Tin (Sn) plating provides a lead-free, environmentally friendly alternative to tin-lead (SnPb) plating, offering excellent solderability and corrosion resistance for electronic components. SnPb plating remains favored for its superior wettability and reliability in harsh conditions, especially in legacy systems requiring robust mechanical strength. Choosing between Sn and SnPb plating depends on specific application requirements, balancing ecological compliance with performance and durability.
Table of Comparison
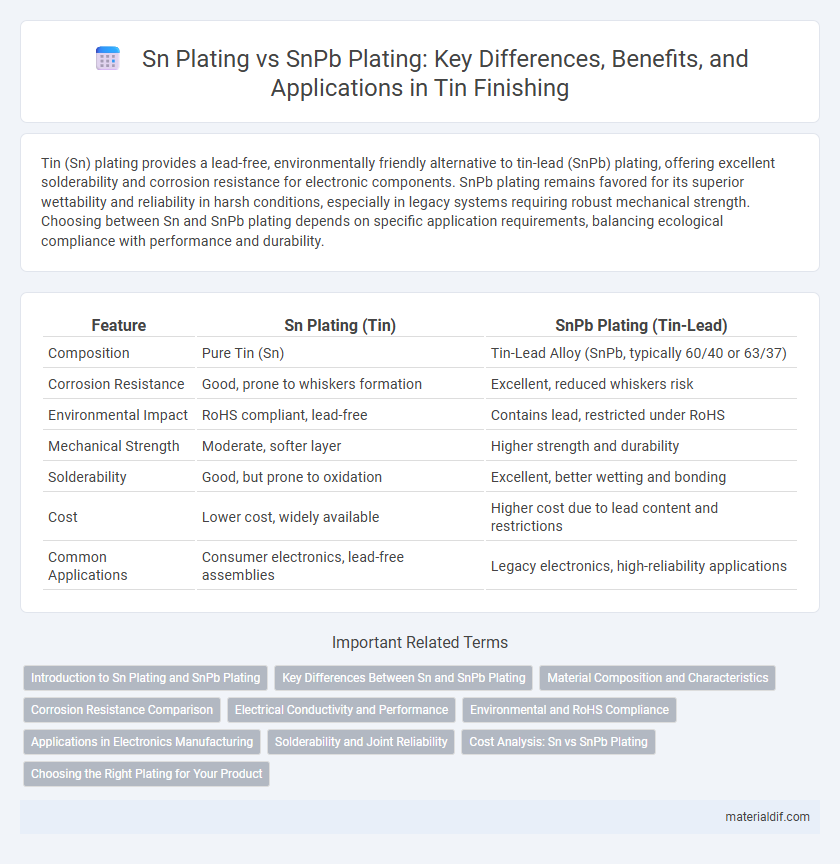
| Feature | Sn Plating (Tin) | SnPb Plating (Tin-Lead) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure Tin (Sn) | Tin-Lead Alloy (SnPb, typically 60/40 or 63/37) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, prone to whiskers formation | Excellent, reduced whiskers risk |
| Environmental Impact | RoHS compliant, lead-free | Contains lead, restricted under RoHS |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, softer layer | Higher strength and durability |
| Solderability | Good, but prone to oxidation | Excellent, better wetting and bonding |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to lead content and restrictions |
| Common Applications | Consumer electronics, lead-free assemblies | Legacy electronics, high-reliability applications |
Introduction to Sn Plating and SnPb Plating
Sn plating offers a lead-free, environmentally friendly coating widely used for electronics due to its excellent solderability and corrosion resistance. SnPb plating, a traditional method combining tin and lead, provides superior ductility and solder joint reliability but faces restrictions due to lead's toxicity and RoHS regulations. Both plating types serve critical roles in electrical component protection, with Sn plating gaining preference in lead-free manufacturing environments.
Key Differences Between Sn and SnPb Plating
Sn plating provides a lead-free, environmentally friendly option with excellent solderability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for modern electronics. SnPb plating, comprising a tin-lead alloy, offers superior wear resistance and a lower melting point, enhancing mechanical durability and recrystallization during soldering processes. Key differences include the environmental impact, mechanical strength, and compliance with RoHS regulations, where Sn plating is preferred for lead-free requirements.
Material Composition and Characteristics
Sn plating consists of nearly pure tin, providing excellent solderability and corrosion resistance but lower mechanical strength compared to SnPb plating. SnPb plating, an alloy of about 60% tin and 40% lead, offers superior durability, reduced whisker growth, and enhanced fatigue resistance in electronic components. Material composition differences directly influence properties such as brittleness, melting point, and environmental compliance, with Sn plating favored for lead-free applications and SnPb plating still used where mechanical robustness is critical.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Sn plating exhibits superior corrosion resistance in environments with high humidity and mild chemical exposure due to its pure tin composition that forms a stable oxide layer. SnPb plating, containing lead, offers enhanced resistance against mechanical wear and galvanic corrosion but may suffer from lead leaching and reduced environmental compliance. Studies indicate that Sn plating performs better in electronics exposed to atmospheric conditions, while SnPb plating remains preferred in heavy-duty industrial applications requiring robust mixed-metal protection.
Electrical Conductivity and Performance
Tin (Sn) plating offers superior electrical conductivity compared to SnPb plating, largely due to the absence of lead, which can introduce resistive impurities. The pure tin layer provides consistent low-resistance pathways essential for high-performance electronic connections and signal integrity. Sn plating also enhances solderability and reduces concerns related to lead's environmental and health impacts, maintaining reliable electrical performance in modern electronics.
Environmental and RoHS Compliance
Sn plating offers superior environmental benefits compared to traditional SnPb plating, as it eliminates the use of lead, a toxic heavy metal restricted under RoHS directives. RoHS compliance mandates the reduction of hazardous substances, and Sn plating meets these requirements by being lead-free, thereby reducing environmental pollution and health risks. Sn plating also supports sustainable manufacturing processes by facilitating easier recycling and safer disposal compared to SnPb plating.
Applications in Electronics Manufacturing
Sn plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and solderability, making it ideal for lead-free electronics manufacturing that complies with RoHS regulations. SnPb plating, historically used for its superior mechanical strength and fatigue resistance, remains prevalent in applications requiring high reliability and tolerance to thermal cycling. The choice between Sn and SnPb plating significantly impacts the performance and longevity of electronic components in automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics industries.
Solderability and Joint Reliability
Sn plating offers excellent solderability due to its clean surface and high wettability, enabling strong metallurgical bonds with common solder alloys. SnPb plating, historically preferred for its proven joint reliability, combines the ductility of lead with the corrosion resistance of tin, reducing brittleness and enhancing fatigue resistance in solder joints. Modern lead-free Sn plating alternatives strive to match SnPb's joint reliability while complying with RoHS regulations, emphasizing optimized solder wetting and mechanical stability in electronics assembly.
Cost Analysis: Sn vs SnPb Plating
Sn plating generally offers lower material and processing costs compared to SnPb plating due to the absence of lead and simpler environmental compliance requirements. SnPb plating involves higher expenses linked to lead disposal, regulatory compliance under RoHS exemptions, and potential health risk management. Cost analysis reveals Sn plating as the more economical choice for eco-friendly applications with comparable performance in solderability and corrosion resistance.
Choosing the Right Plating for Your Product
Choosing the right plating for your product depends on factors like environmental compliance, solderability, and corrosion resistance. Sn plating offers lead-free, RoHS-compliant protection with good solderability and is ideal for eco-friendly applications. SnPb plating provides superior fatigue resistance and cost-effectiveness but is restricted in many markets due to lead content and environmental regulations.
Sn plating vs SnPb plating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com