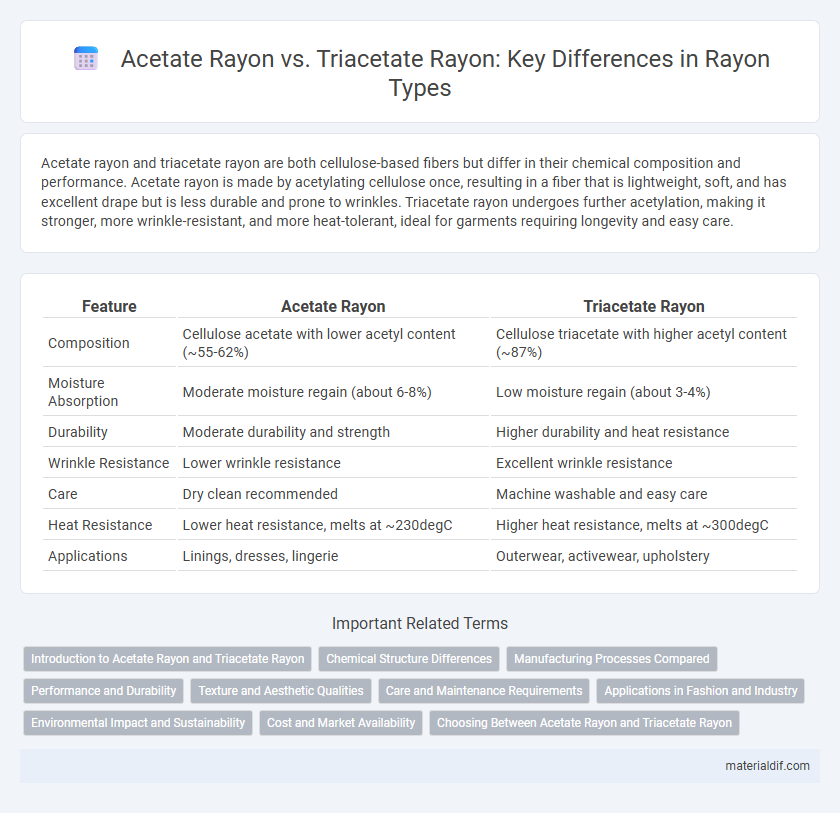
Acetate rayon and triacetate rayon are both cellulose-based fibers but differ in their chemical composition and performance. Acetate rayon is made by acetylating cellulose once, resulting in a fiber that is lightweight, soft, and has excellent drape but is less durable and prone to wrinkles. Triacetate rayon undergoes further acetylation, making it stronger, more wrinkle-resistant, and more heat-tolerant, ideal for garments requiring longevity and easy care.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acetate Rayon | Triacetate Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Cellulose acetate with lower acetyl content (~55-62%) | Cellulose triacetate with higher acetyl content (~87%) |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate moisture regain (about 6-8%) | Low moisture regain (about 3-4%) |
| Durability | Moderate durability and strength | Higher durability and heat resistance |
| Wrinkle Resistance | Lower wrinkle resistance | Excellent wrinkle resistance |
| Care | Dry clean recommended | Machine washable and easy care |
| Heat Resistance | Lower heat resistance, melts at ~230degC | Higher heat resistance, melts at ~300degC |
| Applications | Linings, dresses, lingerie | Outerwear, activewear, upholstery |
Introduction to Acetate Rayon and Triacetate Rayon
Acetate rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber made from cellulose acetate, known for its luxurious silk-like appearance and smooth texture, commonly used in linings, dresses, and upholstery. Triacetate rayon, derived from cellulose triacetate, offers enhanced wrinkle resistance, dimensional stability, and better heat tolerance compared to acetate rayon, making it suitable for activewear and high-performance garments. Both fibers are valued for their breathability and ability to mimic natural fibers while offering distinct benefits in durability and care.
Chemical Structure Differences
Acetate rayon consists of cellulose fibers chemically treated with acetic acid forming cellulose acetate with a degree of substitution typically around 2.5, creating fewer acetate groups per glucose unit. Triacetate rayon undergoes a higher acetylation process, resulting in cellulose triacetate with nearly complete substitution where all three hydroxyl groups of each glucose unit are acetylated. This chemical structure difference leads to triacetate rayon exhibiting greater resistance to moisture and heat compared to acetate rayon, impacting its durability and maintenance properties.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Acetate rayon manufacturing involves partial cellulose acetylation, dissolving cellulose acetate in a solvent before fiber extrusion, resulting in fibers with moderate moisture absorption and dye affinity. Triacetate rayon production entails a higher degree of acetylation of cellulose, necessitating additional chemical treatment steps and precise temperature control during fiber spinning to achieve enhanced dimensional stability and wrinkle resistance. The differences in acetylation levels and solvent systems create distinct processing requirements, impacting fiber properties and end-use applications.
Performance and Durability
Acetate rayon offers moderate durability with a smooth texture and good moisture absorption, making it suitable for lightweight garments but prone to damage from heat and chemicals. Triacetate rayon enhances performance significantly by providing greater wrinkle resistance, improved dimensional stability, and superior durability under high-temperature conditions. This makes triacetate more suitable for long-lasting apparel and textiles requiring frequent cleaning and exposure to harsher environments.
Texture and Aesthetic Qualities
Acetate rayon offers a smooth, glossy texture with a silky feel that enhances its luxurious aesthetic, making it ideal for drapey garments and elegant linings. Triacetate rayon, on the other hand, provides a slightly stiffer texture with greater wrinkle resistance and a subtle sheen, contributing to a crisp and refined appearance suitable for structured apparel. Both fibers exhibit excellent dye affinity, but triacetate tends to maintain color vibrancy longer due to its enhanced fabric stability.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Acetate rayon requires gentle hand washing or dry cleaning to prevent damage and shrinkage, as it is sensitive to heat and moisture. Triacetate rayon is more durable and wrinkle-resistant, allowing for machine washing on a gentle cycle with cold water and low heat drying. Both fibers benefit from low-heat ironing and avoiding exposure to high heat to maintain fabric integrity and appearance.
Applications in Fashion and Industry
Acetate rayon, known for its crisp texture and vibrant dye affinity, is widely used in fashion for linings, dresses, and blouses due to its smooth finish and breathability. Triacetate rayon, with enhanced wrinkle resistance and durability, is favored in both fashion and industrial applications such as uniforms, outerwear, and home furnishings. The choice between acetate and triacetate rayon depends on desired fabric performance, with triacetate providing superior longevity and shape retention for high-wear uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acetate rayon and triacetate rayon differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability due to their chemical composition and production processes. Acetate rayon, made with fewer acetyl groups, tends to biodegrade more readily, reducing long-term environmental burden, whereas triacetate rayon contains a higher degree of acetylation, making it less biodegradable and more resistant to microbial breakdown. The sustainability of acetate rayon is generally favored as it requires less energy-intensive processing and generates fewer harmful byproducts compared to triacetate rayon, which involves more complex acetylation reactions and often relies on synthetic additives.
Cost and Market Availability
Acetate rayon is generally more affordable and widely available in the market due to its simpler production process and established manufacturing infrastructure. Triacetate rayon, being chemically modified for enhanced durability and wrinkle resistance, tends to have a higher cost and is less commonly found in retail outlets. Market demand for acetate rayon remains stronger, driving larger-scale production and lower prices compared to its triacetate counterpart.
Choosing Between Acetate Rayon and Triacetate Rayon
Acetate rayon offers a soft, silky texture with good drape but tends to wrinkle easily and has lower heat resistance, making it ideal for delicate garments and linings. Triacetate rayon provides enhanced durability, better wrinkle recovery, and superior heat resistance due to its triple acetylated fibers, suitable for pleated skirts and suits requiring long-lasting shape retention. When choosing between acetate and triacetate rayon, consider the garment's functional needs, durability expectations, and maintenance preferences to ensure optimal fabric performance.
Acetate rayon vs Triacetate rayon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com