Wood pulp rayon offers a reliable source of fibers derived from sustainably managed forests, providing a soft, breathable fabric suited for a wide range of textile applications. Bamboo rayon, although often marketed as eco-friendly, involves chemical processing that can lessen its environmental benefits compared to wood pulp rayon. Both types share similar properties like moisture-wicking and comfort, but wood pulp rayon typically has a more consistent production process and lower ecological impact.
Table of Comparison
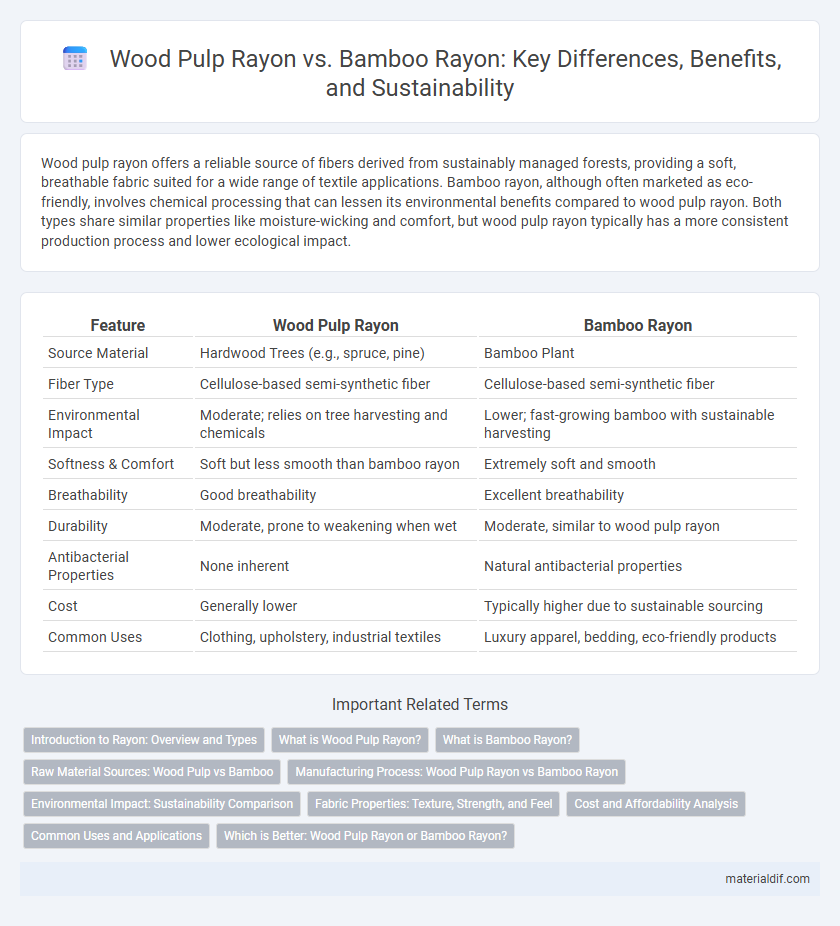
| Feature | Wood Pulp Rayon | Bamboo Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Hardwood Trees (e.g., spruce, pine) | Bamboo Plant |
| Fiber Type | Cellulose-based semi-synthetic fiber | Cellulose-based semi-synthetic fiber |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate; relies on tree harvesting and chemicals | Lower; fast-growing bamboo with sustainable harvesting |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft but less smooth than bamboo rayon | Extremely soft and smooth |
| Breathability | Good breathability | Excellent breathability |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to weakening when wet | Moderate, similar to wood pulp rayon |
| Antibacterial Properties | None inherent | Natural antibacterial properties |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher due to sustainable sourcing |
| Common Uses | Clothing, upholstery, industrial textiles | Luxury apparel, bedding, eco-friendly products |
Introduction to Rayon: Overview and Types
Rayon is a versatile semi-synthetic fiber derived primarily from cellulose, with wood pulp rayon and bamboo rayon being two prominent types. Wood pulp rayon is produced from natural cellulose extracted from wood sources like pine and spruce, offering a soft texture and strong durability suitable for textiles. Bamboo rayon, made by chemically processing bamboo cellulose, is celebrated for its eco-friendly profile and antibacterial properties, positioning it as a sustainable alternative in the rayon market.
What is Wood Pulp Rayon?
Wood pulp rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber produced by chemically processing cellulose extracted from wood pulp, primarily sourced from softwood trees like pine and spruce. This fiber mimics the properties of cotton while offering enhanced softness, breathability, and moisture absorption, making it popular in textiles and apparel. Its production involves dissolving cellulose to create a viscous solution, which is then spun into fibers through the viscose process, distinguishing it from natural fibers and other rayon types like bamboo rayon.
What is Bamboo Rayon?
Bamboo rayon is a type of semi-synthetic fiber made by chemically processing bamboo cellulose into viscose rayon. Unlike wood pulp rayon, which is derived primarily from softwood trees like pine and spruce, bamboo rayon originates from fast-growing bamboo plants that require less water and pesticides. This fiber possesses a smooth texture, moisture-wicking properties, and biodegradability, making it popular in sustainable textile production.
Raw Material Sources: Wood Pulp vs Bamboo
Wood Pulp Rayon is primarily derived from cellulose extracted from hardwood and softwood trees such as pine, spruce, or eucalyptus, making it dependent on traditional forest resources. Bamboo Rayon is produced using cellulose from bamboo plants, which grow rapidly and require less water and pesticides compared to trees, offering a more sustainable raw material source. The difference in raw materials impacts the environmental footprint and renewability of each rayon type, with bamboo presenting a more eco-friendly alternative due to its fast growth cycle and lower resource consumption.
Manufacturing Process: Wood Pulp Rayon vs Bamboo Rayon
Wood pulp rayon is produced through a chemical-intensive process where cellulose from wood fibers undergoes purification, xanthation, and regeneration into viscose fibers, requiring significant use of carbon disulfide. Bamboo rayon involves similar chemical treatments but differs in sourcing cellulose from bamboo plants, which grow faster and require fewer pesticides, although the manufacturing process remains chemically complex and environmentally impactful. Both fibers rely on rayon production techniques that include dissolving cellulose, extrusion, and washing to create semi-synthetic textiles with distinct feedstock origins.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Comparison
Wood pulp rayon and bamboo rayon differ significantly in environmental impact due to their source materials and processing methods. Bamboo rayon utilizes bamboo, a fast-growing and renewable grass that requires minimal pesticides and water, enhancing its sustainability credentials compared to wood pulp rayon derived from timber that often involves deforestation and slower growth cycles. However, both types rely on chemical-intensive processing that can produce harmful effluents, making closed-loop manufacturing systems crucial for reducing their ecological footprint.
Fabric Properties: Texture, Strength, and Feel
Wood pulp rayon offers a smooth texture with moderate strength and a soft, breathable feel, making it ideal for lightweight garments. Bamboo rayon provides a silkier texture with enhanced durability and a naturally moisture-wicking, hypoallergenic feel, perfect for activewear and sensitive skin. Both fabrics exhibit excellent drape, but bamboo rayon tends to retain softness and strength better after multiple washes.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Wood pulp rayon typically offers lower production costs due to the widespread availability and established processing techniques of wood fibers, making it more affordable for mass-market applications. Bamboo rayon, while often promoted for its eco-friendly appeal, involves more complex extraction processes that increase manufacturing expenses, resulting in higher retail prices. Cost efficiency favors wood pulp rayon in large-scale textile production, whereas bamboo rayon's price reflects its niche market positioning and perceived sustainability benefits.
Common Uses and Applications
Wood pulp rayon is widely used in textiles for clothing, upholstery, and industrial products due to its smooth texture and durability, making it ideal for fashion and home furnishings. Bamboo rayon, valued for its natural antibacterial properties and softness, is commonly found in eco-friendly clothing, towels, and bedding, appealing to consumers seeking sustainable and comfortable materials. Both types serve in hygiene products like wipes and medical dressings, but bamboo rayon's renewable source emphasizes environmental benefits in various applications.
Which is Better: Wood Pulp Rayon or Bamboo Rayon?
Wood pulp rayon and bamboo rayon differ primarily in their source materials and environmental impact, with wood pulp rayon derived from hardwood trees and bamboo rayon sourced from fast-growing bamboo plants. Bamboo rayon is often considered more sustainable due to bamboo's rapid growth and natural pest resistance, reducing the need for harmful chemicals. However, both materials undergo similar chemical processing, which can affect their eco-friendliness and softness, making the choice dependent on specific sustainability practices and end-use requirements.
Wood Pulp Rayon vs Bamboo Rayon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com