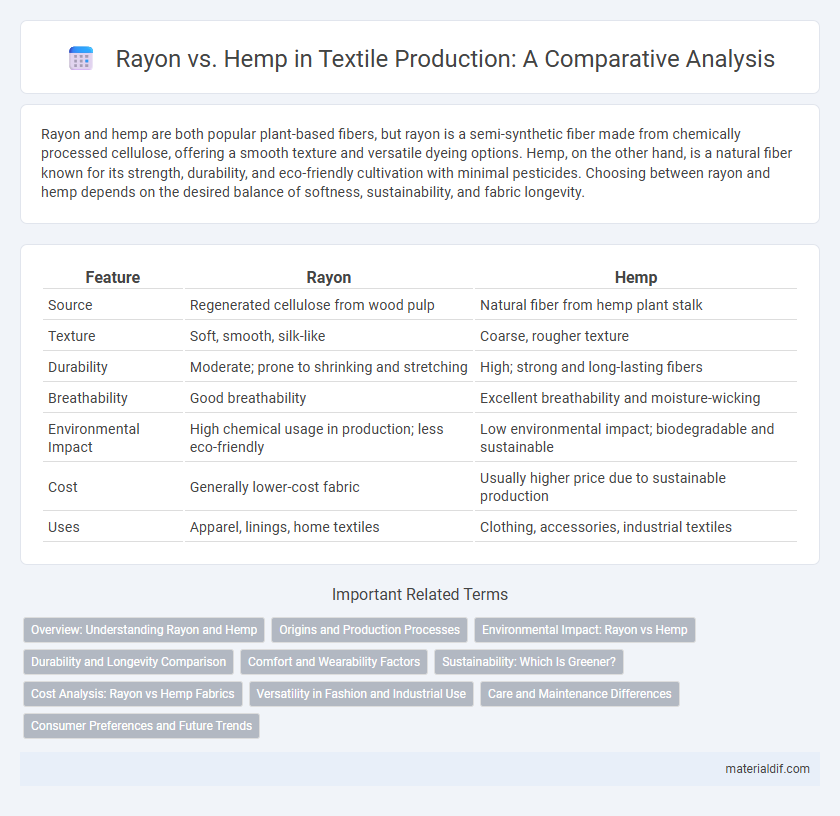
Rayon and hemp are both popular plant-based fibers, but rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber made from chemically processed cellulose, offering a smooth texture and versatile dyeing options. Hemp, on the other hand, is a natural fiber known for its strength, durability, and eco-friendly cultivation with minimal pesticides. Choosing between rayon and hemp depends on the desired balance of softness, sustainability, and fabric longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rayon | Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Regenerated cellulose from wood pulp | Natural fiber from hemp plant stalk |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silk-like | Coarse, rougher texture |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to shrinking and stretching | High; strong and long-lasting fibers |
| Breathability | Good breathability | Excellent breathability and moisture-wicking |
| Environmental Impact | High chemical usage in production; less eco-friendly | Low environmental impact; biodegradable and sustainable |
| Cost | Generally lower-cost fabric | Usually higher price due to sustainable production |
| Uses | Apparel, linings, home textiles | Clothing, accessories, industrial textiles |
Overview: Understanding Rayon and Hemp
Rayon, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from regenerated cellulose, offers a smooth, silk-like texture that enhances comfort and drape in textiles. Hemp, a natural bast fiber from the Cannabis sativa plant, is known for its durability, breathability, and eco-friendly cultivation requiring minimal pesticides or water. While rayon provides softness and flexibility ideal for fashion apparel, hemp excels in strength and sustainability, making it suitable for heavy-duty fabrics and environmentally-conscious consumers.
Origins and Production Processes
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber made from regenerated cellulose typically sourced from wood pulp, primarily derived from trees like beech, pine, and eucalyptus. Hemp is a natural fiber obtained from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, harvested and processed through retting to separate the fibers. The production of rayon involves chemical treatments such as alkali and carbon disulfide, while hemp fibers undergo mechanical and biological processing with minimal chemical intervention.
Environmental Impact: Rayon vs Hemp
Rayon production relies heavily on chemical processing and intensive water use, leading to significant pollution and deforestation concerns, while hemp cultivation requires fewer pesticides, less water, and supports soil health. Hemp fibers are biodegradable and promote carbon sequestration during growth, making hemp a more sustainable option compared to the environmentally taxing rayon manufacturing process. Choosing hemp over rayon helps reduce environmental impact by minimizing chemical waste and conserving natural resources.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Rayon fibers exhibit moderate durability but tend to weaken when repeatedly exposed to moisture, limiting their longevity compared to hemp. Hemp fibers are known for exceptional strength and resistance to wear, resulting in superior durability and a longer lifespan in textiles. This makes hemp fabrics ideal for heavy-duty applications and garments requiring extended use.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Rayon offers superior softness and breathability compared to hemp, making it more comfortable for prolonged wear, especially in warm climates. Hemp fibers, while durable and moisture-wicking, tend to be coarser, which may cause slight abrasion against sensitive skin. The smooth texture and lightweight nature of rayon enhance its wearability, contributing to its popularity in fashion and casual clothing.
Sustainability: Which Is Greener?
Hemp outperforms rayon in sustainability due to its low water usage, rapid growth cycle, and minimal need for pesticides, making it an eco-friendly fiber source. In contrast, traditional rayon production relies heavily on chemically intensive processes and large water consumption, raising environmental concerns. Innovations in closed-loop rayon manufacturing are improving its ecological footprint, but hemp remains the greener choice for sustainable textiles.
Cost Analysis: Rayon vs Hemp Fabrics
Rayon fabric typically costs less than hemp due to its synthetic production process, which allows for large-scale manufacturing and consistent quality. Hemp, while more expensive, offers durability and sustainability benefits that may offset higher initial expenses in long-term use. Cost analysis reveals rayon's advantage in affordability, but hemp's eco-friendly cultivation and longevity appeal to premium market segments.
Versatility in Fashion and Industrial Use
Rayon offers superior versatility in fashion due to its smooth texture, vibrant dye absorption, and ability to mimic natural fibers like silk, cotton, and wool, making it ideal for a broad range of clothing styles. In industrial use, rayon's strength and absorbency enable applications such as tire cords, wipes, and medical dressings, surpassing hemp's more limited fiber properties. Hemp excels in durability and eco-friendliness but lacks the softness and flexibility that make rayon favored for diverse textiles and specialized industrial products.
Care and Maintenance Differences
Rayon requires gentle washing with mild detergents and air drying to prevent shrinking and loss of softness, while hemp is more durable, tolerating machine washing and higher heat drying without significant damage. Rayon fabrics easily wrinkle and may need low-heat ironing, whereas hemp resists wrinkles and can withstand higher ironing temperatures. Proper care extends the lifespan of rayon, which is more delicate, compared to the naturally robust hemp fibers that demand less maintenance.
Consumer Preferences and Future Trends
Consumers increasingly favor hemp over rayon due to its natural, eco-friendly qualities and durability, aligning with growing sustainability concerns in the textile industry. Hemp's biodegradability and minimal chemical processing enhance its appeal compared to the synthetic nature of rayon, which involves intensive use of chemicals like carbon disulfide. Future trends indicate a shift towards hemp as demand rises for organic, sustainable fabrics that support environmental health and ethical production standards.
Rayon vs Hemp Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com