PVC Type I is a rigid, high-impact-resistant plastic commonly used for plumbing pipes and electrical cable insulation due to its strong chemical resistance and durability. PVC Type II possesses greater flexibility and is often utilized in applications requiring softer, more pliable materials, such as inflatable products and certain coatings. Choosing between PVC Type I and Type II depends on the specific requirements for strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance in the intended application.
Table of Comparison
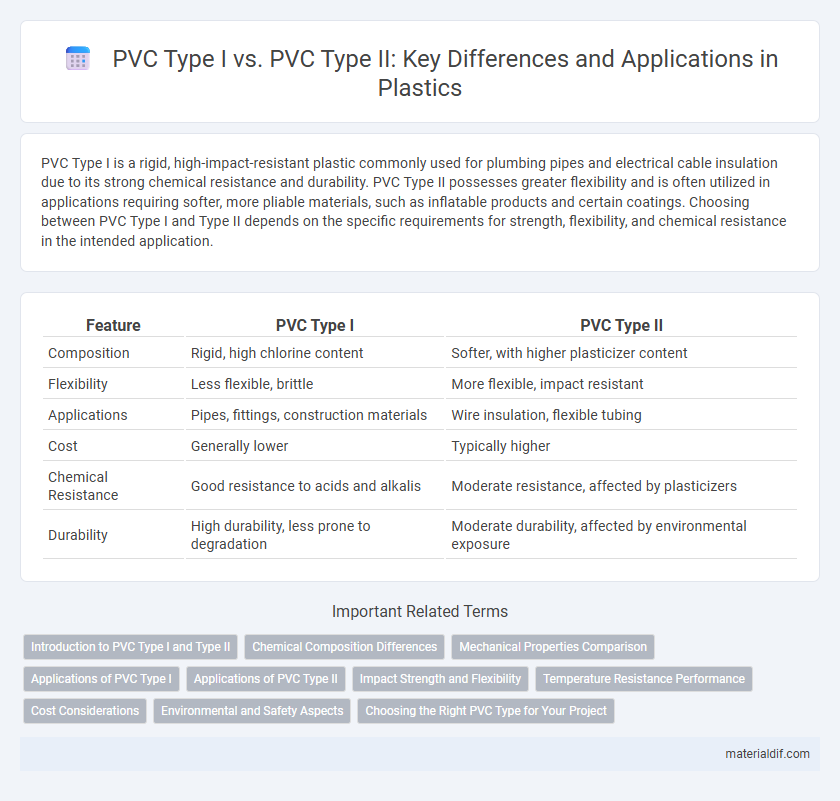
| Feature | PVC Type I | PVC Type II |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Rigid, high chlorine content | Softer, with higher plasticizer content |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, brittle | More flexible, impact resistant |
| Applications | Pipes, fittings, construction materials | Wire insulation, flexible tubing |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Moderate resistance, affected by plasticizers |
| Durability | High durability, less prone to degradation | Moderate durability, affected by environmental exposure |
Introduction to PVC Type I and Type II
PVC Type I and Type II differ primarily in their molecular structure and material properties, impacting their typical applications. PVC Type I is rigid with higher tensile strength, commonly used in construction for pipes and fittings, while PVC Type II contains more plasticizer, offering greater flexibility suitable for electrical insulation and medical tubing. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize material selection based on application requirements for durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
Chemical Composition Differences
PVC Type I, also known as rigid or unplasticized PVC, contains a higher concentration of vinyl chloride monomer with minimal additives, resulting in greater rigidity and chemical resistance. PVC Type II incorporates various plasticizers and stabilizers that modify its chemical composition, enhancing flexibility and impact resistance while reducing brittleness. The primary chemical difference lies in the presence of these plasticizing agents in Type II, which are absent or significantly lower in Type I, affecting their respective physical properties and applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
PVC Type I offers higher tensile strength and enhanced stiffness compared to PVC Type II, making it suitable for structural applications requiring rigidity. PVC Type II exhibits better impact resistance and flexibility due to its greater plasticizer content, which improves toughness under dynamic loading conditions. The mechanical properties of PVC Type I favor load-bearing uses, while PVC Type II's characteristics suit applications needing improved durability and shock absorption.
Applications of PVC Type I
PVC Type I is widely used in applications requiring high impact resistance and durability, such as automotive parts, pipes, and fittings. Its rigid structure and chemical resistance make it suitable for industrial and construction materials that must withstand harsh environments. This type is preferred for producing transparent or opaque products demanding strong mechanical properties and excellent weather resistance.
Applications of PVC Type II
PVC Type II is commonly used in applications requiring enhanced impact resistance and flexibility, such as medical tubing, wire insulation, and flexible packaging. Its superior chemical resistance and durability make it ideal for automotive parts, flooring, and electrical cable jacketing. The material's balanced rigidity and toughness enable effective performance in environments with mechanical stress and variable temperatures.
Impact Strength and Flexibility
PVC Type I exhibits higher impact strength due to its rigid molecular structure, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to mechanical stress. PVC Type II offers greater flexibility, attributed to its modified polymer chains, enhancing its suitability for uses that demand bending and elasticity. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize material selection in industries like construction and medical devices.
Temperature Resistance Performance
PVC Type I exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 140degF (60degC), making it suitable for applications requiring moderate heat endurance. PVC Type II, however, offers enhanced flexibility but typically withstands lower temperatures, around 122degF (50degC), limiting its use in higher-temperature environments. The difference in chlorine content and plasticizer levels directly influences their thermal performance, with Type I being more rigid and thermally stable compared to the softer, less heat-resistant Type II.
Cost Considerations
PVC Type I generally incurs higher production costs due to its enhanced purity and superior chemical resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications. PVC Type II offers a more cost-effective alternative with moderate chemical resistance and slightly lower durability, appealing to budget-sensitive projects. Cost savings with PVC Type II often translate into broader use in consumer goods, while Type I is preferred in industrial and medical environments where performance justifies expense.
Environmental and Safety Aspects
PVC Type I and PVC Type II differ significantly in environmental impact and safety profiles, with Type II exhibiting enhanced resistance to chemical leaching and reduced harmful plasticizer migration. Type II PVC formulations often use stabilizers and additives that lower toxicity risks during manufacturing and disposal compared to Type I. Enhanced durability and improved fire retardancy in Type II also contribute to safer indoor air quality and reduced environmental contamination over the product lifecycle.
Choosing the Right PVC Type for Your Project
PVC Type I offers a denser, more rigid structure ideal for applications requiring high strength and chemical resistance, such as pipes and industrial containers. PVC Type II provides greater flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for products like electrical cable insulation and flexible tubing. Selecting the right PVC type depends on the project's requirements for durability, flexibility, and environmental exposure.
PVC Type I vs PVC Type II Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com