Acrylic plastic offers superior optical clarity and scratch resistance, making it ideal for display cases and signage, while PETG provides enhanced impact resistance and flexibility, suited for protective covers and packaging. Acrylic is more rigid and prone to cracking under stress, whereas PETG's toughness allows for better durability in dynamic environments. Both materials are lightweight and transparent, but the choice depends on the specific application requirements regarding strength and brittleness.
Table of Comparison
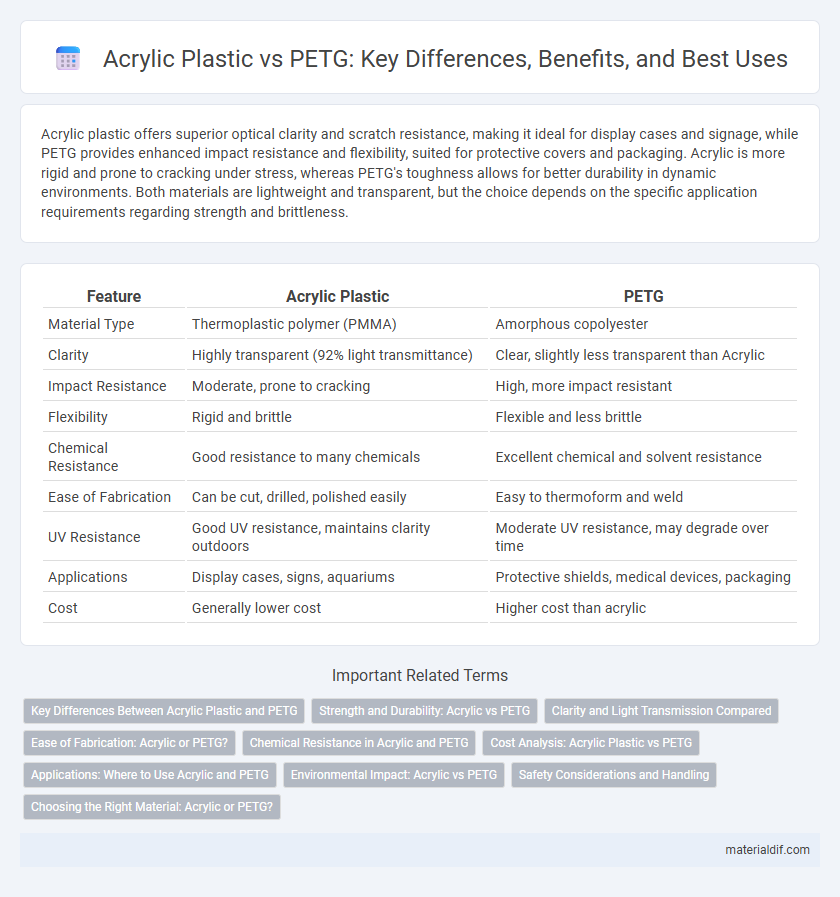
| Feature | Acrylic Plastic | PETG |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer (PMMA) | Amorphous copolyester |
| Clarity | Highly transparent (92% light transmittance) | Clear, slightly less transparent than Acrylic |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, more impact resistant |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Flexible and less brittle |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to many chemicals | Excellent chemical and solvent resistance |
| Ease of Fabrication | Can be cut, drilled, polished easily | Easy to thermoform and weld |
| UV Resistance | Good UV resistance, maintains clarity outdoors | Moderate UV resistance, may degrade over time |
| Applications | Display cases, signs, aquariums | Protective shields, medical devices, packaging |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost than acrylic |
Key Differences Between Acrylic Plastic and PETG
Acrylic plastic offers superior clarity and scratch resistance compared to PETG, which is more impact-resistant and flexible. PETG exhibits better chemical resistance and is easier to thermoform and weld, making it ideal for complex shapes. Acrylic's brittleness contrasts with PETG's toughness, influencing their applications in displays, signage, and protective barriers.
Strength and Durability: Acrylic vs PETG
Acrylic plastic offers excellent rigidity and scratch resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring clear, sturdy materials. PETG boasts superior impact resistance and flexibility, enhancing durability in environments subject to bending or shocks. When comparing strength and durability, PETG outperforms acrylic in impact tolerance, while acrylic maintains higher stiffness and clarity over time.
Clarity and Light Transmission Compared
Acrylic plastic offers superior clarity with a light transmission rate of approximately 92%, making it one of the clearest transparent plastics available. PETG, while also transparent, typically has a slightly lower light transmission rate around 89%, resulting in less optical clarity compared to acrylic. The higher refractive index of acrylic enhances its brilliance and sharpness, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum visual clarity.
Ease of Fabrication: Acrylic or PETG?
Acrylic plastic offers superior ease of fabrication compared to PETG due to its excellent machinability, allowing precise cutting, drilling, and polishing without cracking. PETG, though more impact-resistant and flexible, often requires specialized tools and slower processing speeds to avoid melting or warping during fabrication. For projects demanding sharp edges and high optical clarity, acrylic remains the preferred choice for both professionals and hobbyists.
Chemical Resistance in Acrylic and PETG
Acrylic plastic exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly against acids and alkalis, making it ideal for applications requiring durability in harsh environments. PETG offers moderate chemical resistance but is more susceptible to attack by solvents like ketones and chlorinated hydrocarbons. Understanding these differences ensures proper material selection for chemical exposure and long-term performance.
Cost Analysis: Acrylic Plastic vs PETG
Acrylic plastic typically costs less per sheet compared to PETG, making it a more budget-friendly option for many applications. However, PETG offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, which can reduce long-term costs related to damage and replacement. When analyzing cost efficiency, consider both initial material expenses and performance factors such as durability and maintenance.
Applications: Where to Use Acrylic and PETG
Acrylic plastic is widely used in applications requiring superior clarity and UV resistance, such as display cases, signage, and aquariums, where long-term outdoor exposure is common. PETG is preferred in environments demanding higher impact resistance and easier fabrication, making it ideal for medical device housings, food packaging, and protective barriers. Both materials are versatile but choosing acrylic or PETG depends on factors like durability needs, optical quality, and environmental exposure.
Environmental Impact: Acrylic vs PETG
Acrylic plastic is less recyclable compared to PETG, leading to higher environmental impact due to longer degradation times in landfills. PETG offers better recyclability and lower energy consumption during processing, reducing its overall carbon footprint. Both materials originate from petroleum, but PETG's enhanced recycling capabilities make it a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious applications.
Safety Considerations and Handling
Acrylic plastic is known for its rigidity and clarity but is more prone to cracking and emits potentially harmful fumes when cut or welded, requiring adequate ventilation and protective gear during handling. PETG is safer to work with due to its higher impact resistance, lower risk of cracking, and fewer toxic emissions when heated or shaped, making it a preferred choice in environments prioritizing safety. Both materials should be handled with gloves and eye protection, but PETG's flexible nature reduces injury risk during transport and installation.
Choosing the Right Material: Acrylic or PETG?
Acrylic plastic offers superior clarity, scratch resistance, and UV stability, making it ideal for outdoor displays and high-gloss applications, while PETG excels in impact resistance, flexibility, and ease of thermoforming, suitable for protective barriers and complex shapes. Consider acrylic for projects requiring rigidity and optical clarity, and PETG when durability and chemical resistance are priorities. Evaluating environmental factors and application-specific demands ensures selecting the optimal material between acrylic and PETG for durability and performance.
Acrylic Plastic vs PETG Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com