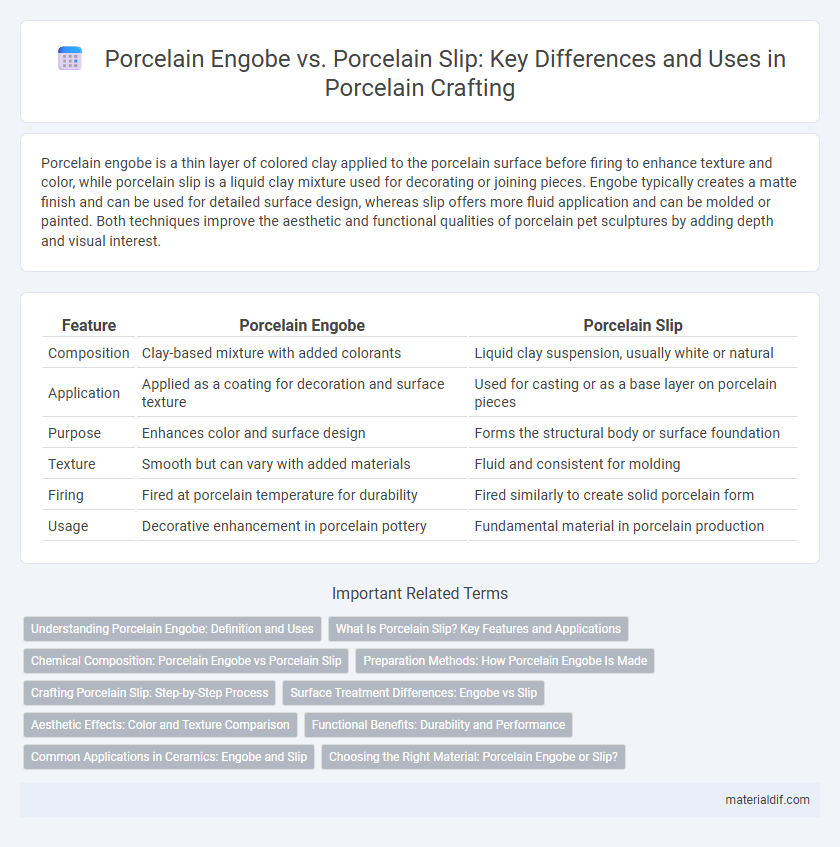
Porcelain engobe is a thin layer of colored clay applied to the porcelain surface before firing to enhance texture and color, while porcelain slip is a liquid clay mixture used for decorating or joining pieces. Engobe typically creates a matte finish and can be used for detailed surface design, whereas slip offers more fluid application and can be molded or painted. Both techniques improve the aesthetic and functional qualities of porcelain pet sculptures by adding depth and visual interest.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Porcelain Engobe | Porcelain Slip |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay-based mixture with added colorants | Liquid clay suspension, usually white or natural |
| Application | Applied as a coating for decoration and surface texture | Used for casting or as a base layer on porcelain pieces |
| Purpose | Enhances color and surface design | Forms the structural body or surface foundation |
| Texture | Smooth but can vary with added materials | Fluid and consistent for molding |
| Firing | Fired at porcelain temperature for durability | Fired similarly to create solid porcelain form |
| Usage | Decorative enhancement in porcelain pottery | Fundamental material in porcelain production |
Understanding Porcelain Engobe: Definition and Uses
Porcelain engobe is a liquid clay mixture applied to the surface of porcelain pieces before firing, used to enhance color, texture, and surface design with a smooth, matte finish. Unlike porcelain slip, which is primarily for construction and joining pieces, engobe serves as a decorative coating that can mask imperfections or add contrast without altering the porcelain's inherent strength. It is commonly used in ceramics to achieve precise aesthetic effects while maintaining the durability and translucency characteristic of porcelain.
What Is Porcelain Slip? Key Features and Applications
Porcelain slip is a liquid mixture of porcelain clay and water used mainly for casting and decoration in ceramics, offering smooth consistency ideal for molding intricate shapes. It features high plasticity, a fine particle size, and excellent adhesion properties that enhance surface detail and durability after firing. Common applications include slip casting, surface decoration, and joining porcelain parts, making it essential for artists and manufacturers aiming for precise and refined ceramic ware.
Chemical Composition: Porcelain Engobe vs Porcelain Slip
Porcelain engobe typically contains a higher concentration of fluxes such as feldspar and kaolin, promoting better adhesion and surface smoothness when applied to porcelain bodies. In contrast, porcelain slip is generally composed of a more balanced mixture of clay, silica, and fluxes, allowing for easier application as a liquid layer and enhanced plasticity. The chemical composition of engobe emphasizes coating properties, while slip focuses on forming and shaping porcelain pieces prior to firing.
Preparation Methods: How Porcelain Engobe Is Made
Porcelain engobe is prepared by mixing finely ground porcelain clay with water and specific fluxing agents to create a smooth, paintable slurry. This mixture is carefully sieved to remove impurities and achieve a consistent texture, ensuring it adheres well to the porcelain body. The precise balance of materials in engobe enhances surface decoration and improves color application compared to traditional porcelain slip.
Crafting Porcelain Slip: Step-by-Step Process
Crafting porcelain slip involves mixing finely ground porcelain clay with water to create a smooth, viscous liquid ideal for casting or decorating. The process begins by thoroughly combining clay powder with water until achieving a consistent, creamy texture, followed by filtering the mixture to remove impurities and air bubbles. The resulting slip can be used for precise applications like slip casting or engobe decoration, offering controlled fluidity and excellent adhesion to porcelain surfaces.
Surface Treatment Differences: Engobe vs Slip
Porcelain engobe is a colored clay slip applied to the surface before firing, creating a smooth, matte finish that enhances color vibrancy and texture depth. Porcelain slip, typically a liquid clay mixture, serves as a basic surface coating for refining texture or joining pieces, offering a more uniform and subtle surface without added pigmentation. The primary difference lies in engobe's pigmentation and decorative purpose versus slip's functional role in surface preparation and structural integration.
Aesthetic Effects: Color and Texture Comparison
Porcelain engobe offers vivid color variations and smooth texture, enhancing surface brightness and visual depth, while porcelain slip provides a softer, matte finish with subtle color tones that emphasize natural clay qualities. Engobe's finer particle size allows for more precise detailing and sharper contrasts, making it ideal for decorative applications requiring high definition. Slip's thicker consistency results in a more tactile, organic feel, suitable for rustic or traditional porcelain styles emphasizing texture.
Functional Benefits: Durability and Performance
Porcelain engobe enhances surface durability by providing a strong, protective layer that resists chipping and wear, making it ideal for functional ware requiring long-lasting performance. Porcelain slip, applied before firing, improves structural integrity and bonding, ensuring consistent strength and reduced risk of cracking during the firing process. Both materials optimize the porcelain's overall durability and performance, with engobe emphasizing surface protection and slip enhancing foundational strength.
Common Applications in Ceramics: Engobe and Slip
Porcelain engobe is commonly applied as a decorative coating to alter surface color and texture before firing, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of ceramic pieces without compromising the porcelain body's strength. Porcelain slip, a liquid clay mixture, is primarily used for casting molds, joining parts, or as a base layer for further decoration, providing versatility in shaping and detailing porcelain objects. Both engobe and slip serve critical roles in ceramic production, with engobe focusing on surface finish and slip emphasizing structural and functional applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Porcelain Engobe or Slip?
Porcelain engobe offers a smooth, colored surface layer that enhances texture and color control, making it ideal for detailed decorative work, while porcelain slip provides a more fluid consistency suited for casting and joining pieces. Selecting the right material depends on the desired finish and application technique, with engobe favored for surface aesthetics and slip preferred for structural bonding and molding. Understanding the differences in composition and functionality ensures optimal results in porcelain crafting and ceramics.
Porcelain Engobe vs Porcelain Slip Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com