Wet spun rayon offers a smoother texture and higher tensile strength due to its fiber formation in a coagulating bath, making it ideal for fine textiles and apparel. Dry spun rayon, produced by evaporating solvents, results in a more porous and lightweight fiber suited for breathable fabrics and summer clothing. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right rayon type for specific fabric performance and end-use applications.
Table of Comparison
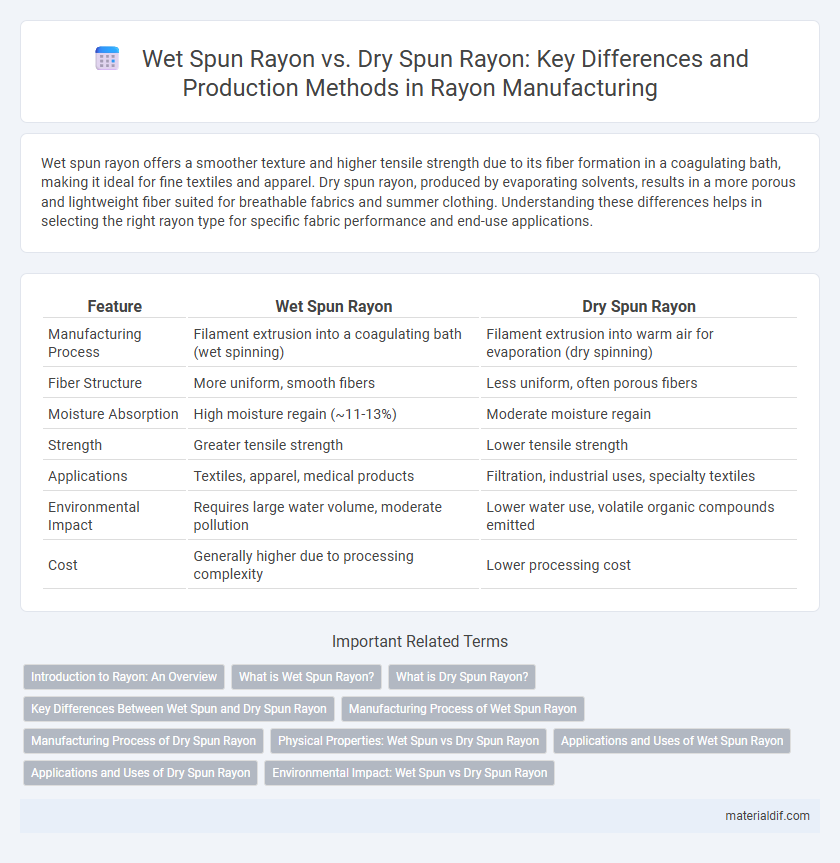
| Feature | Wet Spun Rayon | Dry Spun Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Filament extrusion into a coagulating bath (wet spinning) | Filament extrusion into warm air for evaporation (dry spinning) |
| Fiber Structure | More uniform, smooth fibers | Less uniform, often porous fibers |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture regain (~11-13%) | Moderate moisture regain |
| Strength | Greater tensile strength | Lower tensile strength |
| Applications | Textiles, apparel, medical products | Filtration, industrial uses, specialty textiles |
| Environmental Impact | Requires large water volume, moderate pollution | Lower water use, volatile organic compounds emitted |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing complexity | Lower processing cost |
Introduction to Rayon: An Overview
Wet spun rayon is produced by extruding cellulose solution into a chemical bath, resulting in fibers with higher tensile strength and smooth texture, making it ideal for textiles requiring durability and softness. Dry spun rayon involves evaporating the solvent in warm air after extrusion, yielding fibers with greater elasticity and lustrous appearance, commonly used in apparel and home furnishings. Both processes utilize regenerated cellulose, offering versatile fabric options with distinct physical properties tailored to various industrial applications.
What is Wet Spun Rayon?
Wet spun rayon is a type of regenerated cellulose fiber produced by extruding cellulose solution through fine spinnerets into a chemical bath, which solidifies the fibers through coagulation. This process imparts high moisture absorbency and a soft, smooth texture, making wet spun rayon ideal for textiles requiring breathability and comfort. The wet spinning method ensures superior fiber strength and uniformity compared to dry spun rayon, often resulting in higher quality fabric performance.
What is Dry Spun Rayon?
Dry spun rayon is a type of regenerated cellulose fiber produced through a solvent evaporation process where the cellulose solution is forced through spinnerets into warm air, causing the solvent to evaporate and fibers to solidify. This method results in fibers with smooth surfaces, high tenacity, and low elongation, making dry spun rayon suitable for durable textiles and industrial applications. Unlike wet spun rayon, dry spun fibers exhibit superior strength and elasticity due to the rapid drying and fiber formation process.
Key Differences Between Wet Spun and Dry Spun Rayon
Wet spun rayon is produced by extruding viscose through a spinneret into a chemical bath, resulting in fibers with higher strength and smoother texture, while dry spun rayon involves evaporation of solvents in hot air, leading to more breathable and elastic fibers. Wet spun fibers typically exhibit superior tensile strength and luster, making them ideal for high-quality textiles, whereas dry spun rayon offers greater flexibility and moisture absorption suited for lightweight apparel. The choice between wet spun and dry spun rayon significantly impacts fabric properties such as durability, comfort, and application in fashion and industrial uses.
Manufacturing Process of Wet Spun Rayon
Wet spun rayon is produced through a manufacturing process where cellulose cellulose solution is extruded into a chemical bath, causing the fibers to coagulate and solidify. This method allows for better control over fiber strength and uniformity, resulting in high-quality rayon with a smooth texture. The chemical coagulation step distinguishes wet spinning from dry spinning, where fibers solidify through evaporation rather than immersion.
Manufacturing Process of Dry Spun Rayon
The manufacturing process of dry spun rayon involves dissolving cellulose in a solvent to create a viscous solution, which is then extruded through spinnerets into warm air where the filaments solidify as the solvent evaporates. This method produces fibers with a smooth surface and high tensile strength, making dry spun rayon suitable for fine textiles and delicate fabrics. The controlled evaporation environment ensures uniform fiber formation and enhanced durability compared to wet spun rayon.
Physical Properties: Wet Spun vs Dry Spun Rayon
Wet spun rayon fibers exhibit higher tensile strength and greater elongation compared to dry spun rayon due to the regeneration process involving a coagulating bath, which enhances molecular alignment. Dry spun rayon tends to have a smoother surface and higher luster but is generally less resilient and more prone to shrinkage. The moisture absorption capacity of wet spun rayon is superior, making it more suitable for applications requiring breathability and comfort.
Applications and Uses of Wet Spun Rayon
Wet spun rayon is primarily used in textile applications requiring high strength and durability, such as tire cords, industrial yarns, and medical sutures. Its superior tenacity and dimensional stability make it ideal for products exposed to moisture or stress. This form of rayon also finds use in luxurious apparel and home furnishings due to its smooth texture and excellent dyeability.
Applications and Uses of Dry Spun Rayon
Dry spun rayon is primarily utilized in the production of high-strength fibers for textiles like lingerie, hosiery, and activewear due to its smooth texture and excellent durability. Its cellular structure makes it ideal for applications requiring breathability and moisture absorption, including upholstery and medical textiles. The versatility of dry spun rayon extends to industrial uses, such as tire cords and conveyor belts, benefiting from its enhanced tensile properties.
Environmental Impact: Wet Spun vs Dry Spun Rayon
Wet spun rayon production consumes significantly more water and energy compared to dry spun rayon, leading to a larger environmental footprint. Wet spun processes often involve toxic chemicals like carbon disulfide that pose risks to aquatic ecosystems during disposal. Dry spun rayon uses less harmful solvents and generates fewer emissions, making it a more sustainable choice in textile manufacturing.
Wet Spun Rayon vs Dry Spun Rayon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com