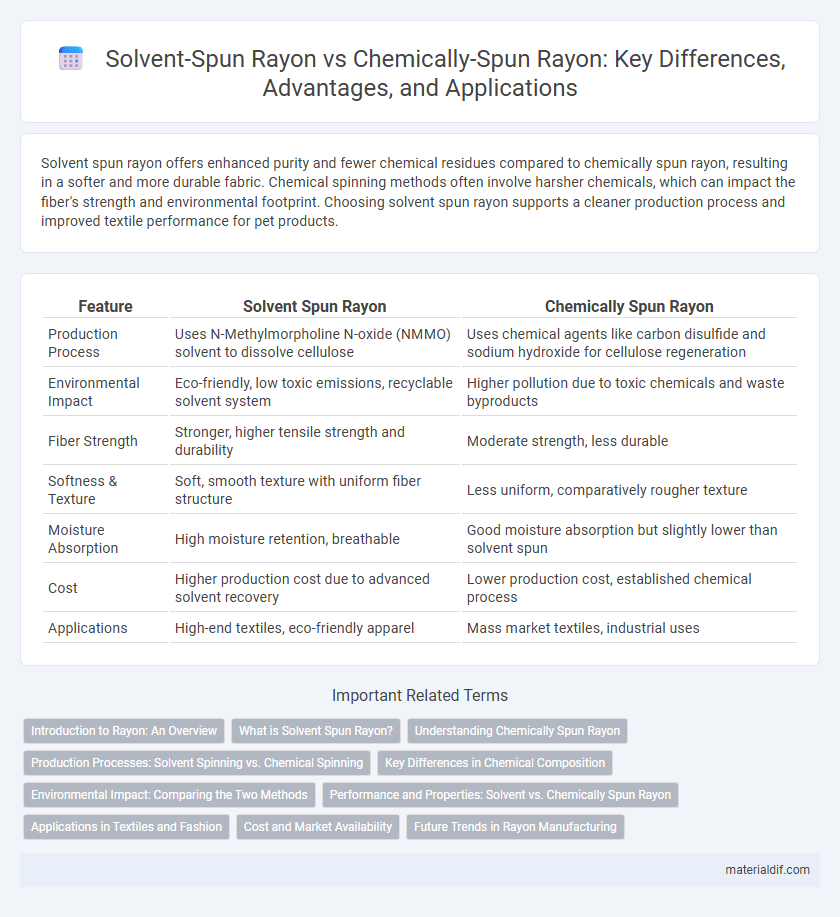
Solvent spun rayon offers enhanced purity and fewer chemical residues compared to chemically spun rayon, resulting in a softer and more durable fabric. Chemical spinning methods often involve harsher chemicals, which can impact the fiber's strength and environmental footprint. Choosing solvent spun rayon supports a cleaner production process and improved textile performance for pet products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solvent Spun Rayon | Chemically Spun Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Production Process | Uses N-Methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) solvent to dissolve cellulose | Uses chemical agents like carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide for cellulose regeneration |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, low toxic emissions, recyclable solvent system | Higher pollution due to toxic chemicals and waste byproducts |
| Fiber Strength | Stronger, higher tensile strength and durability | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Softness & Texture | Soft, smooth texture with uniform fiber structure | Less uniform, comparatively rougher texture |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture retention, breathable | Good moisture absorption but slightly lower than solvent spun |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to advanced solvent recovery | Lower production cost, established chemical process |
| Applications | High-end textiles, eco-friendly apparel | Mass market textiles, industrial uses |
Introduction to Rayon: An Overview
Solvent spun rayon is produced using a cleaner, eco-friendly process that dissolves cellulose without harmful chemicals, enhancing fiber strength and softness. Chemically spun rayon involves chemical treatments like the viscose method, which uses carbon disulfide and other pollutants, often resulting in environmental concerns. Both types of rayon originate from regenerated cellulose, with key differences in processing impacting sustainability and fiber quality.
What is Solvent Spun Rayon?
Solvent Spun Rayon is produced by dissolving cellulose in a non-toxic solvent to create a fiber through a closed-loop process, emphasizing environmental sustainability and reduced chemical waste. This method contrasts with Chemically Spun Rayon, which uses harsh chemicals like carbon disulfide and sulfuric acid, leading to greater environmental and health concerns. Solvent Spun Rayon offers enhanced quality, strength, and eco-friendly characteristics, making it a preferred choice for sustainable textile manufacturing.
Understanding Chemically Spun Rayon
Chemically spun rayon is produced through a wet-spinning process where cellulose is dissolved in chemicals like carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide before extrusion. This method allows for better control over fiber thickness, strength, and uniformity compared to solvent spinning. The resulting fibers exhibit high absorbency, softness, and a smooth texture, making chemically spun rayon ideal for textile applications demanding comfort and durability.
Production Processes: Solvent Spinning vs. Chemical Spinning
Solvent spun rayon production involves dissolving cellulose in a non-toxic solvent, followed by extrusion through spinnerets to form fibers with less environmental impact. Chemical spinning, or viscose process, uses hazardous chemicals such as carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide, which pose health and ecological risks during cellulose regeneration and fiber formation. The solvent spinning method offers a cleaner, more sustainable alternative by minimizing harmful chemical usage compared to traditional chemical spinning processes.
Key Differences in Chemical Composition
Solvent spun rayon utilizes cellulose dissolved in a non-toxic solvent, primarily amine oxide, resulting in fewer chemical residues and a more environmentally friendly process. Chemically spun rayon involves aggressive chemicals like carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide, contributing to higher toxicity and environmental concerns. The chemical composition difference directly affects the biodegradability, fiber strength, and softness, making solvent spun rayon a preferable option for sustainable textile production.
Environmental Impact: Comparing the Two Methods
Solvent spun rayon utilizes environmentally friendly solvents that are often recycled during production, significantly reducing chemical emissions and water pollution compared to chemically spun rayon, which relies on harsh chemicals like carbon disulfide that pose toxicity risks and generate hazardous waste. The closed-loop processes in solvent spun rayon minimize air and water contaminants, enhancing sustainability and lowering the overall carbon footprint. Chemically spun rayon methods typically require more energy and generate greater environmental burdens due to chemical disposal challenges and increased water consumption.
Performance and Properties: Solvent vs. Chemically Spun Rayon
Solvent spun rayon typically demonstrates superior tensile strength and uniform fiber morphology compared to chemically spun rayon, resulting in enhanced durability and consistent fabric texture. Chemically spun rayon often exhibits higher variability in fiber diameter and lower thermal stability due to residual chemicals, which can affect its performance under stress and heat exposure. The solvent spinning process produces rayon with better moisture absorption and dye uptake qualities, making it favorable for high-performance textile applications.
Applications in Textiles and Fashion
Solvent spun rayon, produced through a closed-loop process using NMMO solvent, offers superior fiber strength and eco-friendly attributes, making it ideal for high-end fashion and sustainable textile applications. Chemically spun rayon, typically derived from viscose production involving carbon disulfide, is widely used in mass-market apparel and home textiles due to cost efficiency and versatility. Both fiber types support diverse fabric textures and drapes, with solvent spun rayon gaining preference in eco-conscious fashion brands.
Cost and Market Availability
Solvent spun rayon is generally more expensive due to its environmentally friendly production process and the use of safer solvents, which limit its large-scale market availability. Chemically spun rayon, produced via the viscose method, offers lower costs and wider market penetration but involves toxic chemicals and greater environmental concerns. Cost-efficiency and mass production capabilities make chemically spun rayon dominant in the textile industry, while solvent spun rayon occupies a niche market focused on sustainable practices.
Future Trends in Rayon Manufacturing
Future trends in rayon manufacturing emphasize sustainable processes, with solvent spun rayon gaining traction due to its eco-friendly closed-loop production that minimizes chemical waste. Chemically spun rayon, while traditionally dominant, faces challenges from environmental regulations and consumer demand for greener textiles. Innovations in solvent spinning techniques promise enhanced fiber quality and reduced carbon footprint, positioning it as the preferred method for next-generation rayon production.
Solvent Spun Rayon vs Chemically Spun Rayon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com