Rayon and bamboo both come from natural cellulose fibers, but rayon is chemically processed, often using harsh chemicals that impact its sustainability. Bamboo fibers are more eco-friendly when mechanically processed, preserving the plant's natural properties and reducing environmental harm. Choosing bamboo over rayon supports a greener option with softer, breathable fabric ideal for pet products.
Table of Comparison
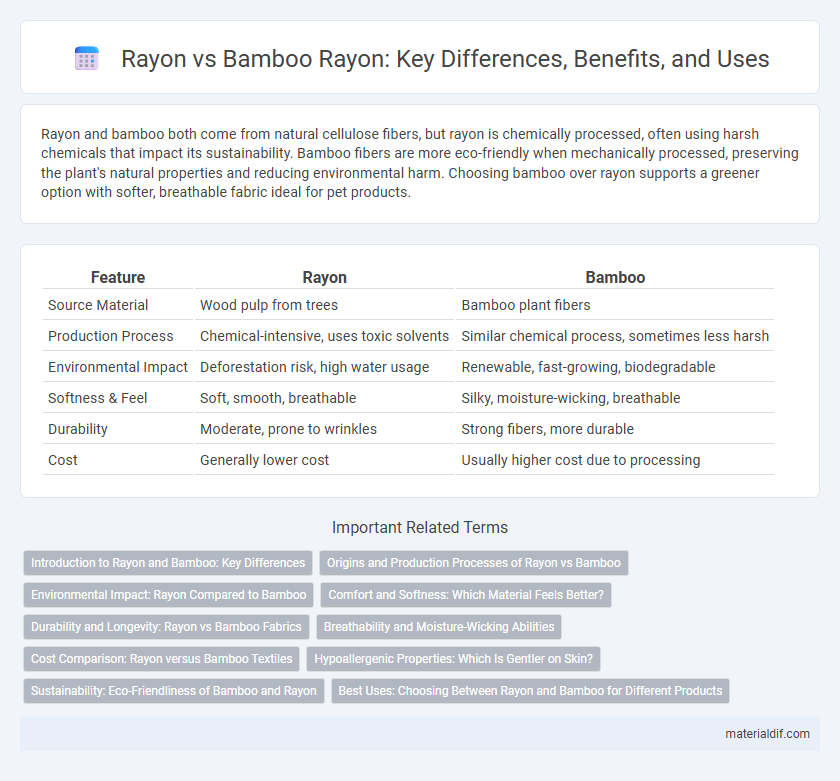
| Feature | Rayon | Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Wood pulp from trees | Bamboo plant fibers |
| Production Process | Chemical-intensive, uses toxic solvents | Similar chemical process, sometimes less harsh |
| Environmental Impact | Deforestation risk, high water usage | Renewable, fast-growing, biodegradable |
| Softness & Feel | Soft, smooth, breathable | Silky, moisture-wicking, breathable |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wrinkles | Strong fibers, more durable |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Usually higher cost due to processing |
Introduction to Rayon and Bamboo: Key Differences
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber made from regenerated cellulose, commonly derived from wood pulp, while bamboo fabric originates from bamboo plants processed into viscose or lyocell fibers. Rayon tends to have a softer texture and higher breathability, whereas bamboo fabric offers natural antibacterial properties and greater environmental sustainability. Both fibers differ significantly in production methods and eco-impact, influencing their usage in textiles and fashion industries.
Origins and Production Processes of Rayon vs Bamboo
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber derived primarily from cellulose extracted from wood pulp, most commonly sourced from hardwood trees like beech, pine, or eucalyptus. Bamboo fiber, often marketed as eco-friendly, is typically processed into viscose rayon through chemically intensive methods involving sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide, which are similar to traditional rayon production techniques. The environmental impact of bamboo rayon depends heavily on the extent of chemical treatment and the sustainability of bamboo cultivation, contrasting with primarily wood-based rayon whose production also varies by raw material sourcing and processing technology.
Environmental Impact: Rayon Compared to Bamboo
Rayon production involves significant chemical processing and considerable water and energy consumption, resulting in higher environmental pollution compared to bamboo. Bamboo, a fast-growing and renewable resource, generally requires fewer chemicals and less water during its cultivation and processing when manufactured sustainably. However, bamboo-based rayon can still pose environmental risks if not produced under eco-friendly practices, making certified methods crucial for reducing the overall ecological footprint.
Comfort and Softness: Which Material Feels Better?
Rayon offers a smooth and breathable texture that drapes well on the skin, providing superior comfort compared to bamboo fabric, which can sometimes feel coarser due to its natural cellulose structure. Bamboo fabric, while eco-friendly, often requires chemical processing that affects its softness and durability, making rayon a preferred choice for garments requiring a softer feel. Consumers seeking ultimate softness often favor rayon because of its silky touch and ability to maintain comfort throughout extended wear.
Durability and Longevity: Rayon vs Bamboo Fabrics
Rayon fabric, derived from cellulose fibers, typically offers moderate durability but tends to weaken when wet, leading to reduced longevity compared to bamboo fabric. Bamboo fabric, known for its natural strength and resilience, maintains better structural integrity over time and resists wear and tear more effectively than rayon. The inherent antimicrobial properties of bamboo also contribute to the fabric's long-lasting freshness and durability in everyday use.
Breathability and Moisture-Wicking Abilities
Rayon, derived from cellulose fibers, offers superior breathability compared to bamboo fabric, allowing better air circulation and enhanced comfort in warm conditions. Its moisture-wicking properties efficiently draw sweat away from the skin, promoting faster evaporation and dryness. Bamboo rayon, while also breathable, often contains additives that can reduce its moisture management effectiveness compared to pure rayon fibers.
Cost Comparison: Rayon versus Bamboo Textiles
Rayon textiles typically cost less to produce than bamboo textiles due to simpler manufacturing processes and lower raw material expenses. Bamboo fabric often incurs higher costs because of the additional chemical treatments and sustainability certifications required. Price differences influence market availability, making rayon a more affordable choice for mass-produced clothing compared to bamboo's premium positioning.
Hypoallergenic Properties: Which Is Gentler on Skin?
Rayon and bamboo fabrics both exhibit hypoallergenic properties, but bamboo rayon is generally considered gentler on sensitive skin due to its natural antimicrobial qualities and breathability. Bamboo fibers contain natural compounds that inhibit bacterial growth, reducing irritation and allergic reactions compared to conventional rayon derived from wood pulp. Consumers with delicate skin often prefer bamboo rayon for its moisture-wicking ability and softness, which enhance comfort and reduce the likelihood of skin sensitivities.
Sustainability: Eco-Friendliness of Bamboo and Rayon
Bamboo is often considered more sustainable than rayon due to its rapid growth and minimal need for pesticides or fertilizers, making it an eco-friendly raw material. Rayon, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, undergoes intensive chemical processing that can generate environmental pollutants if not managed responsibly. While bamboo's eco-friendliness stems from its natural cultivation, the sustainability of rayon depends heavily on manufacturing practices and the use of closed-loop systems to reduce chemical waste.
Best Uses: Choosing Between Rayon and Bamboo for Different Products
Rayon, derived from cellulose fibers, excels in apparel like formal wear and linings due to its smooth texture and breathability, while bamboo fibers offer superior natural antibacterial properties and moisture-wicking, ideal for activewear and eco-friendly textiles. Bamboo's faster growth and renewable nature make it sustainable, yet rayon's versatility in fabric blends provides enhanced durability and drape. Selecting between rayon and bamboo hinges on product application requirements such as comfort, environmental impact, and functional performance.
Rayon vs Bamboo Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com