Zinc-Nickel coating offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced durability compared to Zinc-Iron coating, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. Zinc-Iron coatings provide excellent adhesion and are cost-effective, suitable for general industrial uses with moderate corrosion protection requirements. Choosing between these coatings depends on specific performance needs, balancing corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
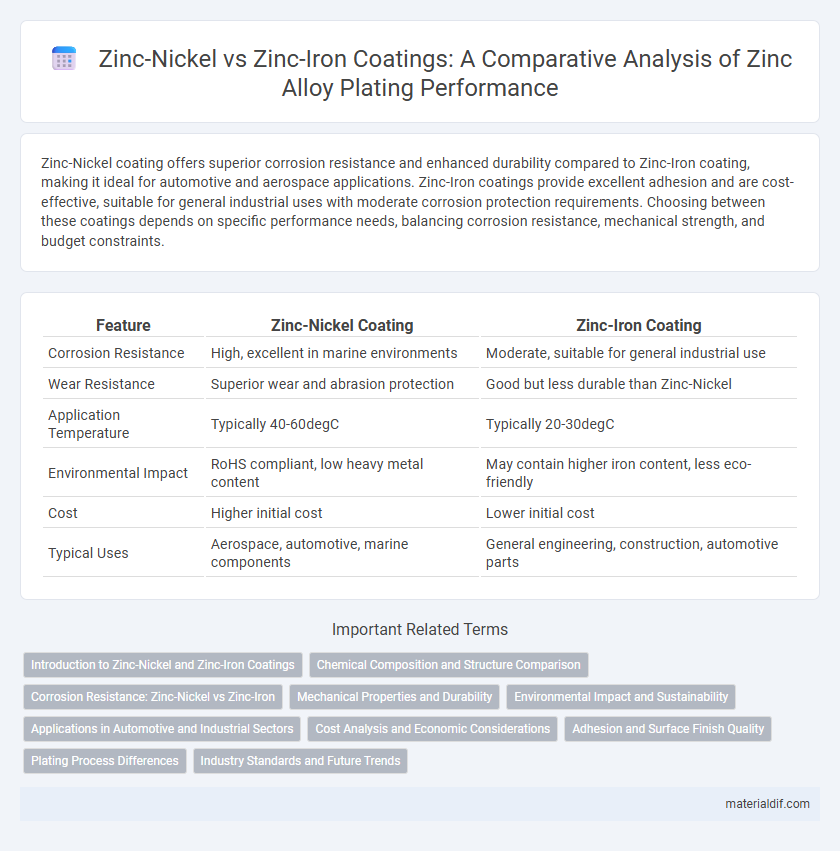
| Feature | Zinc-Nickel Coating | Zinc-Iron Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High, excellent in marine environments | Moderate, suitable for general industrial use |
| Wear Resistance | Superior wear and abrasion protection | Good but less durable than Zinc-Nickel |
| Application Temperature | Typically 40-60degC | Typically 20-30degC |
| Environmental Impact | RoHS compliant, low heavy metal content | May contain higher iron content, less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Typical Uses | Aerospace, automotive, marine components | General engineering, construction, automotive parts |
Introduction to Zinc-Nickel and Zinc-Iron Coatings
Zinc-Nickel coatings offer enhanced corrosion resistance and higher hardness compared to traditional zinc coatings, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace applications where durability is critical. Zinc-Iron coatings provide a cost-effective alternative with good adhesion and corrosion protection, commonly used in industrial and construction environments. Both coatings utilize an electrodeposition process, but Zinc-Nickel alloys typically contain 10-15% nickel for improved performance, while Zinc-Iron coatings incorporate a small iron percentage to enhance bonding and surface properties.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Zinc-Nickel coatings consist primarily of a zinc matrix alloyed with nickel, creating a compact, corrosion-resistant microstructure with high hardness and enhanced passivation properties, typically containing 12-15% nickel. Zinc-Iron coatings feature a zinc base alloyed with iron, forming a layered, heterogeneous structure with iron-rich intermetallic phases that improve adhesion but offer lower corrosion resistance compared to Zinc-Nickel. The chemical composition difference directly affects the structural morphology, where Zinc-Nickel coatings exhibit uniformity and superior barrier protection, while Zinc-Iron coatings provide improved mechanical bonding and cost-efficiency in industrial applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Zinc-Nickel vs Zinc-Iron
Zinc-nickel coatings exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc-iron coatings due to the formation of a compact and stable passive layer that significantly enhances protection against rust and environmental degradation. The nickel content in zinc-nickel alloys improves galvanic corrosion resistance, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace applications exposed to harsh conditions. Zinc-iron coatings, while offering some corrosion protection, typically demonstrate lower durability and faster corrosion rates under aggressive environments.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Zinc-nickel coatings offer superior mechanical properties such as higher hardness and enhanced wear resistance compared to zinc-iron coatings, making them ideal for applications requiring robust performance under stress. The zinc-nickel alloy provides excellent corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments, due to its denser microstructure and better passivation behavior. In contrast, zinc-iron coatings generally exhibit lower durability and mechanical strength but may offer cost advantages for less demanding conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zinc-nickel coatings exhibit higher corrosion resistance and longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of reapplications and minimizing environmental waste compared to zinc-iron coatings. Zinc-iron coatings involve more intensive energy consumption and generate higher levels of hazardous byproducts during the plating process. Sustainable manufacturing practices favor zinc-nickel coatings due to their reduced ecological footprint and enhanced recyclability.
Applications in Automotive and Industrial Sectors
Zinc-Nickel coating offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced adhesion, making it ideal for automotive components such as fasteners, brackets, and chassis parts exposed to harsh environments. Zinc-Iron coating provides excellent wear resistance and is commonly used in industrial equipment and heavy machinery where durability against mechanical stress is critical. Both coatings support eco-friendly practices by eliminating hexavalent chromium, aligning with industry regulations in automotive and industrial sectors.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Zinc-nickel coating generally offers superior corrosion resistance and higher durability compared to zinc-iron coating, but it comes at a higher initial material and processing cost. Zinc-iron coatings provide a more cost-effective solution for applications requiring moderate protection, making them suitable for budget-sensitive projects with less stringent performance demands. Economic considerations must balance the long-term maintenance savings of zinc-nickel coatings against the lower upfront expenses of zinc-iron alternatives, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace where lifecycle costs are critical.
Adhesion and Surface Finish Quality
Zinc-Nickel coating exhibits superior adhesion properties compared to Zinc-Iron coating, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability and corrosion resistance. The surface finish quality of Zinc-Nickel is typically smoother and more uniform, providing better aesthetic appeal and uniformity in protective layers. Zinc-Iron coatings tend to have a rougher texture and lower adhesion strength, which can impact long-term performance under stress.
Plating Process Differences
Zinc-nickel coating involves electrodeposition of a zinc-nickel alloy, typically with 12-15% nickel content, offering excellent corrosion resistance and uniform plating on complex geometries. Zinc-iron coating uses a zinc deposit with an incorporated iron layer, applied through electroplating or mechanical plating methods, enhancing adhesion and hardness but providing different corrosion properties than zinc-nickel. The plating process for zinc-nickel requires precise bath composition and temperature control to maintain alloy consistency, whereas zinc-iron plating emphasizes iron content regulation for optimal coating performance.
Industry Standards and Future Trends
Zinc-Nickel coating adheres to stringent industry standards such as SAE AMS 2417, offering superior corrosion resistance and enhanced hardness, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. Zinc-Iron coating complies with standards like ASTM B633, providing cost-effective protection with moderate corrosion resistance suitable for general industrial use. Future trends indicate growing adoption of Zinc-Nickel systems driven by environmental regulations and performance demands, while Zinc-Iron coatings evolve through improved alloy formulations and eco-friendly plating technologies.
Zinc-Nickel Coating vs Zinc-Iron Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com