Hot spun rayon offers a denser fiber structure and increased durability compared to wet spun rayon, making it ideal for sturdy fabrics and industrial applications. Wet spun rayon, produced through a dissolving and regenerating process, results in softer, more lustrous fibers favored in apparel and luxury textiles. Selecting between hot spun and wet spun rayon depends on the desired fabric texture, strength, and end-use requirements.
Table of Comparison
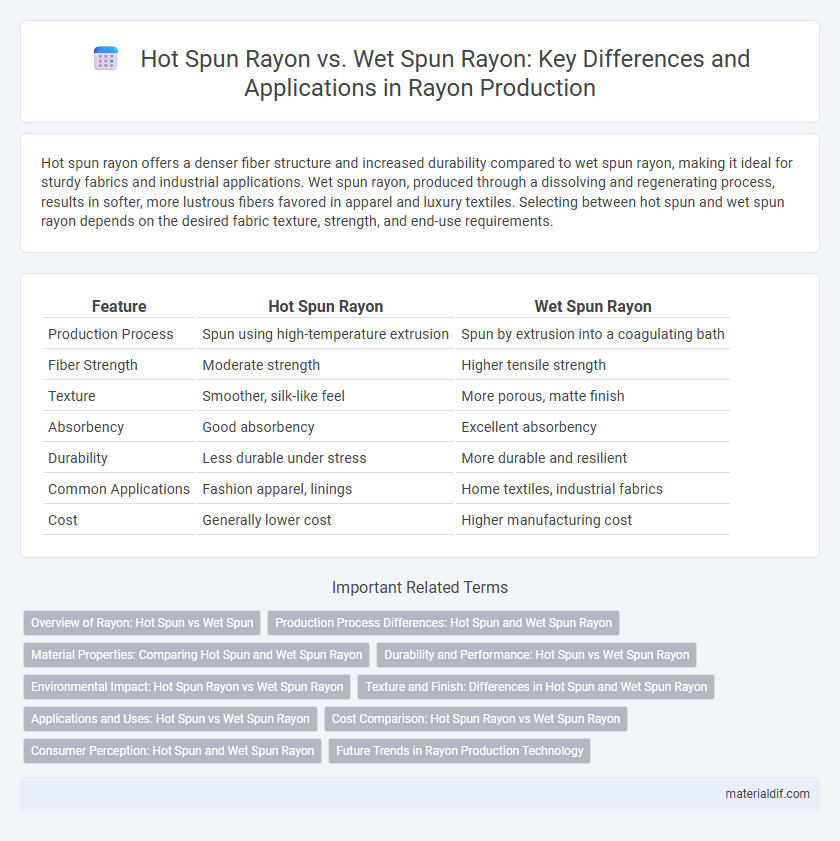
| Feature | Hot Spun Rayon | Wet Spun Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Production Process | Spun using high-temperature extrusion | Spun by extrusion into a coagulating bath |
| Fiber Strength | Moderate strength | Higher tensile strength |
| Texture | Smoother, silk-like feel | More porous, matte finish |
| Absorbency | Good absorbency | Excellent absorbency |
| Durability | Less durable under stress | More durable and resilient |
| Common Applications | Fashion apparel, linings | Home textiles, industrial fabrics |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
Overview of Rayon: Hot Spun vs Wet Spun
Hot spun rayon is produced using the dry spinning method, resulting in stronger fibers with a smoother texture ideal for textiles requiring durability. Wet spun rayon involves extruding cellulose into a chemical bath, creating fibers with higher absorbency and softness suited for clothing and upholstery. Both methods influence rayon's physical properties, impacting applications in fashion, home textiles, and industrial fabrics.
Production Process Differences: Hot Spun and Wet Spun Rayon
Hot spun rayon production involves extruding cellulose solution through heated spinnerets, allowing rapid solvent evaporation and fiber solidification, resulting in a more crystalline and stronger fiber structure. In contrast, wet spun rayon is manufactured by extruding cellulose solution into a coagulation bath, where the solvent diffuses out and the fiber solidifies slowly, producing softer and more flexible fibers with higher moisture retention. The distinct production processes for hot spun and wet spun rayon directly influence their mechanical properties and end-use applications in textiles.
Material Properties: Comparing Hot Spun and Wet Spun Rayon
Hot spun rayon exhibits higher tensile strength and improved dimensional stability compared to wet spun rayon, making it suitable for durable textile applications. Wet spun rayon, characterized by its smoother surface and higher moisture absorbency, is preferred for breathable and lightweight fabrics. Differences in crystallinity and fiber morphology between the two spinning methods directly influence their mechanical properties and end-use performance.
Durability and Performance: Hot Spun vs Wet Spun Rayon
Hot spun rayon exhibits enhanced durability due to its fiber alignment and heat setting process, resulting in improved strength and resistance to abrasion compared to wet spun rayon. Wet spun rayon, while softer and more absorbent, tends to have lower tensile strength and is more prone to pilling and wear over time. Performance-wise, hot spun rayon is better suited for applications requiring robust textiles, while wet spun rayon excels in comfort-focused, lightweight fabrics.
Environmental Impact: Hot Spun Rayon vs Wet Spun Rayon
Hot spun rayon production involves higher energy consumption due to elevated temperatures required in the drying process, leading to a larger carbon footprint compared to wet spun rayon. Wet spun rayon uses a more water-intensive process but allows for greater recovery and recycling of chemicals, reducing environmental contamination. Overall, wet spun rayon is considered more environmentally sustainable due to better chemical management despite higher water usage.
Texture and Finish: Differences in Hot Spun and Wet Spun Rayon
Hot spun rayon features a rougher texture and a matte finish due to its fiber formation process at elevated temperatures, resulting in a coarser feel suitable for durable textiles. Wet spun rayon, produced by extruding fibers into a chemical bath, offers a smoother texture and a lustrous finish, making it ideal for luxurious fabrics with a silky appearance. These differences in texture and finish directly impact the end-use applications and aesthetic qualities of rayon products.
Applications and Uses: Hot Spun vs Wet Spun Rayon
Hot spun rayon is commonly used in textile products requiring high strength and durability, such as upholstery, industrial fabrics, and heavy-duty clothing. Wet spun rayon excels in applications needing fine, soft, and breathable fabrics, including apparel, lingerie, and medical textiles. The choice between hot spun and wet spun rayon depends on the specific performance characteristics demanded by end-use applications.
Cost Comparison: Hot Spun Rayon vs Wet Spun Rayon
Hot Spun Rayon typically incurs lower production costs due to its faster spinning process and reduced water usage compared to Wet Spun Rayon. Wet Spun Rayon involves more complex processing steps and higher water consumption, leading to increased operational expenses. Manufacturers often choose Hot Spun Rayon when prioritizing cost efficiency without compromising fiber quality.
Consumer Perception: Hot Spun and Wet Spun Rayon
Consumers perceive hot spun rayon as more affordable and less refined due to its coarser texture and greater variability in fiber quality. Wet spun rayon is favored for its superior softness, durability, and vibrant dye uptake, leading to a higher-end appeal in textiles. Market trends show preference for wet spun rayon in premium apparel, while hot spun rayon is commonly used in budget-friendly, everyday garments.
Future Trends in Rayon Production Technology
Hot spun rayon, produced through high-temperature extrusion, offers faster production rates and improved fiber uniformity, while wet spun rayon involves dissolving cellulose in a chemical solution for finer and stronger fibers. Future trends in rayon production technology focus on eco-friendly processes such as solvent recovery systems, bio-based solvents, and energy-efficient spinning methods to reduce environmental impact. Innovations in nanotechnology and enzymatic treatments aim to enhance fiber properties and sustainability, positioning rayon as a competitive alternative in the textile industry.
Hot Spun Rayon vs Wet Spun Rayon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com