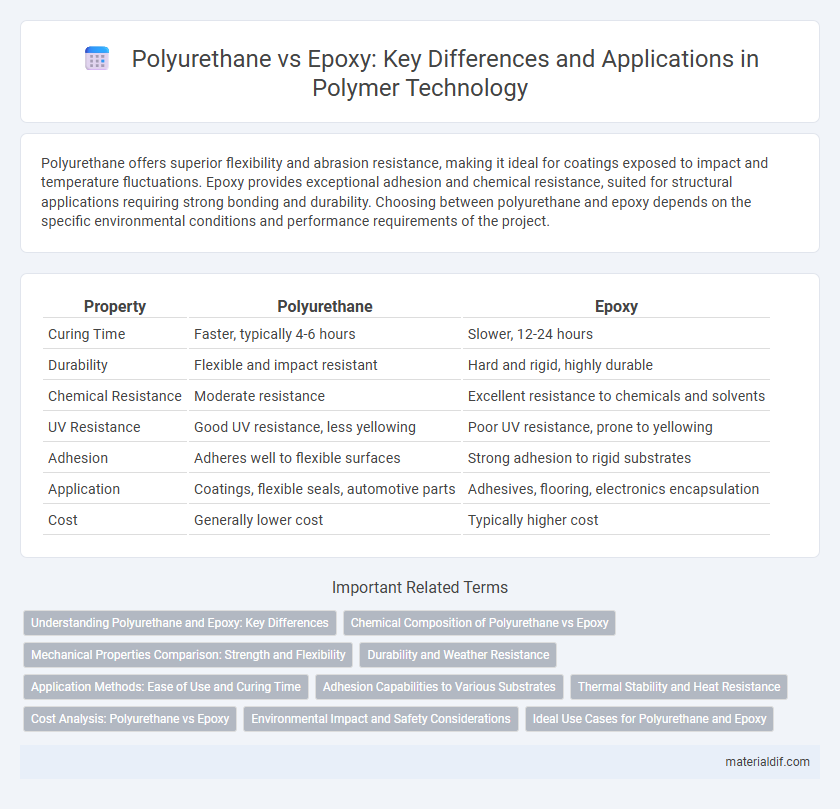
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for coatings exposed to impact and temperature fluctuations. Epoxy provides exceptional adhesion and chemical resistance, suited for structural applications requiring strong bonding and durability. Choosing between polyurethane and epoxy depends on the specific environmental conditions and performance requirements of the project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane | Epoxy |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Time | Faster, typically 4-6 hours | Slower, 12-24 hours |
| Durability | Flexible and impact resistant | Hard and rigid, highly durable |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| UV Resistance | Good UV resistance, less yellowing | Poor UV resistance, prone to yellowing |
| Adhesion | Adheres well to flexible surfaces | Strong adhesion to rigid substrates |
| Application | Coatings, flexible seals, automotive parts | Adhesives, flooring, electronics encapsulation |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
Understanding Polyurethane and Epoxy: Key Differences
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer known for its flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion, commonly used in coatings and foams. Epoxy, a thermosetting polymer, boasts superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for industrial coatings and adhesives. Key differences lie in their curing processes and applications: polyurethane cures through moisture or heat, providing elasticity, while epoxy cures via a chemical reaction between resin and hardener, resulting in a rigid, high-strength material.
Chemical Composition of Polyurethane vs Epoxy
Polyurethane consists of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links, formed from the reaction between polyols and diisocyanates or polymeric isocyanates. Epoxy resins are primarily composed of epoxide groups, typically generated by the reaction of epichlorohydrin with bisphenol-A or other polyphenols. The chemical composition of polyurethane allows for flexibility and elasticity, while the epoxy's structure lends it high rigidity and strong adhesion properties.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: Strength and Flexibility
Polyurethane exhibits superior flexibility and impact resistance due to its elastomeric nature, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under dynamic stress. Epoxy demonstrates higher compressive and tensile strength, providing exceptional rigidity and chemical resistance for structural bonding and coating purposes. The choice between polyurethane and epoxy depends on the balance needed between mechanical flexibility and strength for specific industrial or construction applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Polyurethane exhibits superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, maintaining durability under UV exposure and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Epoxy offers excellent hardness and chemical resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged sunlight and moisture, limiting its weather resistance. Selecting polyurethane over epoxy ensures enhanced longevity and consistent performance in demanding environmental conditions.
Application Methods: Ease of Use and Curing Time
Polyurethane offers versatile application methods, including brushing, spraying, and dipping, with flexible curing times ranging from a few hours to several days depending on formulation and environmental conditions. Epoxy typically requires precise mixing ratios and is applied through brushing, rolling, or pouring, with curing times varying from 6 to 24 hours, often necessitating controlled temperature for optimal hardening. The ease of use favors polyurethane for quick projects and less controlled environments, while epoxy is preferred for high-strength, durable coatings requiring meticulous application.
Adhesion Capabilities to Various Substrates
Polyurethane exhibits superior adhesion to flexible substrates like rubber and fabrics due to its elasticity and chemical compatibility, making it ideal for applications requiring durability against mechanical stress. Epoxy provides exceptional bonding strength on rigid surfaces such as metals, concrete, and ceramics, forming a hard, chemically resistant layer suitable for structural and industrial uses. Both polymers demonstrate excellent adhesive properties, but the choice depends on substrate type and performance requirements in specific environments.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyurethane exhibits moderate thermal stability with heat resistance typically ranging between 80degC to 120degC, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility and impact resistance under moderate temperatures. Epoxy demonstrates superior thermal stability, often withstanding continuous exposure up to 150degC or higher, which allows for its use in high-performance coatings and electrical insulation. The enhanced heat resistance of epoxy results from its highly cross-linked molecular structure, providing durability in harsh thermal environments compared to the more flexible but less heat-resistant polyurethane.
Cost Analysis: Polyurethane vs Epoxy
Polyurethane typically costs less upfront compared to epoxy, with average prices ranging from $3 to $7 per square foot for coatings, while epoxy coatings often range from $4 to $12 per square foot due to higher material and preparation expenses. Epoxy's superior durability and chemical resistance can reduce long-term maintenance costs, making it more cost-effective for industrial applications despite its higher initial investment. Polyurethane offers flexibility and UV resistance at a lower price, making it suitable for outdoor and decorative uses where budget constraints are a priority.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Polyurethane exhibits lower environmental toxicity compared to epoxy due to its reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during curing, making it a safer choice for indoor applications. Epoxy resins often contain bisphenol-A and other hazardous chemicals, posing higher risks to both human health and the environment through potential allergenic and carcinogenic effects. Both polymers require careful handling and proper ventilation to minimize respiratory exposure and environmental contamination, but polyurethane generally offers a more eco-friendly profile in industrial and consumer settings.
Ideal Use Cases for Polyurethane and Epoxy
Polyurethane excels in flexible applications such as coatings, adhesives, and sealants where elasticity and abrasion resistance are crucial, commonly used in automotive parts and footwear. Epoxy is ideal for high-strength bonding and structural applications, including aerospace components, flooring, and electronics encapsulation, due to its superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance. Selecting between polyurethane and epoxy depends on the required flexibility, durability, and environmental exposure of the final product.
Polyurethane vs Epoxy Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com