Porcelain enamel offers superior durability and resistance to scratches and chemicals compared to glass enamel, making it ideal for high-use applications like pet dishes and decorative items. The smooth, non-porous surface of porcelain enamel prevents bacteria buildup, ensuring safer and more hygienic environments for pets. While glass enamel provides vibrant colors, porcelain enamel's enhanced strength and longevity make it the preferred choice for quality pet products.
Table of Comparison
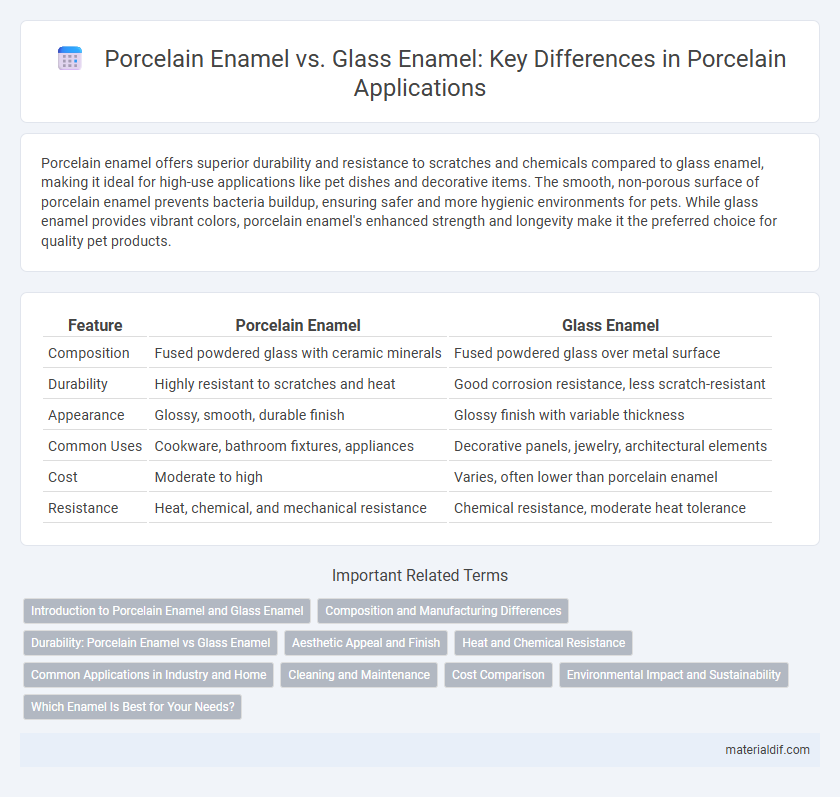
| Feature | Porcelain Enamel | Glass Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fused powdered glass with ceramic minerals | Fused powdered glass over metal surface |
| Durability | Highly resistant to scratches and heat | Good corrosion resistance, less scratch-resistant |
| Appearance | Glossy, smooth, durable finish | Glossy finish with variable thickness |
| Common Uses | Cookware, bathroom fixtures, appliances | Decorative panels, jewelry, architectural elements |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Varies, often lower than porcelain enamel |
| Resistance | Heat, chemical, and mechanical resistance | Chemical resistance, moderate heat tolerance |
Introduction to Porcelain Enamel and Glass Enamel
Porcelain enamel is a durable coating made by fusing powdered glass to a substrate through high-temperature firing, resulting in a smooth, glossy surface resistant to corrosion and wear. Glass enamel shares a similar composition but typically emphasizes transparency and thinner layers, often used for decorative purposes. Both materials combine the benefits of glass and metal to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal in various applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Porcelain enamel is a glassy coating made by fusing powdered glass to a substrate through firing at high temperatures, primarily composed of silica, fluxes, and metal oxides. Glass enamel, while similar, often has a higher silica content and a more varied composition that can include boron and alumina, giving it different thermal and chemical properties. Manufacturing porcelain enamel involves firing on metal surfaces to create a durable, chip-resistant finish, whereas glass enamel can be used on ceramics and metals, with firing processes tailored to its composition for desired gloss and hardness.
Durability: Porcelain Enamel vs Glass Enamel
Porcelain enamel offers superior durability due to its thicker, fused glass layer that resists chipping, scratching, and chemical corrosion more effectively than glass enamel. While both coatings are made from glass, porcelain enamel undergoes higher firing temperatures, resulting in a harder, more resilient surface. This makes porcelain enamel ideal for heavy-use applications requiring long-lasting protection.
Aesthetic Appeal and Finish
Porcelain enamel offers a smooth, glossy finish with vibrant, long-lasting colors that resist fading and chipping, making it highly valued for both aesthetic appeal and durability. Glass enamel, while also providing a shiny surface, often has a more translucent and delicate appearance that can enhance subtle design details but may be less resistant to wear. Both materials are prized in decorative applications, yet porcelain enamel's robust finish often makes it the preferred choice for high-traffic or outdoor surfaces requiring both beauty and resilience.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Porcelain enamel offers superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1400degF, making it ideal for high-heat applications like cookware and industrial equipment. Glass enamel, while also heat resistant, generally tolerates lower temperatures around 1100degF and can be less durable against thermal shock. Chemically, porcelain enamel provides enhanced resistance to acids and alkalis, preserving its surface integrity better than glass enamel in harsh environments.
Common Applications in Industry and Home
Porcelain enamel is commonly used in cookware, bathtubs, and industrial appliances due to its durability, resistance to chemicals, and high-temperature tolerance. Glass enamel finds frequent application in decorative items, signage, and electronic components because of its smooth finish and excellent insulating properties. Both enamels provide protective coatings, but porcelain enamel is preferred for heavy-duty industrial use while glass enamel suits decorative and precision uses in homes and electronics.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Porcelain enamel offers superior durability and stain resistance compared to glass enamel, making it easier to clean with non-abrasive cleaners and soft cloths. Glass enamel tends to be more prone to chipping and staining, requiring gentler maintenance and specialized cleaning products. Both surfaces benefit from prompt cleaning to prevent buildup, but porcelain enamel's dense composition reduces the frequency and intensity of upkeep.
Cost Comparison
Porcelain enamel typically costs more than glass enamel due to its durability and higher firing temperatures, which require specialized equipment and longer production times. Glass enamel is generally less expensive, making it a cost-effective choice for decorative applications and mass production. While porcelain enamel provides superior resistance to chipping and corrosion, the initial investment is higher compared to glass enamel coatings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Porcelain enamel and glass enamel differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with porcelain enamel typically using natural clays and minimal synthetic additives, resulting in lower carbon emissions during production. Glass enamel often relies on higher energy-intensive processes and raw materials that can contribute to greater ecological footprints. Sustainable practices favor porcelain enamel due to its durability, recyclability, and reduced reliance on hazardous chemicals, making it a more eco-friendly choice in coatings and finishes.
Which Enamel Is Best for Your Needs?
Porcelain enamel offers superior durability and resistance to scratching and heat, making it ideal for cookware and industrial applications, while glass enamel provides a smoother, more transparent finish preferred in decorative items and architectural surfaces. Porcelain enamel's composition includes a higher percentage of feldspar, enhancing its strength and longevity compared to the silica-rich glass enamel that excels in aesthetic versatility. Choosing the right enamel depends on whether durability and wear resistance or visual appeal and surface smoothness are the primary requirements for your project.
Porcelain Enamel vs Glass Enamel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com