Porcelain vitrification refers to the process where the ceramic material becomes fully glass-like, resulting in a highly durable, non-porous surface that resists stains and moisture. Semi-vitrified porcelain, while still strong and water-resistant, retains a slightly porous structure, making it less dense and more cost-effective than fully vitrified porcelain. Choosing between vitrified and semi-vitrified porcelain depends on the desired balance of durability, weight, and price for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
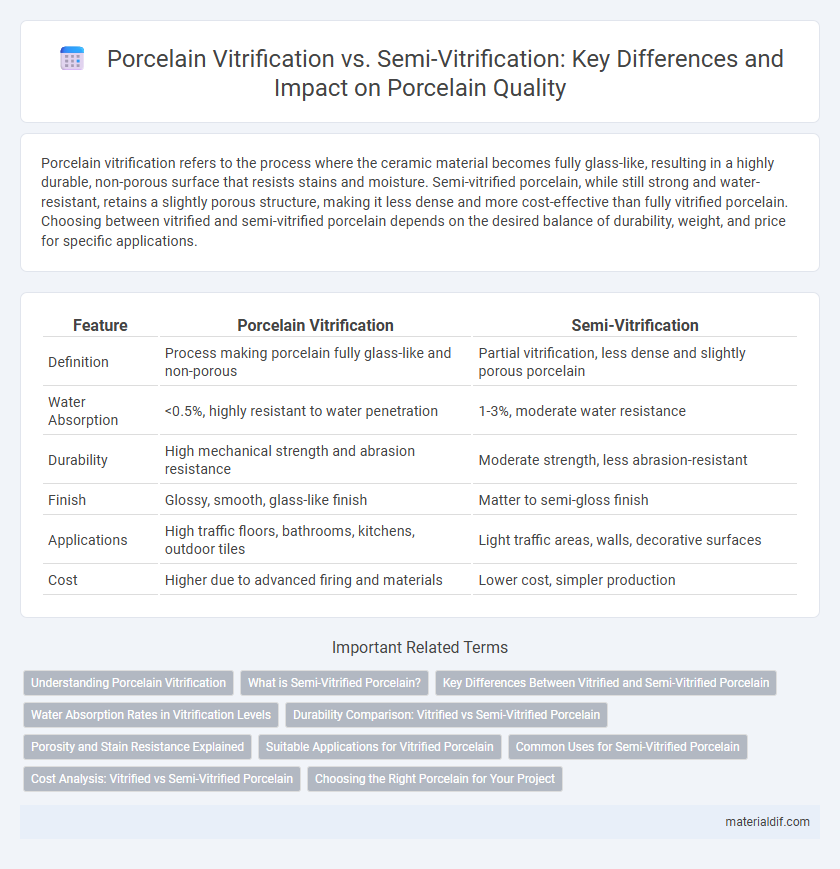
| Feature | Porcelain Vitrification | Semi-Vitrification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process making porcelain fully glass-like and non-porous | Partial vitrification, less dense and slightly porous porcelain |
| Water Absorption | <0.5%, highly resistant to water penetration | 1-3%, moderate water resistance |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate strength, less abrasion-resistant |
| Finish | Glossy, smooth, glass-like finish | Matter to semi-gloss finish |
| Applications | High traffic floors, bathrooms, kitchens, outdoor tiles | Light traffic areas, walls, decorative surfaces |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced firing and materials | Lower cost, simpler production |
Understanding Porcelain Vitrification
Porcelain vitrification refers to the process where porcelain achieves a glass-like, non-porous surface through high-temperature firing, enhancing its durability, water resistance, and stain resistance. Semi-vitrified porcelain undergoes a lower firing temperature, resulting in partial vitrification that offers moderate strength and porosity. Understanding the degree of vitrification helps determine the suitability of porcelain for applications requiring high resistance to moisture and wear, such as flooring and bathroom tiles.
What is Semi-Vitrified Porcelain?
Semi-vitrified porcelain is a type of ceramic material with partial vitrification, meaning it absorbs more water than fully vitrified porcelain but less than non-vitrified ceramics, making it moderately water-resistant and durable. It achieves a balance between strength and porosity, suitable for residential flooring and wall applications where moderate moisture exposure occurs. This semi-vitrification process involves firing the porcelain at temperatures that create a dense, partially glass-like structure, offering an economical alternative with decent hardness and stain resistance.
Key Differences Between Vitrified and Semi-Vitrified Porcelain
Vitrified porcelain undergoes a high-temperature process that fuses the particles, resulting in a dense, non-porous surface with superior strength and water resistance, making it ideal for heavy-traffic areas and outdoor use. Semi-vitrified porcelain is partially vitrified, offering moderate porosity and slightly lower strength, suitable for interior spaces with less wear and moisture exposure. The key differences lie in their porosity, durability, and resistance to stains and water, with vitrified porcelain being more robust and low-maintenance compared to semi-vitrified options.
Water Absorption Rates in Vitrification Levels
Porcelain vitrification results in significantly lower water absorption rates, typically below 0.5%, making it highly resistant to moisture and ideal for durability. Semi-vitrified porcelain exhibits higher water absorption rates, usually ranging from 0.5% to 3%, reflecting partial vitrification and moderate porosity. The degree of vitrification strongly influences the tile's density, strength, and suitability for high-traffic or moisture-prone environments.
Durability Comparison: Vitrified vs Semi-Vitrified Porcelain
Vitrified porcelain tiles undergo a high-temperature firing process that results in a dense, non-porous surface, making them highly resistant to wear, stains, and moisture, thus significantly enhancing durability. Semi-vitrified porcelain tiles have a slightly higher porosity, which reduces resistance to water absorption and surface abrasion compared to fully vitrified options. When comparing durability, vitrified porcelain is preferred for high-traffic and moisture-prone areas due to its superior strength and longevity, whereas semi-vitrified porcelain suits medium-traffic residential spaces with moderate durability needs.
Porosity and Stain Resistance Explained
Porcelain vitrification results in a highly dense, low-porosity surface that significantly enhances stain resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and easy maintenance. Semi-vitrified porcelain has moderate porosity, allowing for some water absorption which can reduce its stain resistance compared to fully vitrified counterparts. Understanding the porosity differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate porcelain type in environments prone to staining and moisture exposure.
Suitable Applications for Vitrified Porcelain
Vitrified porcelain exhibits low porosity and high density, making it ideal for applications requiring superior strength and moisture resistance, such as flooring in commercial spaces and exterior cladding. Its enhanced durability ensures longevity in high-traffic areas and environments exposed to weather variations. Semi-vitrified porcelain, while durable, is better suited for indoor use where moisture exposure is limited.
Common Uses for Semi-Vitrified Porcelain
Semi-vitrified porcelain is commonly used in flooring and wall tiles for commercial spaces, including offices, malls, and public buildings, due to its balance of strength and water resistance. Its moderate porosity allows for easier cutting and installation compared to fully vitrified tiles, making it suitable for areas requiring customized designs. This type of porcelain also offers cost-effective durability for medium-traffic areas without the high production costs associated with fully vitrified porcelain.
Cost Analysis: Vitrified vs Semi-Vitrified Porcelain
Vitrified porcelain tiles are generally more expensive due to their higher density, lower porosity, and superior durability, making them a cost-effective choice for high-traffic or outdoor areas despite the initial investment. Semi-vitrified porcelain offers a lower upfront cost, suitable for indoor applications with moderate wear, but may require more frequent replacements or maintenance over time. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, vitrified porcelain provides better long-term value through enhanced resistance to moisture, stains, and wear.
Choosing the Right Porcelain for Your Project
Porcelain vitrification significantly impacts durability and water resistance, making fully vitrified porcelain ideal for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas. Semi-vitrified porcelain offers a balance between cost and performance, suitable for moderate use environments where some level of porosity is acceptable. Selecting the right porcelain depends on evaluating project demands such as exposure to wear, moisture levels, and budget constraints to ensure optimal longevity and aesthetics.
Porcelain Vitrification vs Semi-Vitrification Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com