Rayon staple fibers are short fibers typically cut to specific lengths, producing soft, breathable fabrics ideal for clothing and upholstery. Rayon filament fibers consist of continuous, long strands that create smoother, stronger, and more lustrous textiles often used in high-quality garments and home furnishings. Choosing between rayon staple and filament depends on the desired texture, durability, and finish for the final product.
Table of Comparison
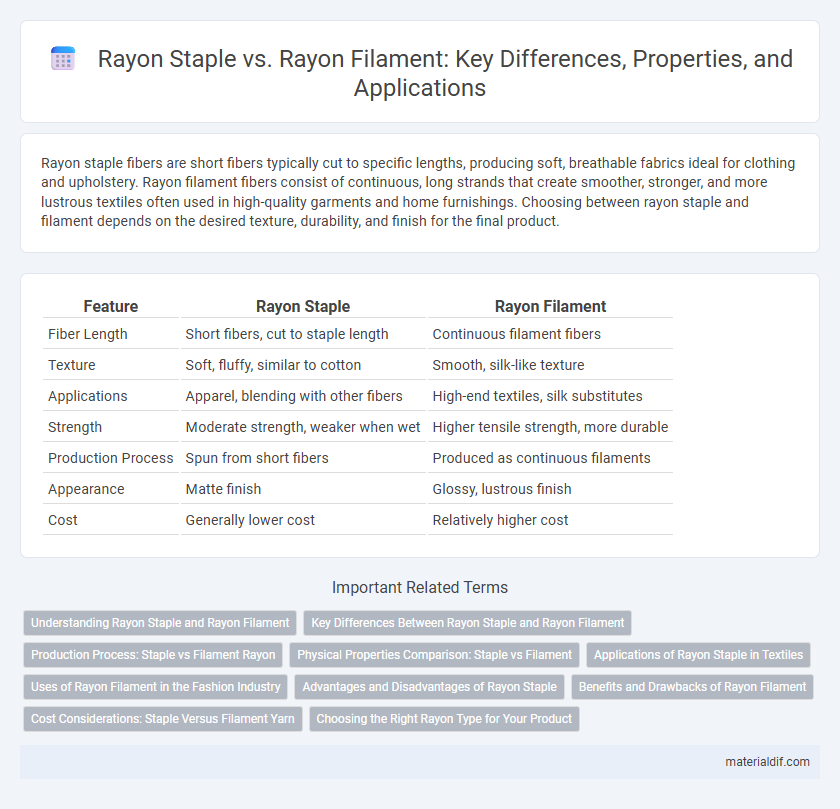
| Feature | Rayon Staple | Rayon Filament |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Length | Short fibers, cut to staple length | Continuous filament fibers |
| Texture | Soft, fluffy, similar to cotton | Smooth, silk-like texture |
| Applications | Apparel, blending with other fibers | High-end textiles, silk substitutes |
| Strength | Moderate strength, weaker when wet | Higher tensile strength, more durable |
| Production Process | Spun from short fibers | Produced as continuous filaments |
| Appearance | Matte finish | Glossy, lustrous finish |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Relatively higher cost |
Understanding Rayon Staple and Rayon Filament
Rayon staple consists of short fibers typically cut to a uniform length, offering a soft texture and high absorbency suitable for blending with other fibers in textiles. Rayon filament features continuous, long fibers that provide a smooth, lustrous appearance and enhanced strength, making them ideal for producing silky fabrics. Understanding the distinction between rayon staple and filament is crucial for selecting the appropriate fiber type in textile manufacturing based on desired fabric characteristics.
Key Differences Between Rayon Staple and Rayon Filament
Rayon staple fibers are short-length fibers typically measured in inches, offering a soft, breathable texture often used in apparel and home textiles. Rayon filament fibers are continuous long strands that provide a smooth, lustrous finish ideal for high-quality textiles and industrial applications. The key differences include fiber length, texture, production process, and resulting fabric qualities, with staple fibers favoring bulk and comfort, while filament fibers emphasize strength and sheen.
Production Process: Staple vs Filament Rayon
Rayon staple fibers are produced by mechanically cutting regenerated cellulose fibers into short lengths, creating a staple form similar to natural fibers like cotton or wool. In contrast, rayon filament fibers are manufactured as continuous, long filaments through a steady extrusion process of the cellulose solution, resulting in smooth and uniform threads. The staple rayon production involves spinning, cutting, and carding, whereas filament rayon relies on a controlled spinning process to maintain fiber continuity and strength.
Physical Properties Comparison: Staple vs Filament
Rayon staple fibers are short and cut into lengths similar to natural fibers, offering a soft texture and higher breathability, while rayon filament fibers are continuous, resulting in a smoother surface and stronger tensile strength. Staple rayon tends to have a matte finish and greater moisture absorption, making it suitable for casual wear, whereas filament rayon boasts a lustrous appearance and better resistance to wrinkling, ideal for formal garments. The physical properties of rayon fiber types directly influence the fabric's durability, drape, and comfort, with staple fibers providing warmth and filament fibers enhancing sheen and smoothness.
Applications of Rayon Staple in Textiles
Rayon staple fibers are widely used in textile applications such as clothing, home furnishings, and upholstery due to their excellent dye affinity, softness, and breathability. Unlike rayon filament, staple fibers blend easily with natural fibers like cotton or wool, enhancing fabric durability and comfort in products like shirts, dresses, and bed linens. Their shorter fiber length also facilitates diverse textile manufacturing processes, enabling versatile fabric textures and finishes.
Uses of Rayon Filament in the Fashion Industry
Rayon Filament is highly favored in the fashion industry for its smooth texture, lustrous appearance, and excellent draping qualities, making it ideal for high-end garments such as evening wear, blouses, and linings. Its continuous filament fibers provide strength and durability, which enhances the longevity of delicate fashion pieces. The fiber's versatility allows designers to create luxurious fabrics that mimic silk while remaining more affordable and sustainable.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rayon Staple
Rayon staple fibers offer advantages such as enhanced texture variety and better moisture absorption compared to rayon filament, making them ideal for soft, breathable fabrics. However, staple fibers tend to have lower tensile strength and higher lint production, which can affect fabric durability and require more maintenance. The shorter fiber length also limits their smoothness and sheen compared to the continuous filament form.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Rayon Filament
Rayon filament fibers offer enhanced strength and a smoother texture compared to staple fibers, resulting in fabrics with a lustrous appearance and improved durability. However, rayon filament production is more complex and costly, which can limit its widespread use in everyday apparel. Despite higher expenses, its resistance to pilling and excellent drape make rayon filament ideal for high-end garments and textiles requiring a silk-like finish.
Cost Considerations: Staple Versus Filament Yarn
Rayon staple yarn generally incurs higher production costs due to the additional processing required to cut and spin short fibers, whereas rayon filament yarn benefits from a continuous filament process that reduces manufacturing expenses. Staple yarns often demand more machinery and labor, increasing overall costs compared to filament yarns, which are produced in a streamlined, automated manner. The choice between rayon staple and filament yarns largely depends on budget constraints and the desired end-product characteristics, balancing cost with fabric texture and strength.
Choosing the Right Rayon Type for Your Product
Rayon staple fibers, known for their short, fluffy texture, provide excellent breathability and softness, making them ideal for casual apparel and home textiles where comfort is key. Rayon filament fibers, longer and smoother, offer a lustrous finish and superior strength, preferred for high-end fashion and luxury fabrics requiring durability and sheen. Selecting between rayon staple and filament depends on the desired fabric characteristics--opt for staple for softness and absorbency, or filament for smoothness and strength.
Rayon Staple vs Rayon Filament Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com