Compression molding is ideal for producing large, simple rubber parts with excellent strength and minimal waste, as it involves placing raw rubber into a heated mold cavity before applying pressure to shape it. Injection molding offers faster cycle times and high precision, making it suitable for complex designs and high-volume production by injecting molten rubber into a closed mold. Choosing between compression molding and injection molding depends on part complexity, production volume, and cost efficiency.
Table of Comparison
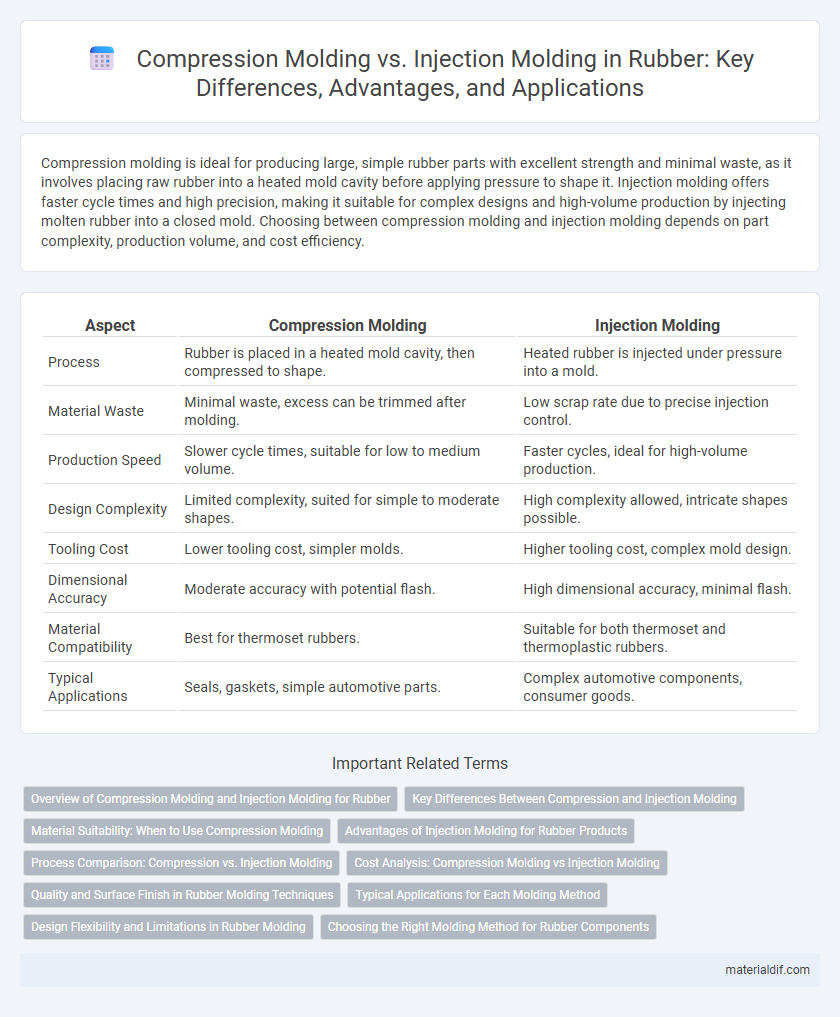
| Aspect | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Rubber is placed in a heated mold cavity, then compressed to shape. | Heated rubber is injected under pressure into a mold. |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste, excess can be trimmed after molding. | Low scrap rate due to precise injection control. |
| Production Speed | Slower cycle times, suitable for low to medium volume. | Faster cycles, ideal for high-volume production. |
| Design Complexity | Limited complexity, suited for simple to moderate shapes. | High complexity allowed, intricate shapes possible. |
| Tooling Cost | Lower tooling cost, simpler molds. | Higher tooling cost, complex mold design. |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Moderate accuracy with potential flash. | High dimensional accuracy, minimal flash. |
| Material Compatibility | Best for thermoset rubbers. | Suitable for both thermoset and thermoplastic rubbers. |
| Typical Applications | Seals, gaskets, simple automotive parts. | Complex automotive components, consumer goods. |
Overview of Compression Molding and Injection Molding for Rubber
Compression molding of rubber involves placing pre-measured raw material into a heated mold cavity where pressure is applied to shape and cure the material, offering excellent control over part thickness and minimizing waste. Injection molding injects heated rubber compounds into a closed mold under high pressure, allowing for faster cycle times and the production of complex geometries with high dimensional accuracy. Both methods are essential in rubber manufacturing, with compression molding preferred for larger, simpler parts and injection molding favored for intricate, high-volume production.
Key Differences Between Compression and Injection Molding
Compression molding involves placing pre-measured rubber material into a heated mold cavity where pressure is applied to form the shape, making it ideal for large, simple parts with lower tooling costs. Injection molding injects molten rubber into a closed mold under high pressure, enabling high precision, fast cycle times, and complex geometries with consistent repeatability. Key differences include compression molding's suitability for lower volume production and simpler designs versus injection molding's efficiency in high-volume, intricate part manufacturing with finer details.
Material Suitability: When to Use Compression Molding
Compression molding suits large, simple rubber parts requiring high strength and heat resistance, such as automotive seals and gaskets. It is ideal for materials like silicone, natural rubber, and thermosetting elastomers that demand precise curing under heat and pressure. This method ensures uniformity in thick sections and is preferred when maintaining material integrity and reducing waste are crucial.
Advantages of Injection Molding for Rubber Products
Injection molding offers superior precision and repeatability for rubber products, enabling complex geometries and tight tolerances that compression molding often cannot achieve. The process allows higher production speeds and automation, significantly reducing labor costs and increasing output efficiency. Its ability to produce consistent, high-quality parts with minimal waste makes injection molding ideal for large-volume manufacturing of rubber components.
Process Comparison: Compression vs. Injection Molding
Compression molding involves placing preheated rubber material into a heated mold cavity, where pressure is applied to shape and cure the part, making it ideal for large, simple geometries with lower tooling costs. Injection molding injects molten rubber into a closed mold under high pressure, providing precise, complex shapes with faster cycle times and higher production volumes. Compression molding offers better control over material flow and reduced waste, while injection molding excels in automation and reproducibility for high-volume manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Compression Molding vs Injection Molding
Compression molding typically involves lower initial tooling costs compared to injection molding, making it more economical for small production runs and prototype development in rubber manufacturing. Injection molding has higher upfront expenses due to complex mold design and machinery but offers lower per-unit costs and faster production rates for large-scale rubber parts manufacturing. Cost analysis reveals compression molding suits low to medium volume jobs with simpler geometries, while injection molding is cost-effective for high-volume, intricate rubber components requiring tight tolerances.
Quality and Surface Finish in Rubber Molding Techniques
Compression molding in rubber manufacturing offers superior surface finish and consistent material distribution, resulting in fewer defects and enhanced part quality. Injection molding enables more intricate designs with tight tolerances but may require additional finishing to achieve optimal surface smoothness. Both techniques influence the final aesthetic and functional properties, with compression molding favoring higher-quality finishes and injection molding excelling in complex geometries.
Typical Applications for Each Molding Method
Compression molding is typically used for manufacturing large, durable rubber products such as automotive seals, gaskets, and industrial components that require high strength and heat resistance. Injection molding excels in producing intricate rubber parts with complex geometries, including medical devices, footwear soles, and small automotive components demanding precision and high volume production. Each molding method caters to specific application needs, balancing factors like production speed, part complexity, and material properties.
Design Flexibility and Limitations in Rubber Molding
Compression molding offers greater design flexibility for large, simple rubber parts with uniform wall thickness, allowing for intricate textures and inserts. Injection molding excels in producing complex, detailed geometries with precise dimensional control but is limited by higher tooling costs and constraints on material flow for very thick or large components. Both methods require careful consideration of part complexity, volume, and mold design to optimize production efficiency and material properties.
Choosing the Right Molding Method for Rubber Components
Compression molding offers precise control over rubber part dimensions and is ideal for large, simple shapes requiring high strength and durability. Injection molding suits complex, high-volume rubber components with intricate designs, providing faster cycle times and reduced labor costs. Selecting the right molding method depends on factors such as part complexity, production volume, material properties, and cost-effectiveness to optimize performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Compression Molding vs Injection Molding Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com