Bamboo rayon is made from bamboo pulp, offering a more sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional rayon that primarily uses wood pulp from trees. Bamboo rayon tends to be softer and more breathable, making it ideal for comfortable clothing and textiles, whereas traditional rayon can sometimes feel heavier and less moisture-wicking. Both types undergo similar chemical processing, but bamboo rayon's renewable source contributes to reduced environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
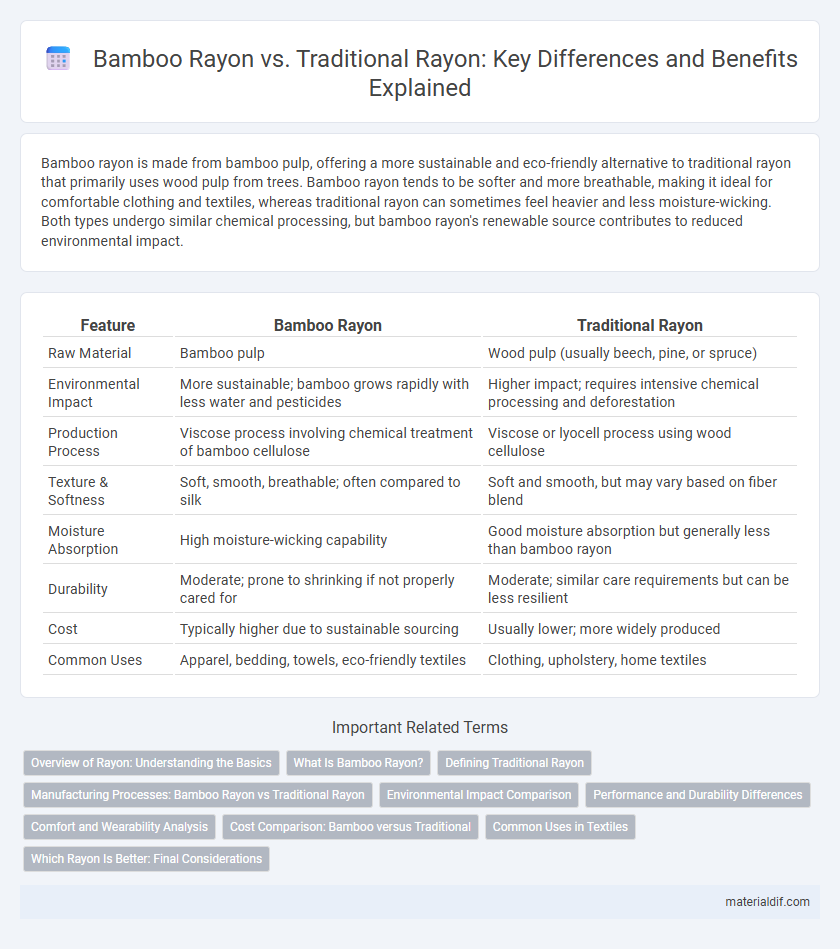
| Feature | Bamboo Rayon | Traditional Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Bamboo pulp | Wood pulp (usually beech, pine, or spruce) |
| Environmental Impact | More sustainable; bamboo grows rapidly with less water and pesticides | Higher impact; requires intensive chemical processing and deforestation |
| Production Process | Viscose process involving chemical treatment of bamboo cellulose | Viscose or lyocell process using wood cellulose |
| Texture & Softness | Soft, smooth, breathable; often compared to silk | Soft and smooth, but may vary based on fiber blend |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture-wicking capability | Good moisture absorption but generally less than bamboo rayon |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to shrinking if not properly cared for | Moderate; similar care requirements but can be less resilient |
| Cost | Typically higher due to sustainable sourcing | Usually lower; more widely produced |
| Common Uses | Apparel, bedding, towels, eco-friendly textiles | Clothing, upholstery, home textiles |
Overview of Rayon: Understanding the Basics
Rayon is a versatile semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, primarily used in textiles for its silk-like feel and breathability. Bamboo rayon, a subtype of rayon, is produced by chemically processing bamboo pulp, offering enhanced sustainability due to bamboo's rapid growth and minimal pesticide requirements compared to wood pulp used in traditional rayon. Both bamboo rayon and traditional rayon share similar softness and moisture absorption properties, but bamboo rayon stands out for its eco-friendly cultivation and potential antimicrobial benefits.
What Is Bamboo Rayon?
Bamboo rayon is a type of regenerated cellulose fiber made from bamboo pulp through a chemical process involving sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide, resulting in a soft, breathable fabric similar to traditional rayon. Unlike traditional rayon, typically derived from wood pulp such as beech or eucalyptus, bamboo rayon emphasizes sustainability due to bamboo's rapid growth and low pesticide requirements. Its unique production method offers eco-friendly advantages while maintaining the comfort and versatility associated with conventional rayon textiles.
Defining Traditional Rayon
Traditional Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber made from regenerated cellulose derived primarily from wood pulp, typically using the viscose process. This process involves chemically treating cellulose with sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide to create a soluble compound that can be spun into fibers. Unlike bamboo rayon, traditional rayon does not specifically utilize bamboo as its raw material and often involves more intensive chemical processing.
Manufacturing Processes: Bamboo Rayon vs Traditional Rayon
Bamboo rayon is produced by chemically treating bamboo cellulose through processes like the viscose method, similar to traditional rayon, but it begins with bamboo fibers that have a higher natural cellulose content. Traditional rayon often uses wood pulp or cotton linters as the raw material, requiring extensive purification and bleaching stages. Although both manufacturing processes share core steps such as cellulose extraction, alkalization, and spinning, bamboo rayon is praised for its eco-friendlier raw source and potentially lower chemical waste generation.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bamboo rayon is often marketed as a more sustainable alternative to traditional rayon due to bamboo's rapid growth and minimal land requirements, but the chemical-intensive process to convert bamboo fibers into rayon can contribute to water pollution and toxic waste. Traditional rayon, typically derived from wood pulp from trees like beech or pine, involves similarly harmful chemical processing, causing deforestation and environmental degradation if not sourced from sustainably managed forests. Both bamboo rayon and traditional rayon have significant environmental footprints, making the adoption of closed-loop production and eco-friendly chemicals critical for reducing their overall environmental impact.
Performance and Durability Differences
Bamboo rayon exhibits higher moisture-wicking capabilities and superior breathability compared to traditional rayon, enhancing comfort in active wear and hot climates. Its fiber structure contributes to improved tensile strength and resistance to pilling, resulting in better durability during repeated washing and extended use. In contrast, traditional rayon tends to weaken faster and shows more signs of wear, making bamboo rayon a preferred choice for performance-oriented textiles.
Comfort and Wearability Analysis
Bamboo rayon fibers exhibit superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional rayon, enhancing comfort during prolonged wear. The natural antibacterial qualities of bamboo rayon reduce odor, making it more suitable for active or sensitive skin. Furthermore, the fabric's softness and flexibility contribute to better wearability, minimizing irritation and increasing overall garment longevity.
Cost Comparison: Bamboo versus Traditional
Bamboo rayon generally incurs higher production costs than traditional rayon due to the more complex and eco-friendly extraction processes required for bamboo fibers. Traditional rayon, derived primarily from wood pulp, benefits from established large-scale manufacturing techniques that reduce expenses and improve efficiency. Despite its higher initial cost, bamboo rayon offers sustainability advantages that can offset long-term environmental costs compared to conventional rayon production.
Common Uses in Textiles
Bamboo rayon is widely used in textiles for its softness, breathability, and eco-friendly attributes, making it ideal for activewear, underwear, and baby clothing. Traditional rayon, derived from wood pulp, is commonly utilized in apparel such as dresses, linings, and blouses due to its smooth texture and excellent dye retention. Both fibers serve distinct purposes in textile manufacturing, with bamboo rayon favored for comfort and sustainability, while traditional rayon is valued for versatility and affordability.
Which Rayon Is Better: Final Considerations
Bamboo rayon offers superior sustainability benefits compared to traditional rayon, as it is derived from a rapidly renewable resource with less environmental impact during cultivation. Traditional rayon, often produced from wood pulp, typically involves more chemical-intensive processes that contribute to higher ecological footprints. Choosing bamboo rayon supports eco-friendly fashion initiatives while maintaining the same softness and durability found in conventional rayon fabrics.
Bamboo Rayon vs Traditional Rayon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com