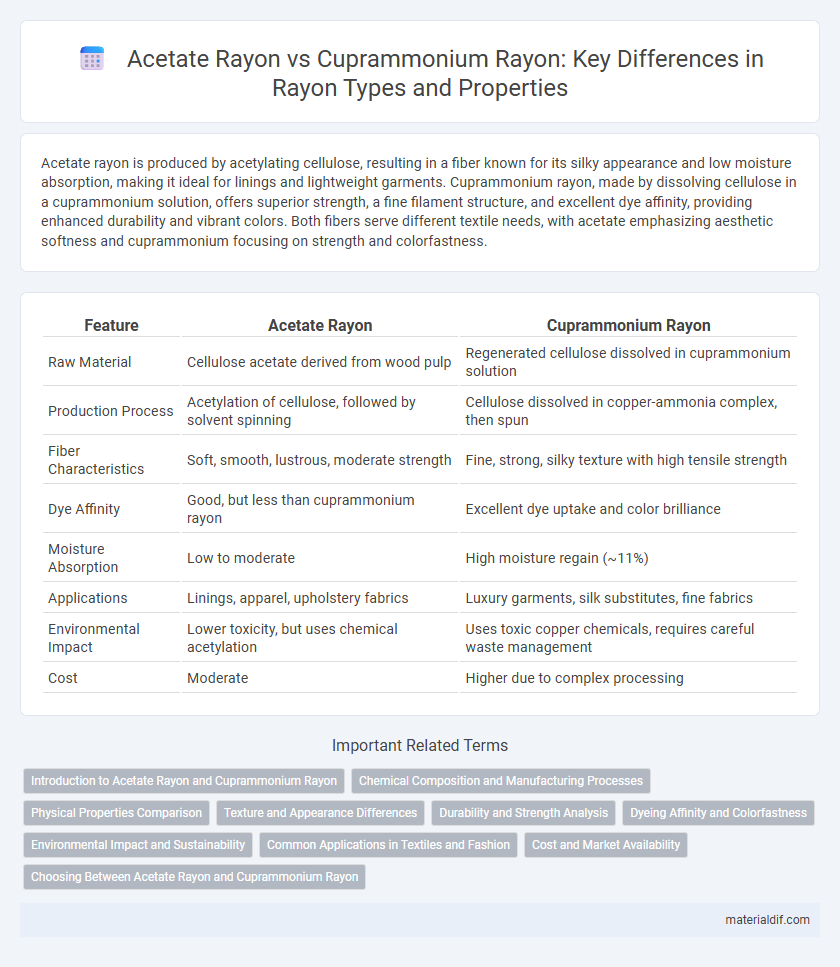
Acetate rayon is produced by acetylating cellulose, resulting in a fiber known for its silky appearance and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for linings and lightweight garments. Cuprammonium rayon, made by dissolving cellulose in a cuprammonium solution, offers superior strength, a fine filament structure, and excellent dye affinity, providing enhanced durability and vibrant colors. Both fibers serve different textile needs, with acetate emphasizing aesthetic softness and cuprammonium focusing on strength and colorfastness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acetate Rayon | Cuprammonium Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Cellulose acetate derived from wood pulp | Regenerated cellulose dissolved in cuprammonium solution |
| Production Process | Acetylation of cellulose, followed by solvent spinning | Cellulose dissolved in copper-ammonia complex, then spun |
| Fiber Characteristics | Soft, smooth, lustrous, moderate strength | Fine, strong, silky texture with high tensile strength |
| Dye Affinity | Good, but less than cuprammonium rayon | Excellent dye uptake and color brilliance |
| Moisture Absorption | Low to moderate | High moisture regain (~11%) |
| Applications | Linings, apparel, upholstery fabrics | Luxury garments, silk substitutes, fine fabrics |
| Environmental Impact | Lower toxicity, but uses chemical acetylation | Uses toxic copper chemicals, requires careful waste management |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to complex processing |
Introduction to Acetate Rayon and Cuprammonium Rayon
Acetate Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose acetate, known for its silk-like appearance and excellent draping qualities, widely used in apparel and upholstery. Cuprammonium Rayon, also called Cupro, is a regenerated cellulose fiber produced by dissolving cellulose in a cuprammonium solution, valued for its smooth texture and breathability. Both fibers are biodegradable and offer distinct tactile properties and chemical compositions that influence their end-use applications in the textile industry.
Chemical Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Acetate rayon is primarily composed of cellulose acetate, produced by acetylating cellulose fibers followed by solvent spinning, which imparts a silky texture and resistance to shrinkage. Cuprammonium rayon consists of pure cellulose dissolved in a copper-ammonium hydroxide solution, and its manufacturing involves the cuprammonium process that yields fine, smooth fibers with high tensile strength. The difference in chemical composition, with acetate rayon containing acetate groups and cuprammonium rayon retaining pure cellulose, directly influences their respective production methods and fiber properties.
Physical Properties Comparison
Acetate rayon exhibits a lower tensile strength and higher moisture regain compared to cuprammonium rayon, making it more prone to shrinkage and deformation under stress. Cuprammonium rayon has a smoother texture and greater luster due to its finer filament structure, which enhances its softness and drapeability. Both fibers differ in elongation characteristics, with cuprammonium rayon demonstrating superior elasticity and resilience in textile applications.
Texture and Appearance Differences
Acetate rayon features a smooth, glossy surface with a silk-like texture, often exhibiting vibrant color retention and a subtle sheen that enhances its luxurious appearance. Cuprammonium rayon offers a softer, more delicate feel with a matte finish and fine, uniform filaments that provide a natural silk-like drape. The visual distinction lies in acetate's brighter luster compared to cuprammonium's muted and more natural texture.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Acetate rayon exhibits higher durability due to its chemical structure, which provides greater resistance to moisture and wear, making it suitable for long-lasting textile applications. In contrast, cuprammonium rayon demonstrates superior tensile strength thanks to its fine filament formation, enhancing fabric elasticity but reducing overall durability under repeated stress. When comparing both fibers, acetate rayon offers a more robust solution for durable garments while cuprammonium rayon excels in strength for delicate, high-performance fabrics.
Dyeing Affinity and Colorfastness
Acetate rayon exhibits superior dyeing affinity due to its acetylated cellulose structure, allowing vibrant and uniform color absorption, while Cuprammonium rayon, derived from copper-ammonia cellulose complex, shows moderate dye uptake with less intensity. In terms of colorfastness, acetate rayon performs better against washing and light exposure, maintaining color integrity longer, whereas cuprammonium rayon tends to fade more quickly under similar conditions. The molecular differences significantly impact the fibers' dye interaction and long-term color durability in textile applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acetate rayon exhibits a lower environmental impact compared to cuprammonium rayon, primarily due to its less toxic production process and reduced chemical waste generation. Cuprammonium rayon manufacturing involves the use of hazardous copper-ammonia solutions, leading to water pollution and challenges in waste management. Sustainable practices in acetate rayon production, such as closed-loop solvent recovery systems, contribute to improved eco-friendly textile manufacturing.
Common Applications in Textiles and Fashion
Acetate rayon is widely used in lining fabrics, dresses, and blouses due to its silky appearance and excellent drape, making it popular in fashion for formal wear and lingerie. Cuprammonium rayon, known for its fine, smooth texture and strength, is primarily utilized in high-end clothing and delicate textiles such as blouses and scarves. Both fibers offer unique properties that cater to specific applications in the textile industry, balancing aesthetics and functionality.
Cost and Market Availability
Acetate rayon generally costs less to produce and is more widely available in the market due to its simpler manufacturing process and higher demand for apparel and upholstery fabrics. Cuprammonium rayon, produced via a more complex and costly method involving copper-ammonia solvent, is less common and usually found in niche markets such as luxury textiles and specialty applications. The higher production cost and limited scale result in cuprammonium rayon being priced significantly above acetate rayon in global textile markets.
Choosing Between Acetate Rayon and Cuprammonium Rayon
Choosing between acetate rayon and cuprammonium rayon depends on their distinct properties and applications. Acetate rayon offers excellent moisture resistance and a silky finish, making it ideal for luxury apparel and linings, whereas cuprammonium rayon provides superior softness and high tensile strength suitable for fine fabrics and delicate textiles. Consider factors such as fabric durability, texture, and end-use requirements to determine the optimal rayon type for your project.
Acetate Rayon vs Cuprammonium Rayon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com