview of Acrylic (PMMA) and ABS Plastic
Acrylic (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent optical clarity, weather resistance, and high scratch resistance, making it ideal for applications like display cases, signage, and lenses. ABS plastic is an opaque, impact-resistant thermoplastic with good toughness and chemical resistance, commonly used in automotive parts, electronic housings, and toys. Both materials offer unique properties: PMMA excels in clarity and UV resistance, while ABS provides durability and strength in demanding mechanical applications.
Chemical Structure: PMMA vs ABS
Acrylic PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) consists of a linear polymer structure formed by methyl methacrylate monomers, featuring a carbon backbone with ester functional groups that provide clarity and rigidity. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a terpolymer composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene units, offering a more complex, rubbery matrix with improved impact resistance due to the butadiene segment. The chemical difference results in PMMA having superior optical transparency and UV resistance, while ABS boasts enhanced toughness and flexibility.
Physical Properties Comparison
Acrylic (PMMA) exhibits higher clarity and UV resistance compared to ABS plastic, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and outdoor durability. PMMA offers superior hardness and scratch resistance, whereas ABS provides greater impact strength and flexibility. Both materials have different thermal properties, with acrylic having a lower heat resistance but better resistance to weathering than ABS.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Acrylic PMMA offers superior scratch resistance and clarity but is more brittle compared to ABS plastic, which excels in impact resistance and flexibility. ABS plastic withstands heavy impacts and harsh conditions, making it ideal for applications where durability against mechanical stress is crucial. Acrylic PMMA maintains aesthetic appeal in less demanding environments, while ABS surpasses it in toughness for industrial use.
Transparency and Aesthetic Qualities
Acrylic PMMA offers superior transparency with up to 92% light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring clear, glass-like clarity and vibrant color reproduction. ABS plastic, while durable and impact-resistant, has a more opaque appearance and lacks the high optical clarity of acrylic. The aesthetic qualities of acrylic PMMA provide a glossy, smooth finish that enhances visual appeal, whereas ABS plastic usually features a matte or textured surface.
Ease of Fabrication and Machinability
Acrylic PMMA offers superior ease of fabrication and machinability compared to ABS plastic, allowing for precise cutting, drilling, and thermoforming with minimal risk of cracking or melting. Its rigidity and clarity make it ideal for applications requiring smooth finishes and detailed designs, while ABS tends to be more prone to warping or chipping during machining processes. Acrylic's compatibility with laser cutting and polishing further enhances its versatility and quality in fabrication workflows.
Applications: PMMA vs ABS in Industry
Acrylic PMMA is widely used in applications requiring optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, such as automotive lenses, signage, and medical devices. ABS plastic dominates in applications where impact resistance, toughness, and ease of machining are critical, including automotive interior parts, consumer electronics housings, and toys. Industries choose PMMA for aesthetic and transparent components, while ABS is preferred for durable, structural parts with complex geometries.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Acrylic PMMA offers higher cost effectiveness for applications requiring clarity and weather resistance, often priced competitively compared to ABS plastic. ABS plastic, widely available and less expensive upfront, provides robust impact resistance but may incur higher long-term costs due to lower UV stability and potential yellowing. Market availability favors ABS for large-scale manufacturing, while acrylic PMMA is preferred in specialized industries demanding optical clarity and durability.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Acrylic PMMA offers superior environmental benefits compared to ABS plastic due to its high recyclability and ability to be reprocessed into clear sheets or pellets, reducing waste in manufacturing. ABS plastic, derived from petroleum-based sources, presents challenges in recycling because of its complex polymer blend, leading to limited circular reuse and higher landfill accumulation. Choosing PMMA supports sustainable practices by minimizing ecological footprint and enabling more efficient material recovery in the plastics industry.
Choosing the Right Material: PMMA or ABS?
PMMA (Acrylic) offers superior optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and durability. ABS plastic provides higher impact resistance, better machinability, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for structural components and indoor use. Selecting between PMMA and ABS depends on the priority of visual quality versus mechanical strength and environmental exposure.
Acrylic PMMA vs ABS Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com